
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Project Documentation
Arduino UNO-Based Battery-Powered Robotic Arm with Multiple Servos
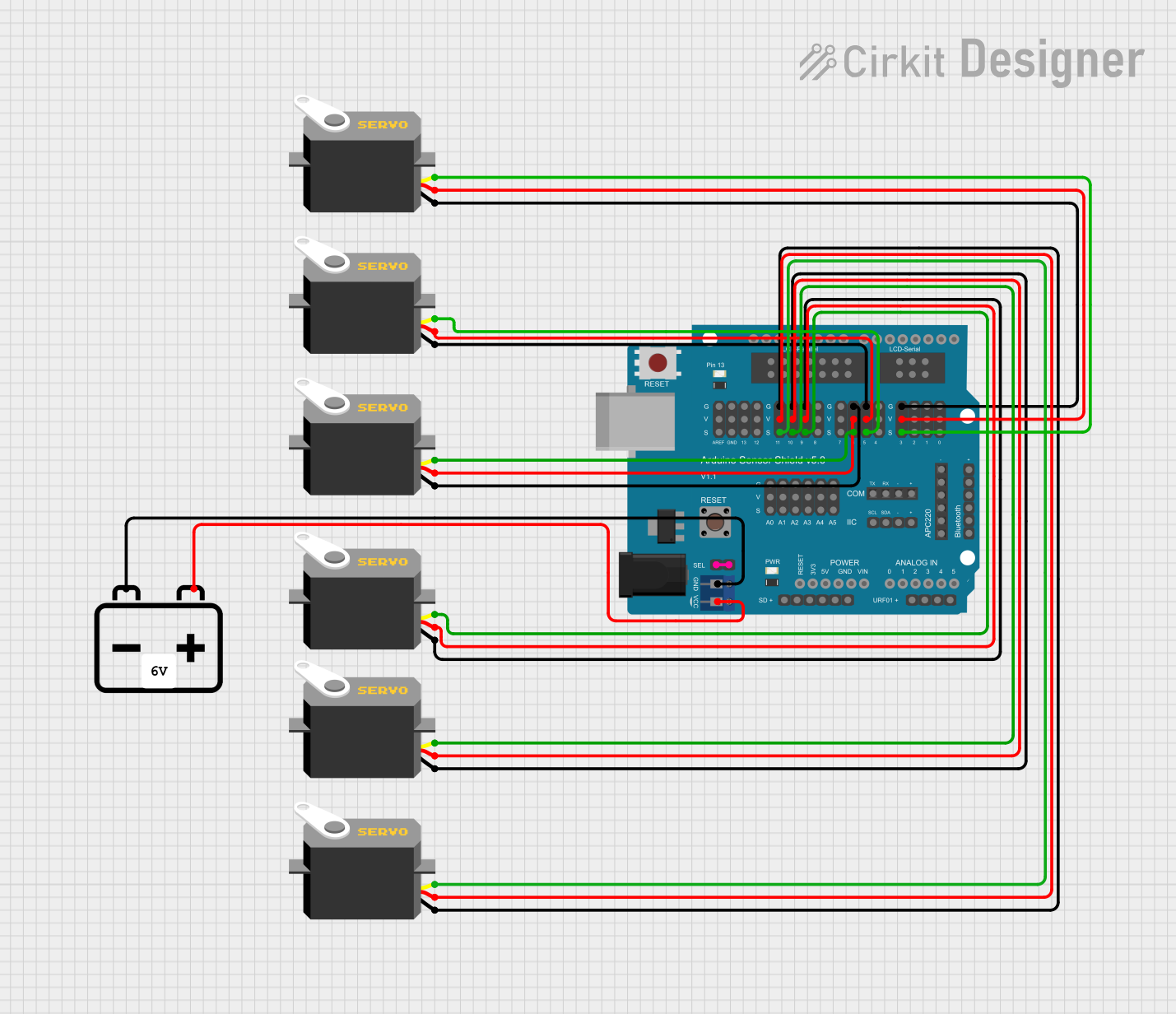
Circuit Documentation
Summary
This circuit is designed to control multiple servos using an Arduino UNO and an Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0. The servos are powered by a 12V battery, and the Arduino UNO is programmed to control the servos based on distance measurements. The circuit includes the following components:
- Arduino UNO
- Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Multiple Servo Motors
- 12V Battery
Component List
Arduino UNO
- Description: A microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P.
- Pins: UNUSED, IOREF, Reset, 3.3V, 5V, GND, Vin, A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, SCL, SDA, AREF, D13, D12, D11, D10, D9, D8, D7, D6, D5, D4, D3, D2, D1, D0
Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Description: A shield that provides easy connections for sensors and servos.
- Pins: VCC, SD-VCC, SD-GND, SD-D11, SD-D10, SD-D13, SD-D12, URF01-VCC, URF01-A0, URF01-A1, URF01-GND, GND, SEL1, SEL2, A0-SIG, A0-VCC, A0-GND, A1-SIG, A1-VCC, A1-GND, A2-SIG, A2-VCC, A2-GND, A3-SIG, A3-VCC, A3-GND, A4-SIG, A4-VCC, A4-GND, A5-SIG, A5-VCC, A5-GND, IIC-SCL, IIC-SDA, IIC-GND, IIC-VCC, COM-TX, COM-RX, COM-GND, COM-VCC, APC220-, APC220-D0, APC220-D1, APC220-VCC, APC220-GND, BLUETOOTH-3V3, BLUETOOTH-GND, BLUETOOTH-D0, BLUETOOTH-D1, BLUETOOTH-VCC, AREF-S, AREF-V, AREF-G, GND-S, GND-V, GND-G, 13-S, 13-V, 13-G, 12-S, 12-V, 12-G, 11-S, 11-V, 11-G, 10-S, 10-V, 10-G, 9-S, 9-V, 9-G, 8-S, 8-V, 8-G, 7-S, 7-V, 7-G, 6-S, 6-V, 6-G, 5-S, 5-V, 5-G, 4-S, 4-V, 4-G, 3-S, 3-V, 3-G, 2-S, 2-V, 2-G, 1-S, 1-V, 1-G, 0-S, 0-V, 0-G, ParallelLCD-VCC, ParallelLCD-D13, ParallelLCD-GND, ParallelLCD-D12, ParallelLCD-D2, ParallelLCD-D11, ParallelLCD-D3, ParallelLCD-D10, ParallelLCD-D4, ParallelLCD-D9, ParallelLCD-D5, ParallelLCD-D8, ParallelLCD-D6, ParallelLCD-D7, SerialLCD-D4, SerialLCD-VCC, SerialLCD-D3, SerialLCD-, SerialLCD-D2, SerialLCD-GND
Servo
- Description: A motor that can be controlled to move to a specific position.
- Pins: gnd, vcc, pulse
12V Battery
- Description: A power source providing 12V.
- Pins: -, +
Wiring Details
Arduino UNO
- Connected to: Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Pins:
- 5V to VCC on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- GND to GND on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Connected to:
- 12V Battery
- Multiple Servo Motors
- Pins:
- VCC to + on 12V Battery
- GND to - on 12V Battery
- SEL1 to SEL2 (internal connection)
- 11-S to pulse on Servo
- 11-V to vcc on Servo
- 11-G to gnd on Servo
- 10-S to pulse on Servo
- 10-V to vcc on Servo
- 10-G to gnd on Servo
- 9-S to pulse on Servo
- 9-V to vcc on Servo
- 9-G to gnd on Servo
- 6-S to pulse on Servo
- 6-V to vcc on Servo
- 6-G to gnd on Servo
- 5-S to pulse on Servo
- 5-V to vcc on Servo
- 5-G to gnd on Servo
- 3-S to pulse on Servo
- 3-V to vcc on Servo
- 3-G to gnd on Servo
Servo
- Connected to: Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Pins:
- pulse to 11-S, 10-S, 9-S, 6-S, 5-S, 3-S on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- vcc to 11-V, 10-V, 9-V, 6-V, 5-V, 3-V on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- gnd to 11-G, 10-G, 9-G, 6-G, 5-G, 3-G on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
12V Battery
- Connected to: Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- Pins:
- to VCC on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
- to GND on Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0
Code Documentation
Arduino UNO Code
#include <Servo.h>
volatile int IN1 = 11;
volatile int IN2 = 6;
volatile int IN3 = 5;
volatile int IN4 = 3;
volatile int rightDistance;
volatile int leftDistance;
Servo servo_4;
void left_side_forward(int speed) {
analogWrite(IN1, speed * 0.92);
analogWrite(IN2, 0);
}
void right_side_forward(int speed) {
analogWrite(IN3, speed);
analogWrite(IN4, 0);
}
void left_side_backward(int speed) {
analogWrite(IN1, 0);
analogWrite(IN2, speed * 0.92);
}
void right_side_backward(int speed) {
analogWrite(IN3, 0);
analogWrite(IN4, speed);
}
float checkdistance_A1_A2() {
digitalWrite(A1, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(A1, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(A1, LOW);
float distance = pulseIn(A2, HIGH) / 58.00;
delay(10);
return distance;
}
void forward(int speed) {
left_side_forward(speed);
right_side_forward(speed);
}
void backward(int speed) {
left_side_backward(speed);
right_side_backward(speed);
}
void left(int speed, int time) {
left_side_backward(speed);
right_side_forward(speed);
delay(time);
stop();
}
void right(int speed, int time) {
left_side_forward(speed);
right_side_backward(speed);
delay(time);
stop();
}
void stop() {
left_side_forward(0);
right_side_forward(0);
}
void setup() {
servo_4.attach(4);
pinMode(A1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(A2, INPUT);
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
servo_4.write(90);
delay(200); // Reduce delay for better responsiveness
float distance = checkdistance_A1_A2();
while (distance > 15) {
forward(150); // Increase speed for faster movement
distance = checkdistance_A1_A2(); // Continuously update distance
}
stop();
delay(100); // Reduce delay for better responsiveness
servo_4.write(0);
delay(200); // Reduce delay for better responsiveness
rightDistance = checkdistance_A1_A2();
servo_4.write(180);
delay(200); // Reduce delay for better responsiveness
leftDistance = checkdistance_A1_A2();
if (rightDistance >= leftDistance) {
right(200, 300); // Reduce rotation time for better precision
} else {
left(200, 300); // Reduce rotation time for better precision
}
}
This code controls the servos connected to the Arduino UNO via the Arduino Sensor Shield v5.0. The servos are used to move the robot forward, backward, left, and right