
Arduino UNO Based Medicine Dispenser with RTC and Servo Control
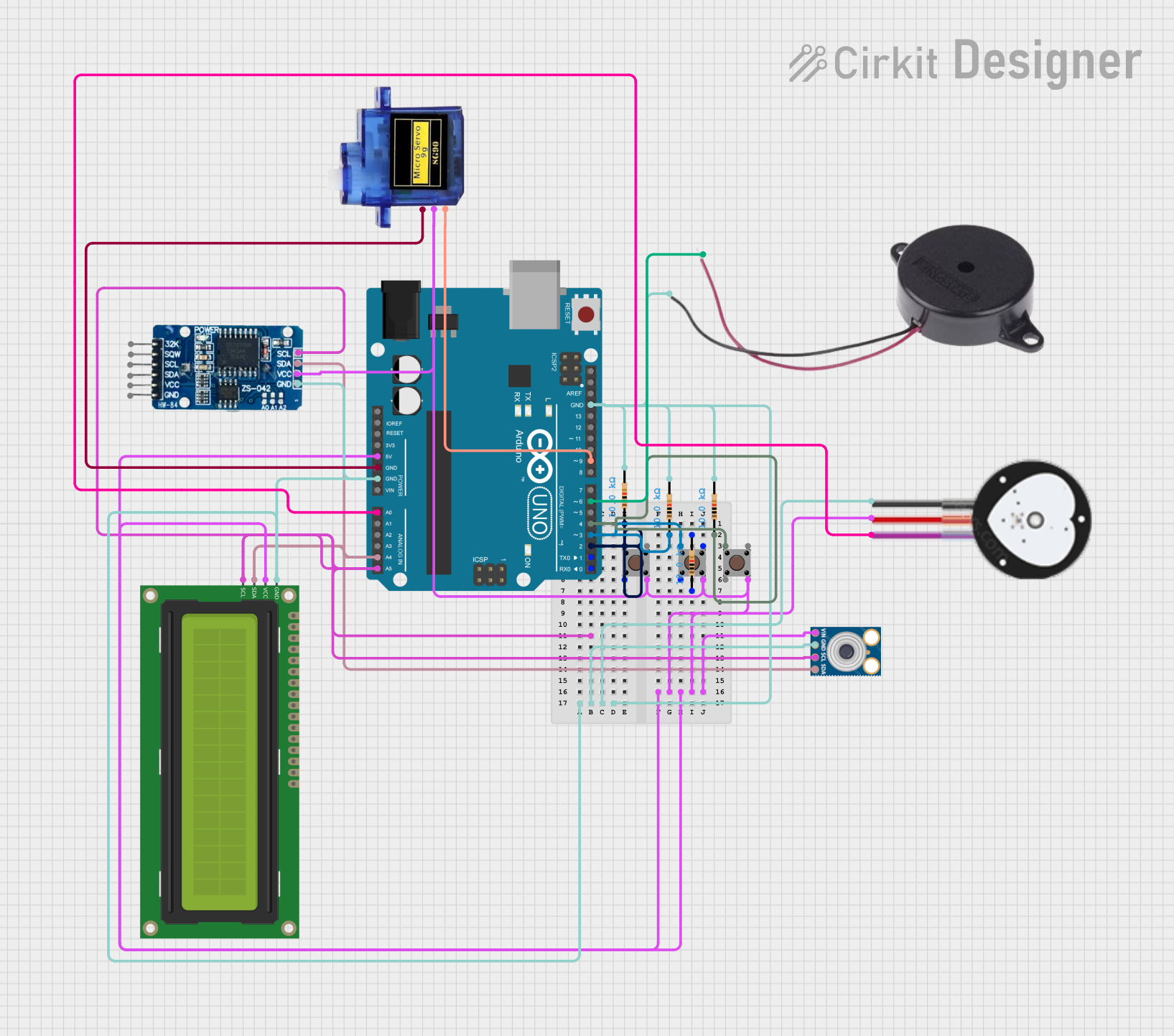
Circuit Documentation
Summary
This circuit is designed to function as a medicine dispenser with a set of features to assist in the timely dispensing of medication. It includes an Arduino UNO microcontroller as the central processing unit, interfaced with a 16x2 I2C LCD for display, a buzzer for audible alerts, a micro servo for mechanical actuation, a Real-Time Clock (RTC) module for timekeeping, multiple pushbuttons for user input, resistors for input protection, a heart pulse sensor for health monitoring, and an mlx90614 infrared temperature sensor for non-contact temperature measurements.
Component List
Arduino UNO
- Microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P
- It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
16x2 I2C LCD
- Alphanumeric liquid crystal display with 16 characters per line and 2 lines.
- It uses the I2C communication protocol for interfacing with the microcontroller.
Buzzer
- An electromechanical component that produces sound when an electrical signal is applied.
Micro servo 9G
- A small and lightweight servo motor suitable for applications requiring simple motion.
RTC DS3231
- A highly accurate I2C real-time clock (RTC) with an integrated temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO) and crystal.
Pushbutton
- A simple switch mechanism for controlling some aspect of a machine or a process.
Resistor (10k Ohms)
- A passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
Heart Pulse Sensor
- A plug-and-play heart-rate sensor for microcontrollers.
mlx90614
- An infrared thermometer for non-contact temperature measurements.
Wiring Details
Arduino UNO
5V&GNDto power the circuit.A0connected to the Heart Pulse Sensor signal output.A4(SDA) &A5(SCL) for I2C communication with the RTC DS3231, 16x2 I2C LCD, and mlx90614 sensor.D9connected to the Micro servo 9G PWM input.D6connected to the Buzzer positive terminal.D2,D3,D4connected to Pushbuttons with corresponding pull-up resistors.
16x2 I2C LCD
GND&VCCfor power supply.SDA&SCLfor I2C communication with the Arduino UNO.
Buzzer
POSITIVEconnected to Arduino UNO pinD6.NEGATIVEconnected to ground.
Micro servo 9G
GND&+5Vfor power supply.PWMconnected to Arduino UNO pinD9.
RTC DS3231
GND&VCCfor power supply.SCL&SDAfor I2C communication with the Arduino UNO.
Pushbuttons
- One side connected to
5Vthrough a pull-up resistor. - The other side connected to respective Arduino UNO input pins (
D2,D3,D4).
Resistor (10k Ohms)
- Connected between pushbuttons and Arduino UNO input pins to form pull-up resistors.
Heart Pulse Sensor
GND&VCCfor power supply.SIGNALconnected to Arduino UNO pinA0.
mlx90614
GND&VINfor power supply.SDA&SCLfor I2C communication with the Arduino UNO.
Documented Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#include <RTClib.h>
#include <Servo.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2); // LCD address may vary, check yours
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
Servo dispenserServo;
const int buttonSetHour = 2;
const int buttonSetMinute = 3;
const int buttonConfirmTime = 4;
const int buzzerPin = 6;
const int servoPin = 9;
int alarmHours[3] = {8, 12, 20}; // Example dispensing times (8 AM, 12 PM, 8 PM)
int alarmMinutes[3] = {0, 0, 0}; // Corresponding minutes for each hour set
bool alarmTriggered[3] = {false, false, false}; // Tracks if alarm has triggered
void setup() {
lcd.begin();
rtc.begin();
dispenserServo.attach(servoPin);
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buttonSetHour, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(buttonSetMinute, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(buttonConfirmTime, INPUT_PULLUP);
lcd.print("Medicine Dispenser");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
}
void loop() {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Time: ");
lcd.print(now.hour());
lcd.print(":");
lcd.print(now.minute());
lcd.print(":");
lcd.print(now.second());
// Check each alarm time
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (now.hour() == alarmHours[i] && now.minute() == alarmMinutes[i] && !alarmTriggered[i]) {
dispenseMedicine(i);
alarmTriggered[i] = true; // Prevent retriggering in the same minute
}
if (now.minute() != alarmMinutes[i]) {
alarmTriggered[i] = false; // Reset trigger for next day
}
}
handleButtonInput();
}
void dispenseMedicine(int alarmIndex) {
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Dispensing Dose ");
lcd.print(alarmIndex + 1);
tone(buzzerPin, 1000); // Sound buzzer
dispenserServo.write(90); // Rotate servo to release pills
delay(1000); // Wait for pill to drop
dispenserServo.write(0); // Return servo to original position
noTone(buzzerPin);
delay(1000); // Extra delay to ensure complete dispensing
}
void handleButtonInput() {
static int settingHour = 8;
static int settingMinute = 0;
static int alarmSettingIndex = 0;
// Increment hour setting
if (digitalRead(buttonSetHour) == LOW) {
settingHour = (settingHour + 1) % 24;
delay(200);
}
// Increment minute setting
if (digitalRead(buttonSetMinute) == LOW) {
settingMinute = (settingMinute + 1) % 60;
delay(200);
}
// Confirm time setting
if (digitalRead(buttonConfirmTime) == LOW) {
alarmHours[alarmSettingIndex] = settingHour;
alarmMinutes[alarmSettingIndex] = settingMinute;
alarmSettingIndex = (alarmSettingIndex + 1) % 3; // Cycle through alarms
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Set Alarm ");
lcd.print(alarmSettingIndex);
lcd.print(": ");
lcd.print(settingHour);
lcd.print(":");
lcd.print(settingMinute);
delay(500);
}
}
This code is responsible for controlling the medicine dispenser's operation, including setting alarm times, dispensing medication, and displaying information on the LCD. It uses the RTC to keep track of the current time and triggers the servo to dispense medicine at preset times. It also listens for button presses to set the alarm times and provides feedback through the buzzer and LCD.