
Arduino-Controlled Ultrasonic Distance Measurement with Dual Servo Motors
Circuit Documentation
Summary
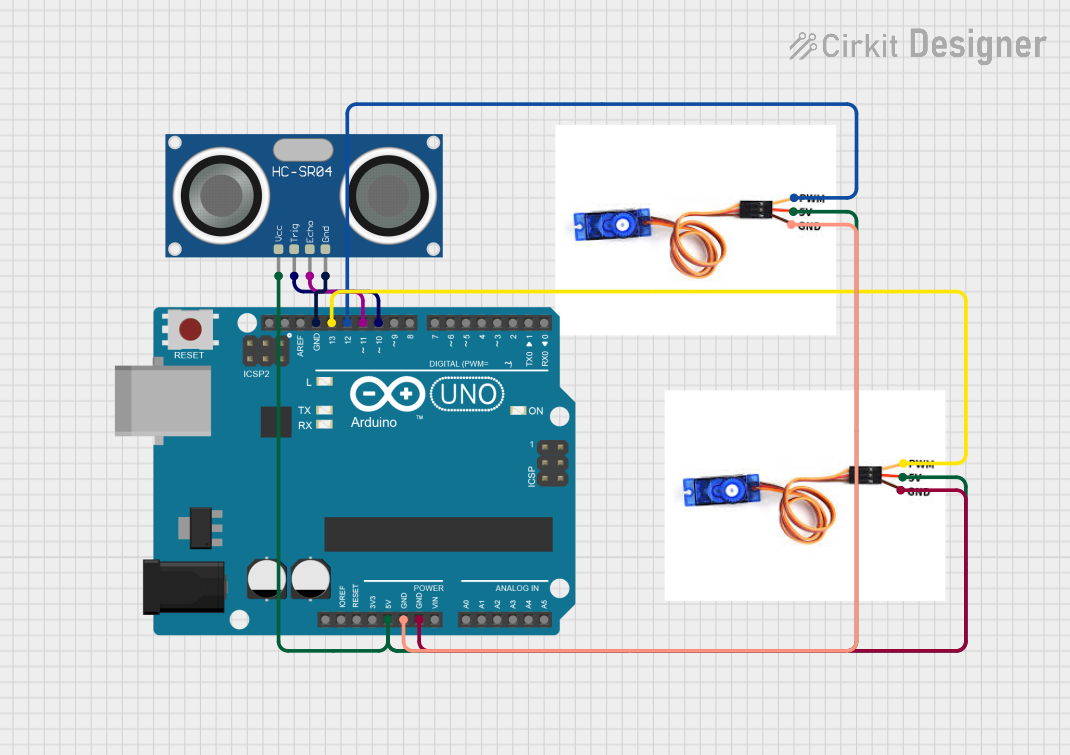
This circuit integrates an HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor and two SG90 servo motors controlled by an Arduino UNO microcontroller. The ultrasonic sensor is used to measure distances, and the servo motors are used to perform mechanical movements based on the sensor's readings. The Arduino UNO reads the distance values from the ultrasonic sensor and controls the position of the servo motors accordingly.
Component List
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
- Pins: VCC, TRIG, ECHO, GND
- Description: This sensor measures distances by emitting ultrasonic waves and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return.
SG90 Servo Motor (2x)
- Pins: PWM, 5V, GND
- Description: These servo motors are controlled using a PWM signal, allowing for precise control over the angle of rotation.
Arduino UNO
- Pins: UNUSED, IOREF, Reset, 3.3V, 5V, GND, Vin, A0-A5, SCL, SDA, AREF, D0-D13
- Description: The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has digital input/output pins, analog inputs, and various other functionalities.
Wiring Details
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
- VCC connected to 5V power supply from Arduino UNO
- TRIG connected to Digital Pin D10 on Arduino UNO
- ECHO connected to Digital Pin D11 on Arduino UNO
- GND connected to GND on Arduino UNO
SG90 Servo Motor 1
- PWM connected to Digital Pin D12 on Arduino UNO
- 5V connected to 5V power supply from Arduino UNO
- GND connected to GND on Arduino UNO
SG90 Servo Motor 2
- PWM connected to Digital Pin D13 on Arduino UNO
- 5V connected to 5V power supply from Arduino UNO
- GND connected to GND on Arduino UNO
Documented Code
// Include the Servo library
#include <Servo.h>
// Define Trig and Echo pins of Ultrasonic sensor
const int trigpin = 10;
const int echopin = 11;
// variables for the duration and the distance
long duration;
int distance;
// Create servo objects for controlling the servo motors
Servo myServo1;
Servo myServo2;
void setup() {
pinMode(trigpin, OUTPUT); // set the trigpin as an Output
pinMode(echopin, INPUT); // set the echopin as an Input
Serial.begin(9600);
myServo1.attach(12); // Defines on which pin is the first servo motor attached
myServo2.attach(13); // Defines on which pin is the second servo motor attached
}
void loop() {
// rotates the first servo motor from 15 to 165 degrees
for (int i = 15; i <= 165; i++) {
myServo1.write(i);
delay(30);
distance = calculateDistance(); // calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the ultrasonic sensor for each degree
Serial.print(i); // Sends the current degree into the Serial port
Serial.print(","); // Sends additional character right next to the previous value needed later in the processing IDE for indexing
Serial.print(distance); // sends the distance value into the serial port
Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value
}
// Repeats the previous line from 165 to 15 degrees
for (int i = 165; i >= 15; i--) {
myServo1.write(i);
delay(30);
distance = calculateDistance();
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(distance);
}
// Check if the ultrasonic sensor detects an obstruction
if (distance <= 10) { // Adjust the distance threshold as needed
// Rotate the second servo motor to 180 degrees immediately
myServo2.write(180);
} else {
// Reset the second servo motor to its original position (e.g., 0 degrees)
myServo2.write(0);
}
}
// Function to calculate the distance measured by the ultrasonic sensor
int calculateDistance() {
// Send a pulse of 10 microseconds to the trigpin
digitalWrite(trigpin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigpin, LOW);
// Measure the time it takes for the pulse to return to the echopin
duration = pulseIn(echopin, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance based on the speed of sound
distance = (duration / 2) * 0.0343; // Assuming the speed of sound is 343 m/s
return distance;
}
The code provided is for the Arduino UNO microcontroller. It includes the setup and loop functions, which are standard in Arduino programming. The setup function initializes the pins and attaches the servo motors to their respective pins. The loop function contains the logic for rotating the servo motors and reading the distance from the ultrasonic sensor. The calculateDistance function calculates the distance based on the duration of the ultrasonic pulse's echo.