
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Project Documentation
Arduino Nano-Based GPS and Health Monitoring System with A9G, MAX30102, and MLX90614
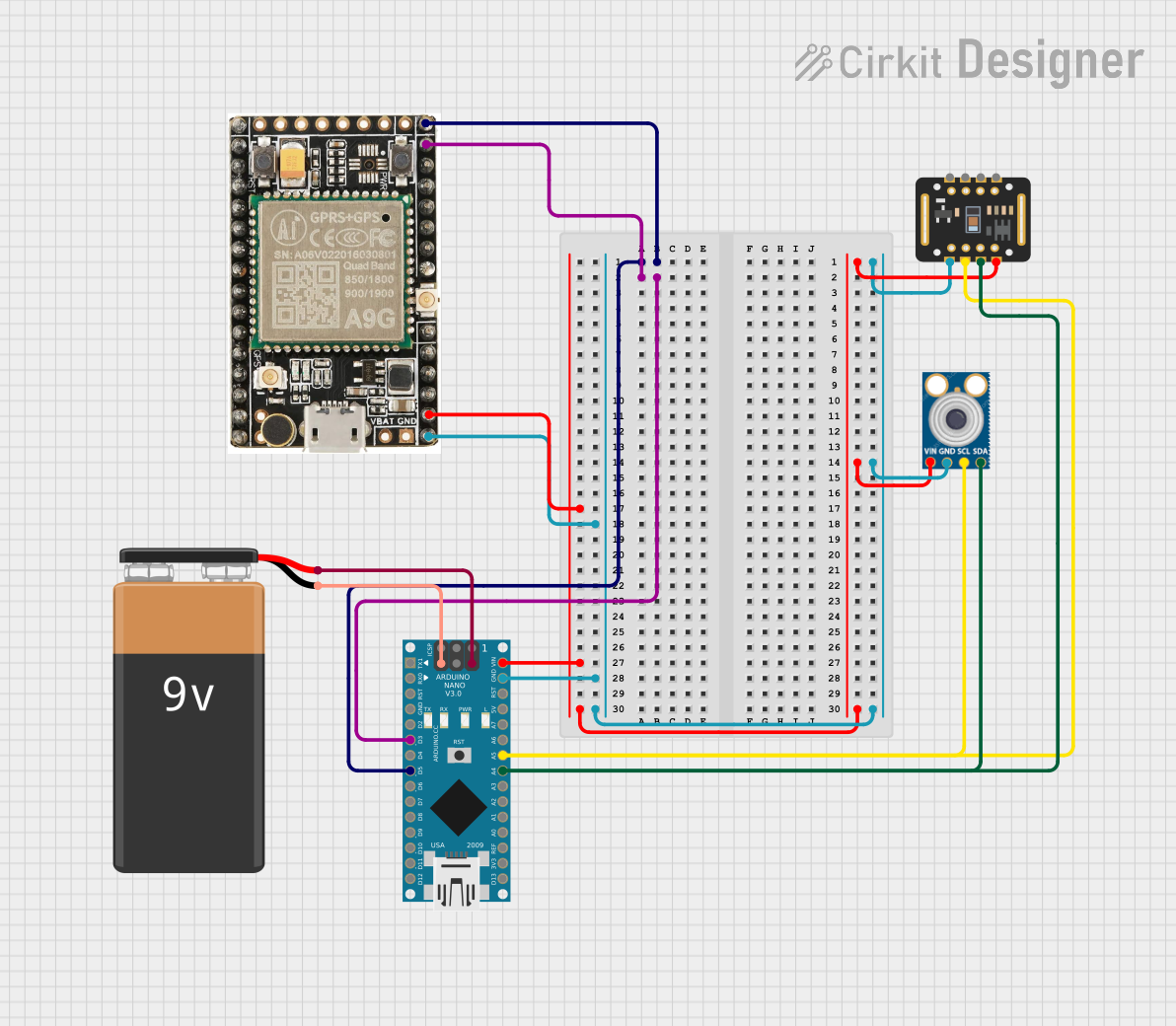
Circuit Documentation
Summary
This circuit integrates multiple sensors and a GPS module with an Arduino Nano to collect and transmit data. The sensors include the MAX30102 pulse oximeter, the MLX90614 infrared thermometer, and the A9G GPS module. The circuit is powered by a 9V battery. The Arduino Nano processes the data from the sensors and the GPS module and transmits it via MQTT.
Component List
A9G GPS Module
- Description: A GPS module used for location tracking.
- Pins: Data Pin 1, Data Pin 2, VCC, GND
MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter
- Description: A sensor used to measure pulse rate and blood oxygen levels.
- Pins: VIN, SDA, SCL, GND, RD, IRD, INT
MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer
- Description: A sensor used to measure temperature without contact.
- Pins: SDA, SCL, GND, VIN
Arduino Nano
- Description: A microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P.
- Pins: D1/TX, D0/RX, RESET, GND, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11/MOSI, D12/MISO, VIN, 5V, A7, A6, A5, A4, A3, A2, A1, A0, AREF, 3V3, D13/SCK
9V Battery
- Description: A power source for the circuit.
- Pins: +, -
Wiring Details
A9G GPS Module
- Data Pin 1 connected to Arduino Nano D5
- Data Pin 2 connected to Arduino Nano D3
- VCC connected to Arduino Nano VIN
- GND connected to Arduino Nano GND
MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter
- VIN connected to Arduino Nano VIN
- SDA connected to Arduino Nano A4
- SCL connected to Arduino Nano A5
- GND connected to Arduino Nano GND
MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer
- SDA connected to Arduino Nano A4
- SCL connected to Arduino Nano A5
- GND connected to Arduino Nano GND
- VIN connected to Arduino Nano VIN
Arduino Nano
- D5 connected to A9G GPS Module Data Pin 1
- D3 connected to A9G GPS Module Data Pin 2
- A4 connected to MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter SDA and MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer SDA
- A5 connected to MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter SCL and MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer SCL
- VIN connected to A9G GPS Module VCC, MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter VIN, and MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer VIN
- GND connected to A9G GPS Module GND, MAX30102 Pulse Oximeter GND, MLX90614 Infrared Thermometer GND, and 9V Battery -
- 5V connected to 9V Battery +
9V Battery
- + connected to Arduino Nano 5V
- - connected to Arduino Nano GND
Documented Code
#include <TinyGPSPlus.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "EmonLib.h"
EnergyMonitor emon1;
int tegangan = 220.0;
int pin_sct = A7;
static const int RXPin = 5, TXPin = 3;
const int ledPin = 4;
String s = "www.google.com/maps/dir/";
unsigned long interval = 10000;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
int data_counter;
const size_t BUFSIZE = 300;
char f_buffer[BUFSIZE];
float *f_buf = (float*)f_buffer;
TinyGPSPlus gps; // The TinyGPSPlus object
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin); // The serial connection to the GPS device
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.println("Starting...");
ss.println("\r");
ss.println("AT\r");
delay(10);
ss.println("\r");
ss.println("AT+GPS=1\r");
delay(100);
ss.println("AT+CREG=2\r");
delay(6000);
ss.println("AT+CGATT=1\r");
delay(6000);
ss.println("AT+CGDCONT=1,\"IP\",\"internet\"\r");
delay(6000);
ss.println("AT+CGACT=1,1\r");
delay(6000);
ss.println("\r");
ss.println("AT+GPS=1\r");
delay(1000);
ss.println("AT+CMGF=1\r");
delay(1000);
ss.println("AT+MQTTCONN=\"broker.hivemq.com\",1883,dazonkitchen,120,0,\"\",\"\"\r");
delay(10000);
ss.println("AT+MQTTPUB=\"dazon\",\"MQTT Connection Successfully\",0,0,0\r");
delay(5000);
emon1.current(pin_sct, 26);
Serial.println("Setup Executed");
}
void loop() {
smartDelay(2000);
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
Serial.println(F("No GPS data received: check wiring"));
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if ((unsigned long)(currentMillis - previousMillis) >= interval) {
send_gps_data();
previousMillis = currentMillis;
}
}
static void smartDelay(unsigned long ms)
{
unsigned long start = millis();
do
{
while (ss.available())
gps.encode(ss.read());
} while (millis() - start < ms);
}
void send_gps_data()
{
if (gps.location.lat() == 0 || gps.location.lng() == 0)
{
Serial.println("Return Executed");
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
return;
}
data_counter++;
double Irms = emon1.calcIrms(1480);
Serial.print("Latitude (deg): ");
f_buf[data_counter] = gps.location.lat();
Serial.println(f_buf[data_counter]);
Serial.print("Longitude (deg): ");
f_buf[data_counter + 1] = gps.location.lng();
Serial.println(f_buf[data_counter + 1]);
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
ss.print("AT+MQTTPUB=\"dazon\",\"");
ss.print(gps.location.lat(),6);
ss.print(", ");
ss.print(gps.location.lng(),6);
ss.print(" Arus = ");
ss.print(Irms);
ss.print("\",0,0,0\r");
Serial.println(data_counter);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Arus yang terbaca : ");
Serial.print(Irms);
Serial.print("Daya yang terbaca : ");
Serial.println(Irms*tegangan);
s += String(gps.location.lat(), 6);
s += ",";
s += String(gps.location.lng(), 6);
s += "/";
Serial.println(s);
if (data_counter >= 10)
{
data_counter = 0;
Serial.println("Sending Message");
ss.println("AT+CMGF=1\r");
delay(1000);
ss.println("AT+CNMI=2,2,0,0,0\r");
delay(1000);
ss.print("AT+CMGS=\"+628111882134\"\r"); // Replace this with your mobile number
delay(1000);
ss.print(s);
ss.write(0x1A);
delay(1000);
s = "www.google.com/maps/dir/";
}
}
This code initializes the GPS module, connects to an MQTT broker, and periodically sends GPS data along with current measurements to the broker. The data is also printed to the serial monitor for debugging purposes.