
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Project Documentation
Arduino UNO Bluetooth Controlled Car with Ultrasonic Sensor
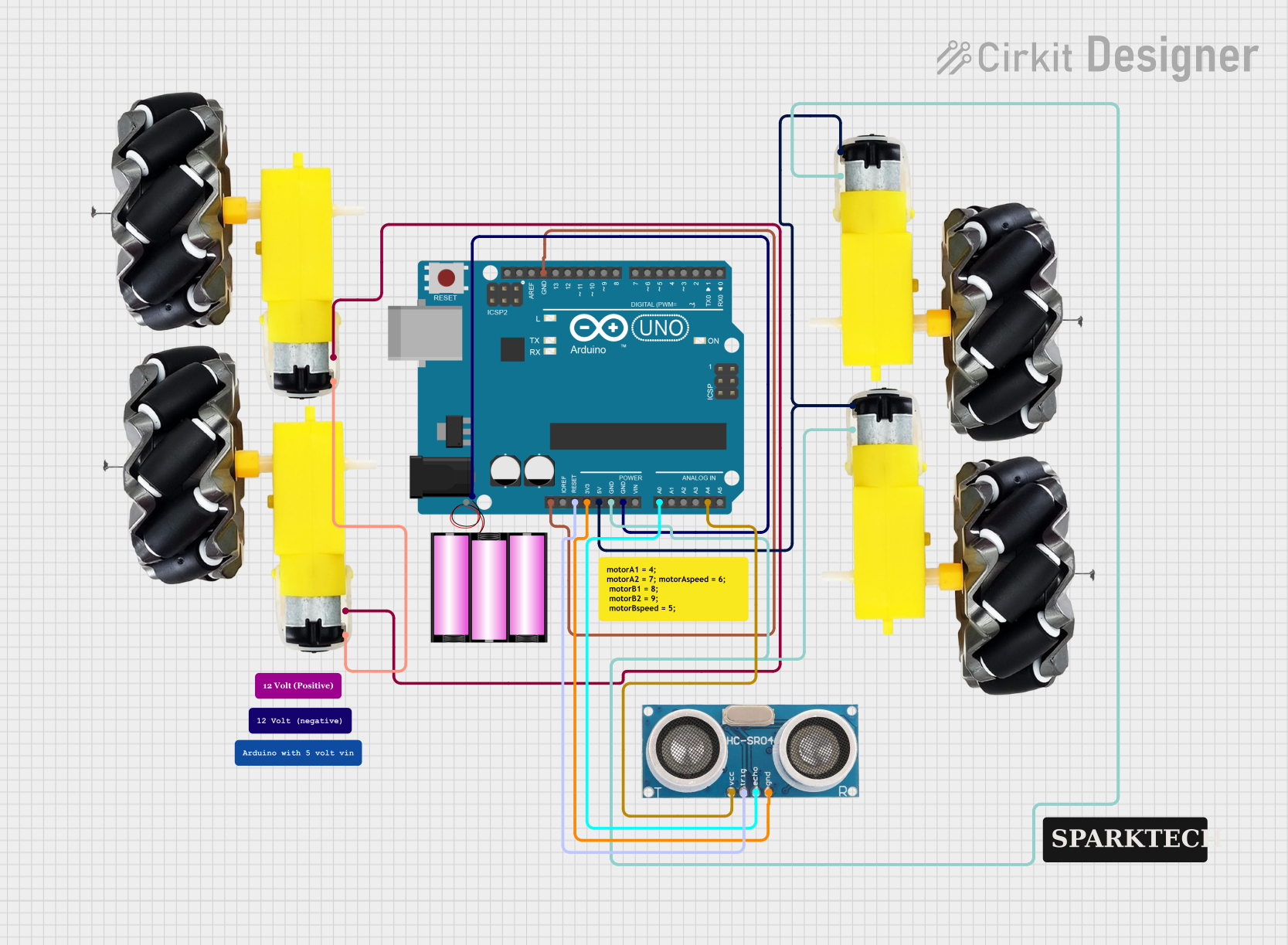
Circuit Documentation
Summary
This document provides a detailed overview of a Bluetooth-controlled car circuit. The circuit includes an Arduino UNO microcontroller, a 12V battery, multiple motor and wheel assemblies, and an ultrasonic sensor. The Arduino UNO is programmed to control the motors based on commands received via Bluetooth, enabling the car to move forward, backward, left, and right. The ultrasonic sensor is used for obstacle detection.
Component List
Arduino UNO
- Description: A microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P.
- Pins: UNUSED, IOREF, Reset, 3.3V, 5V, GND, Vin, A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, SCL, SDA, AREF, D13, D12, D11, D10, D9, D8, D7, D6, D5, D4, D3, D2, D1, D0
Battery 12V
- Description: A 12V battery used to power the circuit.
- Pins: +, -
Motor and Wheels
- Description: Motor and wheel assemblies used for movement.
- Pins: vcc, GND
Ultrasonic Sensor
- Description: A sensor used for obstacle detection.
- Pins: +VCC, Trigger, Echo, GND
Wiring Details
Arduino UNO
- UNUSED connected to GND of Arduino UNO.
- Reset connected to Trigger of Ultrasonic Sensor.
- 3.3V connected to GND of Ultrasonic Sensor.
- 5V connected to vcc of Motor and Wheels (2 instances).
- GND connected to:
- GND of Motor and Wheels (2 instances).
- - of Battery 12V.
- A0 connected to Echo of Ultrasonic Sensor.
- A4 connected to +VCC of Ultrasonic Sensor.
Battery 12V
- - connected to GND of Arduino UNO.
Motor and Wheels
- vcc connected to:
- vcc of another Motor and Wheels instance.
- 5V of Arduino UNO.
- GND connected to:
- GND of another Motor and Wheels instance.
- GND of Arduino UNO.
Ultrasonic Sensor
- Trigger connected to Reset of Arduino UNO.
- GND connected to 3.3V of Arduino UNO.
- Echo connected to A0 of Arduino UNO.
- +VCC connected to A4 of Arduino UNO.
Documented Code
//Arduino Bluetooth Controlled Car
//Before uploading the code you have to install the necessary library
//Note - Disconnect the Bluetooth Module before hitting the upload button otherwise you'll get a compilation error message.
//AFMotor Library https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-motor-shield/library-install
//After downloading the library open Arduino IDE >> go to sketch >> Include Library >> ADD. ZIP Library >> Select the downloaded
//ZIP File >> Open it >> Done
//Now You Can Upload the Code without any problem but make sure the bt module isn't connected with Arduino while uploading code
#include <AFMotor.h>
//initial motors pin
AF_DCMotor motor1(1, MOTOR12_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor2(2, MOTOR12_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor3(3, MOTOR34_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor4(4, MOTOR34_1KHZ);
char command;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Set the baud rate to your Bluetooth module.
}
void loop(){
if(Serial.available() > 0){
command = Serial.read();
Stop(); //initialize with motors stopped
//Change pin mode only if new command is different from previous.
//Serial.println(command);
switch(command){
case 'F':
forward();
break;
case 'B':
back();
break;
case 'L':
left();
break;
case 'R':
right();
break;
}
}
}
void forward()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255);//Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255);//Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
}
void back()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
}
void left()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
}
void right()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
}
void Stop()
{
motor1.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor1.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
motor2.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor2.run(RELEASE); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor3.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
motor4.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor4.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
}
This code is designed to control the motors of the car based on commands received via Bluetooth. The car can move forward, backward, left, and right, and the motors are controlled using the AFMotor library.