
ESP32-Based Accident Detection and GPS Tracking System with GSM Notifications
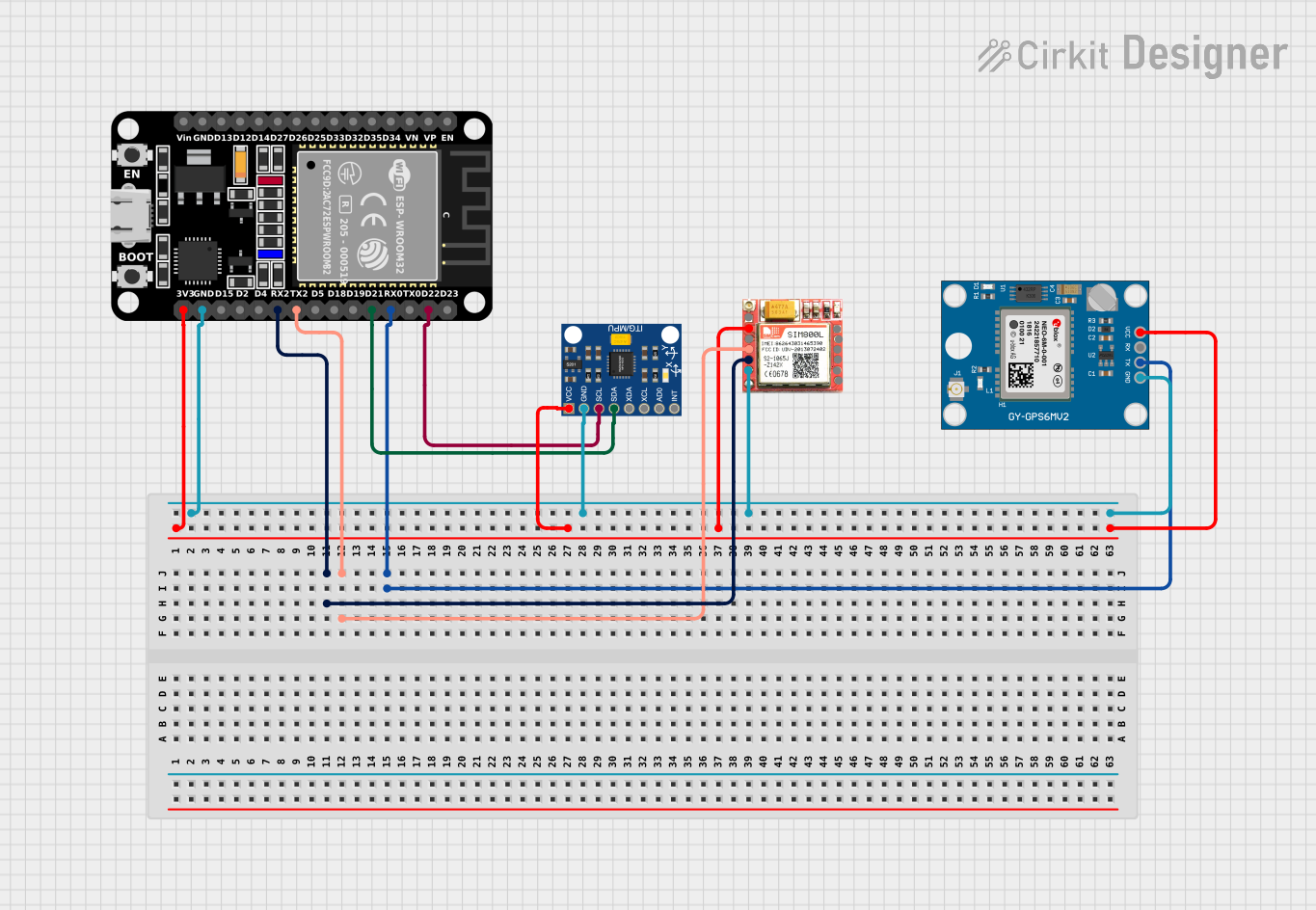
Circuit Documentation
Summary
This circuit integrates a microcontroller (ESP32), a GPS module (Neo 6M), an accelerometer/gyroscope (InvenSense MPU6050), and a GSM module (SIM800L) to create a system capable of detecting accidents and providing location data. The ESP32 serves as the central processing unit, interfacing with the GPS module for location tracking, the MPU6050 for motion detection, and the SIM800L for GSM communication. The system is designed to detect significant accelerations that may indicate an accident and then communicate the event and location data via SMS.
Component List
ESP32 (30 pin)
- Description: A powerful microcontroller with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities.
- Pins: EN, VP, VN, D34, D35, D32, D33, D25, D26, D27, D14, D12, D13, GND, Vin, D23, D22, TX0, RX0, D21, D19, D18, D5, TX2, RX2, D4, D2, D15, 3V3
InvenSense MPU6050
- Description: A 6-axis accelerometer and gyroscope sensor for motion tracking.
- Pins: VCC, GND, SCL, SDA, XDA, XCL, AD0, INT
Neo 6M GPS Module
- Description: A GPS receiver module for satellite-based positioning.
- Pins: GND, TX, RX, VCC
SIM800L
- Description: A GSM/GPRS module for cellular communication.
- Pins: NFT, RING, VCC, DTR, RST, MIC +, RXD, MIC-, TXD, SPK+, GND, SPK-
Wiring Details
ESP32 (30 pin)
- 3V3 connected to VCC of InvenSense MPU6050, SIM800L, and Neo 6M GPS Module
- GND connected to GND of InvenSense MPU6050, SIM800L, and Neo 6M GPS Module
- D22 (SCL) connected to SCL of InvenSense MPU6050
- D21 (SDA) connected to SDA of InvenSense MPU6050
- RX2 connected to TXD of SIM800L
- TX2 connected to RXD of SIM800L
- RX0 connected to TX of Neo 6M GPS Module
InvenSense MPU6050
- VCC connected to 3V3 of ESP32
- GND connected to GND of ESP32
- SCL connected to D22 of ESP32
- SDA connected to D21 of ESP32
Neo 6M GPS Module
- VCC connected to 3V3 of ESP32
- GND connected to GND of ESP32
- TX connected to RX0 of ESP32
SIM800L
- VCC connected to 3V3 of ESP32
- GND connected to GND of ESP32
- TXD connected to RX2 of ESP32
- RXD connected to TX2 of ESP32
Documented Code
ESP32 (30 pin)
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_MPU6050.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
// GPS Module
TinyGPSPlus gps;
HardwareSerial gpsSerial(1); // Use UART1 for GPS
// MPU6050 Accelerometer
Adafruit_MPU6050 mpu;
// GSM Module
HardwareSerial gsmSerial(2); // Use UART2 for GSM
const char* apn = "your_apn"; // Replace with your APN
const char* user = "your_user"; // Replace with your APN username
const char* pass = "your_pass"; // Replace with your APN password
const char* phone_number = "your_phone_number"; // Replace with the recipient's phone number
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize GPS
gpsSerial.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, 16, 17); // RX, TX pins for GPS
Serial.println("GPS module initialized");
// Initialize MPU6050
if (!mpu.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find MPU6050 chip");
while (1) {
delay(10);
}
}
Serial.println("MPU6050 initialized");
mpu.setAccelerometerRange(MPU6050_RANGE_8_G);
mpu.setGyroRange(MPU6050_RANGE_500_DEG);
mpu.setFilterBandwidth(MPU6050_BAND_21_HZ);
// Initialize GSM
gsmSerial.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, 26, 27); // RX, TX pins for GSM
Serial.println("GSM module initialized");
// Connect to GSM network
connectGSM();
}
void loop() {
// Read GPS data
while (gpsSerial.available() > 0) {
gps.encode(gpsSerial.read());
}
if (gps.location.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print("Latitude: ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print("Longitude: ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
// Read accelerometer data
sensors_event_t a, g, temp;
mpu.getEvent(&a, &g, &temp);
// Check for fall detection (example threshold)
if (a.acceleration.z < -9.0) {
Serial.println("Fall detected!");
sendSMS("Fall detected! Location: " + String(gps.location.lat(), 6) + ", " + String(gps.location.lng(), 6));
}
delay(1000);
}
void connectGSM() {
gsmSerial.println("AT");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CPIN?");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CREG?");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CGATT?");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CSTT=\"" + String(apn) + "\",\"" + String(user) + "\",\"" + String(pass) + "\"");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CIICR");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CIFSR");
delay(1000);
}
void sendSMS(String message) {
gsmSerial.println("AT+CMGF=1"); // Set SMS to text mode
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.println("AT+CMGS=\"" + String(phone_number) + "\"");
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.print(message);
delay(1000);
gsmSerial.write(26); // ASCII code for CTRL+Z to send the SMS
delay(1000);
}
InvenSense MPU6050
// Pseudo code for accident detection
if (abs(acceleration.x) > threshold || abs(acceleration.y) > threshold || abs(acceleration.z) > threshold) {
accident_detected = true;
}
Neo 6M GPS Module
double calculateDistance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2) {
// Implement Haversine formula to calculate distance
double dLat = (lat2 - lat1) * DEG_TO_RAD;
double dLon = (lon2 - lon1) * DEG_TO_RAD;
// Compute the distance using earth radius and return value
return distance;
}
SIM800L
gsm.sendSMS("+1234567890", "Accident Detected! Location: https://maps.google.com/?q=" + String(latitude) + "," + String(longitude));
This documentation provides an overview of the circuit's components, their wiring, and the code that governs their behavior. Each section is designed to give a clear understanding of the circuit's functionality and how the components interact with each other.