
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Project Documentation
Arduino UNO Controlled Waste Sorting System with Dual Servos and Metal Detection
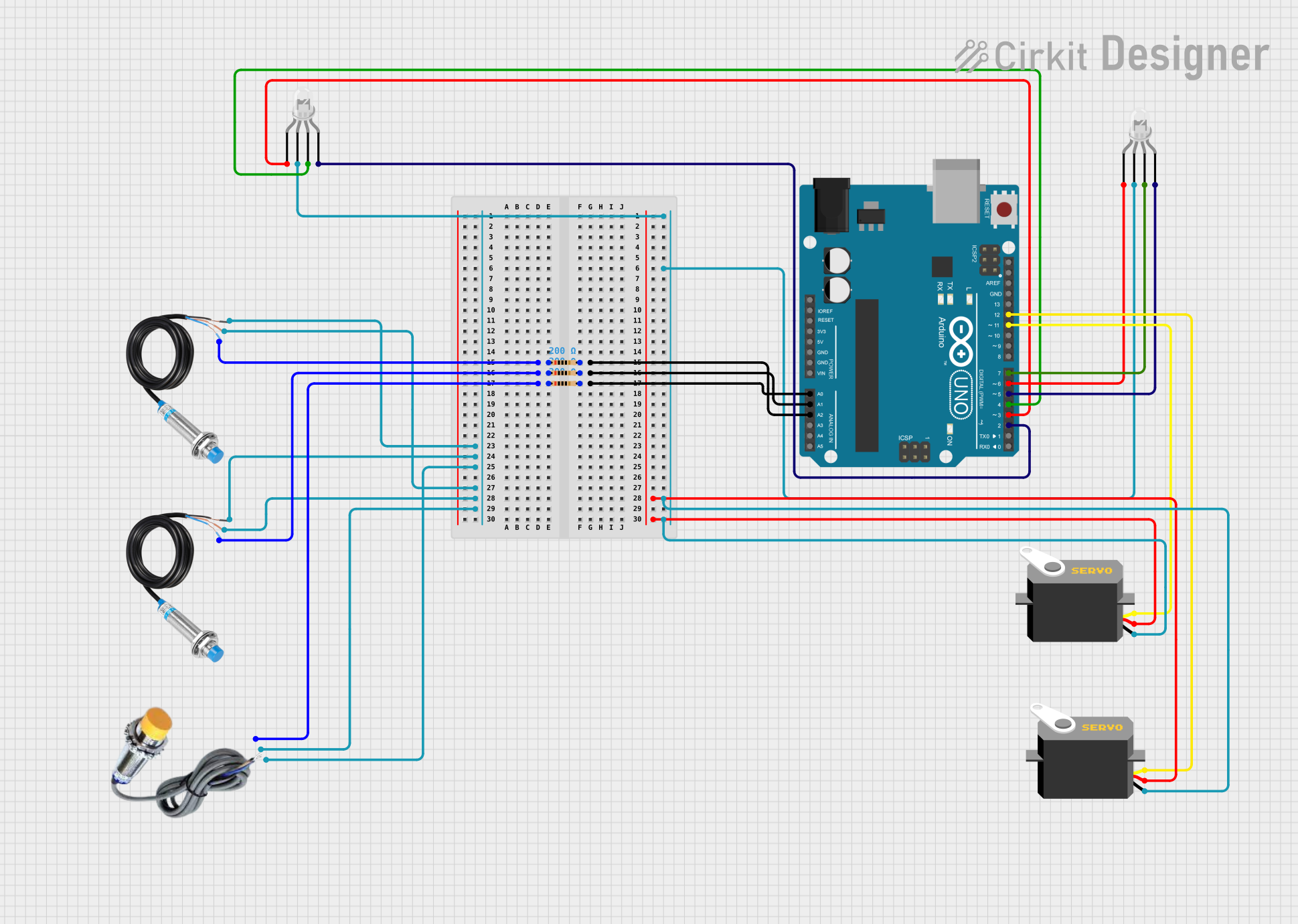
Circuit Documentation
Summary
The circuit is designed to interface with various sensors and actuators using an Arduino UNO microcontroller. It includes metal detection sensors, a capacitive sensor, RGB LEDs, resistors, and servo motors. The circuit is likely intended for a sorting system where different types of sensors detect specific materials or objects, and the servos actuate to sort or direct these materials accordingly. The RGB LEDs may serve as indicators for system status or sorting results.
Component List
Arduino UNO
- Microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P
- It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
LED: Four Pin (Common Cathode)
- RGB LED with a common cathode configuration
- It has separate pins for the red, green, and blue anodes.
Capacitive Sensor
- Sensor used to detect touch or proximity
- It has pins for ground (GND), power (VCC), and signal output (SIGNAL).
Metal Detection Sensor
- Sensor used to detect the presence of metal
- It has pins for power (POWER), ground (GND), and signal output (OUT).
Resistor
- Passive component used to limit current or divide voltages
- It has two pins and a specified resistance value.
Servo
- Motor capable of precise control of angular position
- It has pins for ground (gnd), power (vcc), and control signal (pulse).
Wiring Details
Arduino UNO
- Analog inputs A0, A1, and A2 are connected to the signal outputs of the capacitive sensor and metal detection sensors through resistors.
- Digital pins D2 to D7 are connected to the anodes of two RGB LEDs.
- Digital pins D11 and D12 are connected to the control signal inputs of two servo motors.
LED: Four Pin (Common Cathode)
- The common cathode of each LED is connected to the ground.
- The red, green, and blue anodes are connected to specific digital pins on the Arduino UNO for color control.
Capacitive Sensor
- The SIGNAL pin is connected to the Arduino UNO's A0 analog input through a resistor.
- The VCC pin is connected to the power supply, and the GND pin is connected to the ground.
Metal Detection Sensor
- The OUT pin of each sensor is connected to the Arduino UNO's A1 and A2 analog inputs through resistors.
- The POWER pin is connected to the power supply, and the GND pin is connected to the ground.
Resistor
- Each resistor is connected in series with a signal pin from a sensor and an analog input on the Arduino UNO.
Servo
- The vcc pin of each servo is connected to the power supply.
- The gnd pin is connected to the ground.
- The pulse pin is connected to the Arduino UNO's D11 and D12 digital pins for control signals.
Documented Code
/// include library
#include <Servo.h> // servo motor library
// Pin Definitions
// plastic bin pin
#define redpin 5
#define bluepin 6
#define greenpin 7
#define plasticsensor A0
#define metalsensor A1
#define IR_plastic A3
// metal bin pin definitions
#define redpin_M 8
#define bluepin_M 9
#define greenpin_M 10
#define metalsensor_M A2
#define IR_metal A3
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo on plastic bin
Servo myservo_M; // create servo object to control a servo on metal bin
int pos = 165; // default servo position of plastic bin
int pos_M = 158; // default servo position of metal bin
void setup() {
myservo.attach(11); // attaches the plastic bin servo on pin 11 to the servo object
myservo_M.attach(12); // attaches the metal bin servo on pin 12 to the servo object
// RGB LED on plastic bin
pinMode(redpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluepin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenpin, OUTPUT);
// RGB LED on metal bin
pinMode(redpin_M, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluepin_M, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenpin_M, OUTPUT);
// Create sensor values in pull up condition
pinMode(plasticsensor, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(metalsensor, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(metalsensor_M, INPUT_PULLUP);
// start serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set RGB LED on default values (white)
analogWrite(redpin, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin, 255);
analogWrite(greenpin, 255);
analogWrite(redpin_M, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin_M, 255);
analogWrite(greenpin_M, 255);
}
void loop() {
int sensor_read_plastic = digitalRead(plasticsensor);
int sensor_read_metal = digitalRead(metalsensor);
int sensor_read_metal2 = digitalRead(metalsensor_M);
Serial.println("plastic sensor");
Serial.println(sensor_read_plastic);
Serial.println("metal sensor");
Serial.println(sensor_read_metal);
Serial.println(sensor_read_metal2);
// Check if the trash bin is full
// Plastic bin
if ((sensor_read_plastic == 0) && (sensor_read_metal != 1)) {
for (pos = 160; pos >= 90; pos -= 1) { // goes from 160 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(1); // waits 1ms for the servo to reach the position
}
analogWrite(redpin, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin, 0);
analogWrite(greenpin, 255);
delay(2500);
for (pos = 90; pos <= 160; pos += 1) { // goes from 90 degrees to 160 degrees
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(1); // waits 1ms for the servo to reach the position
}
analogWrite(redpin, 0);
analogWrite(bluepin, 0);
analogWrite(greenpin, 0);
} else {
// keep the door closed
myservo.write(pos);
analogWrite(redpin, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin, 255);
analogWrite(greenpin, 255);
}
// Metal bin
if (sensor_read_metal2 == 1) {
for (pos_M = 160; pos_M >= 90; pos_M -= 1) { // goes from 160 degrees to 90 degrees
myservo_M.write(pos_M); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(1); // waits 1ms for the servo to reach the position
}
analogWrite(redpin_M, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin_M, 0);
analogWrite(greenpin_M, 255);
delay(2500);
for (pos_M = 90; pos_M <= 160; pos_M += 1) { // goes from 90 degrees to 160 degrees
myservo_M.write(pos_M); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(1); // wait 1ms for the servo to reach the position
}
analogWrite(redpin_M, 0);
analogWrite(bluepin_M, 0);
analogWrite(greenpin_M, 0);
} else {
// keep the door closed
myservo_M.write(pos_M);
analogWrite(redpin_M, 255);
analogWrite(bluepin_M, 255);
analogWrite(greenpin_M, 255);
}
}
Note: The code provided has some syntax errors and inconsistencies with the pin definitions and the actual wiring of the circuit. These issues need to be addressed for the code to function correctly with the given hardware configuration.