
Arduino UNO with GPS NEO 6M Data Logger
Circuit Documentation
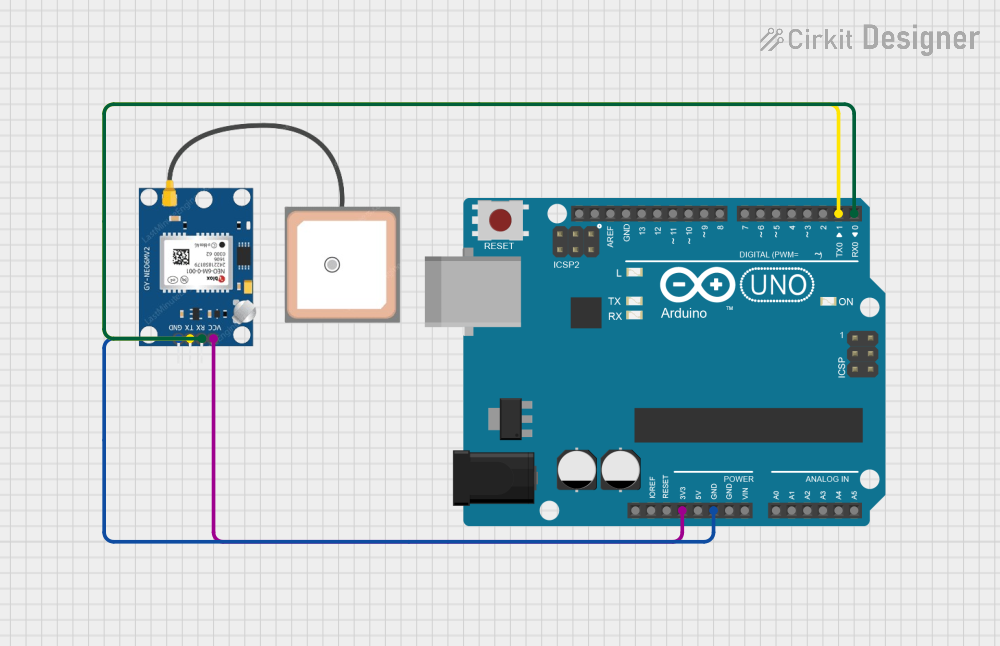
Summary of the Circuit
This circuit integrates an Arduino UNO microcontroller with a GPS NEO 6M module. The Arduino UNO is responsible for interfacing with the GPS module, reading the NMEA sentences provided by the GPS module, and outputting the data through its serial interface. The GPS module receives power from the Arduino and communicates with it using a serial connection. The Arduino's digital pins D0 and D1 are used for this serial communication, facilitated by a software serial port in the embedded code.
Component List
Arduino UNO
- Description: A microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P.
- Pins Used:
IOREFReset3.3V5VGNDVinA0toA5SCLSDAAREFD13toD0
GPS NEO 6M
- Description: A compact GPS module with an onboard antenna.
- Pins Used:
VCCRXTXGND
Wiring Details
Arduino UNO
3.3Vconnected to GPS NEO 6MVCCGNDconnected to GPS NEO 6MGNDD1(TX) connected to GPS NEO 6MRXD0(RX) connected to GPS NEO 6MTX
GPS NEO 6M
VCCconnected to Arduino UNO3.3VGNDconnected to Arduino UNOGNDTXconnected to Arduino UNOD1RXconnected to Arduino UNOD0
Documented Code
The following code is written for the Arduino UNO to interface with the GPS NEO 6M module:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Choose two Arduino pins to use for software serial
int RXPin = 0;
int TXPin = 1;
// Default baud of NEO-6M is 9600
int GPSBaud = 9600;
// Create a software serial port called "gpsSerial"
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup()
{
// Start the Arduino hardware serial port at 9600 baud
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start the software serial port at the GPS's default baud
gpsSerial.begin(GPSBaud);
}
void loop()
{
// Displays information when new sentence is available.
while (gpsSerial.available() > 0)
Serial.write(gpsSerial.read());
}
This code sets up a software serial connection on pins D0 and D1 of the Arduino UNO to communicate with the GPS module. It reads the data from the GPS module and outputs it to the Arduino's hardware serial port for monitoring. The GPS module operates at a default baud rate of 9600 bps, which is set for both the software and hardware serial ports.