
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Project Documentation
Arduino Mega 2560 Controlled Robotic Arm and Vehicle with Bluetooth Interface
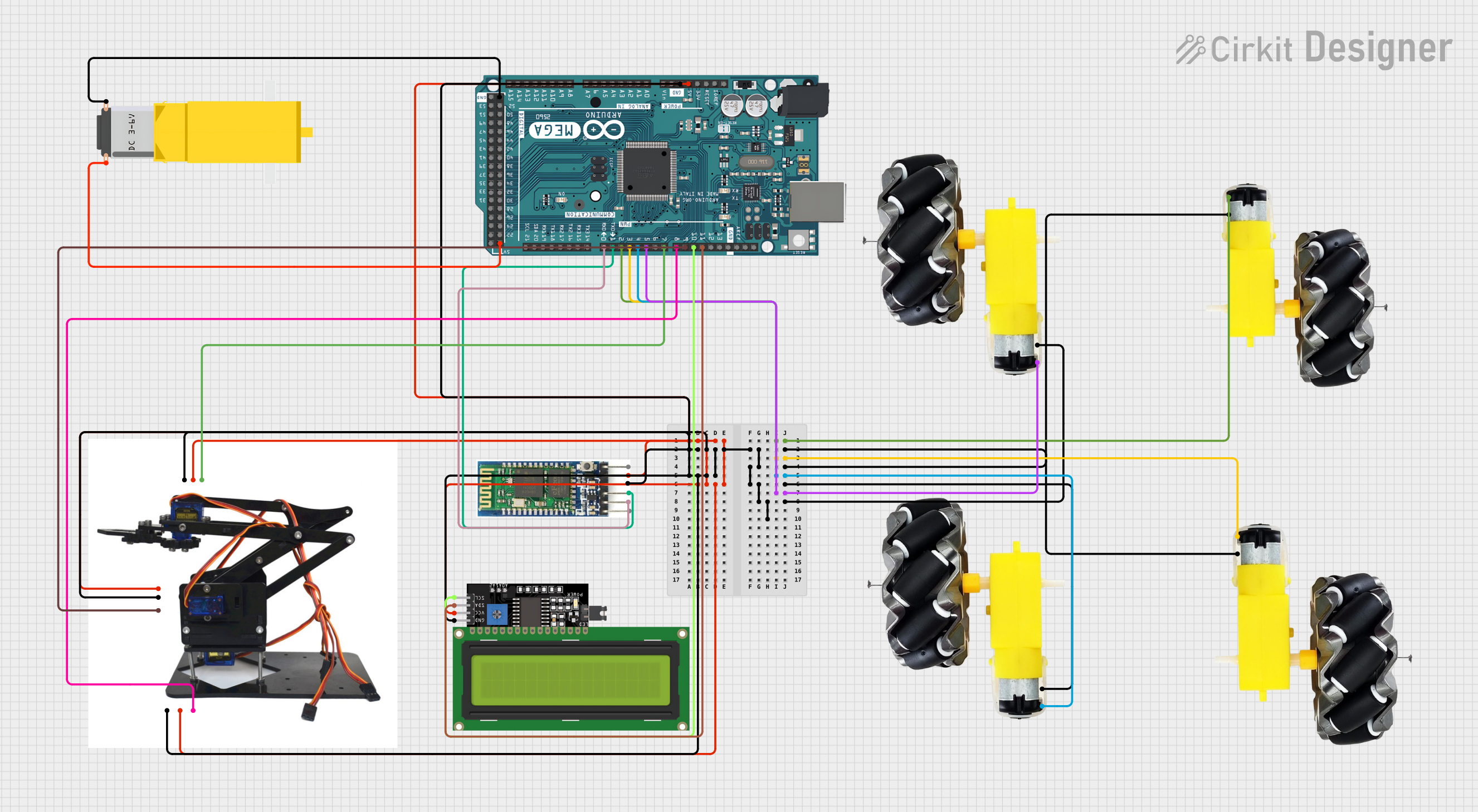
Circuit Documentation
Summary
The circuit in question is designed to control a robotic arm, a set of motors with wheels, a gearmotor, and an LCD display, all interfaced with an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller. The Arduino Mega 2560 is responsible for processing inputs and outputs to control the motors and servos, communicate with a Bluetooth module for wireless control, and display system status on an LCD display. The circuit is powered by the Arduino's 5V output, which is distributed to the various components that require power.
Component List
Arduino Mega 2560
- Microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560
- It has 54 digital input/output pins (of which 15 can be used as PWM outputs), 16 analog inputs, 4 UARTs (hardware serial ports), a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
Motor and Wheels (4 instances)
- A set of motors attached to wheels, likely used for moving a vehicle or robot.
- Each motor has a VCC and GND pin for power connections.
Bluetooth Module
- A wireless communication module that allows for serial communication over Bluetooth.
- The module has pins for enabling (EN), power (VCC), ground (GND), transmit (TXD), receive (RXD), and a state pin (STATE).
Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit
- A robotic arm kit made of acrylic, with servos for articulation.
- The kit includes pins for ground (GND1, GND2, GND3), power (VCC1, VCC2, VCC3), and data (DATA1, DATA2, DATA3) for controlling the servos.
Gearmotor DC
- A DC gearmotor used for applications requiring torque.
- The gearmotor has two pins, Pin1 and Pin2, for power connections.
LCD Display 16x4 I2C
- An LCD display with an I2C interface, which allows for displaying text and numbers.
- The display has pins for I2C data (SDA), I2C clock (SCL), power (VCC), and ground (GND).
Wiring Details
Arduino Mega 2560
- 5V: Connected to VCC pins of the Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit, Bluetooth Module, and LCD Display.
- GND: Connected to GND pins of all components.
- D2 PWM: Connected to the VCC pin of one Motor and Wheels.
- D3 PWM: Connected to the VCC pin of another Motor and Wheels.
- D4 PWM: Connected to the VCC pin of another Motor and Wheels.
- D5 PWM: Connected to the VCC pin of another Motor and Wheels.
- D0 RX0: Connected to the RXD pin of the Bluetooth Module.
- D1 TX0: Connected to the TXD pin of the Bluetooth Module.
- D7 PWM: Connected to the DATA3 pin of the Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit.
- D8 PWM: Connected to the DATA1 pin of the Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit.
- D9 PWM: Connected to the DATA2 pin of the Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit.
- D10 PWM: Connected to the SCL pin of the LCD Display.
- D11 PWM: Connected to the SDA pin of the LCD Display.
Motor and Wheels
- VCC: Connected to various PWM pins on the Arduino Mega 2560 for speed control.
- GND: Connected to the GND pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
Bluetooth Module
- VCC: Connected to the 5V pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- GND: Connected to the GND pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- TXD: Connected to the D1 TX0 pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- RXD: Connected to the D0 RX0 pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
Acrylic Robotic Arm Kit
- VCC1, VCC2, VCC3: Connected to the 5V pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- GND1, GND2, GND3: Connected to the GND pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- DATA1: Connected to the D8 PWM pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- DATA2: Connected to the D9 PWM pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- DATA3: Connected to the D7 PWM pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
Gearmotor DC
- Pin1: Connected to the GND pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- Pin2: Connected to the 5V pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
LCD Display 16x4 I2C
- SCL: Connected to the D10 PWM pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- SDA: Connected to the D11 PWM pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- VCC: Connected to the 5V pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
- GND: Connected to the GND pin on the Arduino Mega 2560.
Documented Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#include <Servo.h>
// Definition of pins for the motors
const int motor1Pin = 2; // Motor 1 connected to D2 PWM
const int motor2Pin = 3; // Motor 2 connected to D3 PWM
const int motor3Pin = 4; // Motor 3 connected to D4 PWM
const int motor4Pin = 5; // Motor 4 connected to D5 PWM
// Definition of pins for the SG90 servos
const int servo1Pin = 8; // Servo 1 connected to D8 PWM
const int servo2Pin = 9; // Servo 2 connected to D9 PWM
const int servo3Pin = 7; // Servo 3 connected to D7 PWM
// Definition of pins for the gearmotor
const int motorreductorPin1 = 6; // Gearmotor Pin1 connected to D6 PWM
const int motorreductorPin2 = 5; // Gearmotor Pin2 connected to D5 PWM
// Initialization of the I2C LCD display
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2); // I2C address 0x27, 16 columns and 2 rows
// Initialization of the servos
Servo servo1;
Servo servo2;
Servo servo3;
void setup() {
// Configure motor pins as outputs
pinMode(motor1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor2Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor3Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor4Pin, OUTPUT);
// Configure servo pins as outputs
servo1.attach(servo1Pin);
servo2.attach(servo2Pin);
servo3.attach(servo3Pin);
// Configure gearmotor pins as outputs
pinMode(motorreductorPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorreductorPin2, OUTPUT);
// Initialize serial communication for the Bluetooth module
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the LCD display
lcd.begin();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("System Started");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the Bluetooth module
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char command = Serial.read(); // Read the command sent
// Display the received command on the LCD
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Cmd: ");
lcd.print(command);
lcd.print(" "); // Blank spaces to clear the line
// Control the motors based on the received command
switch (command) {
case 'F': // Forward
analogWrite(motor1Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor2Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor3Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor4Pin, 255);
break;
case 'B': // Backward
analogWrite(motor1Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor2Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor3Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor4Pin, 0);
break;
case 'L': // Left
analogWrite(motor1Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor2Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor3Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor4Pin, 0);
break;
case 'R': // Right
analogWrite(motor1Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor2Pin, 255);
analogWrite(motor3Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor4Pin, 255);
break;
case 'S': // Stop
analogWrite(motor1Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor2Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor3Pin, 0);
analogWrite(motor4Pin, 0);
break;
case '1': // Move Servo 1
servo1.write(90); // Move servo 1 to 90 degrees
break;
case '2': // Move Servo 2
servo2.write(90); // Move servo 2 to 90 degrees
break;
case '3': // Move Servo 3