
Arduino-Controlled Bluetooth Robotic Car
Circuit Documentation
Summary
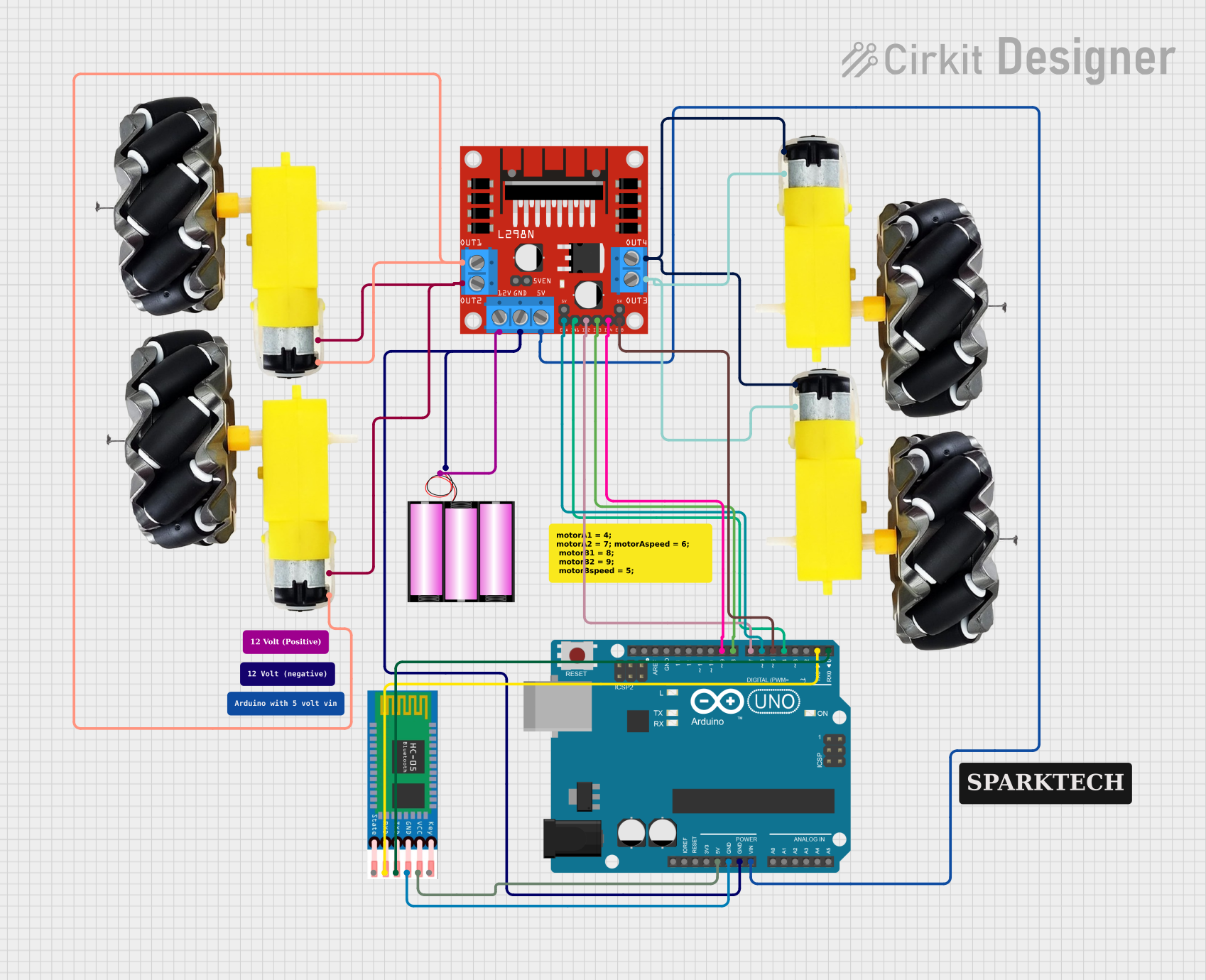
This circuit is designed to control a four-wheeled vehicle using an Arduino UNO microcontroller and a Bluetooth module (HC-05) for wireless communication. The vehicle's motion is driven by four DC motors, which are managed by an L298N DC motor driver. The motors are powered by a 12V battery, and the Arduino UNO is interfaced with the motor driver to control the direction and speed of the motors based on Bluetooth commands received from a paired device.
Component List
L298N DC Motor Driver
- Description: A module used to control up to two DC motors with a maximum current of 2A per channel.
- Pins: OUT1, OUT2, 12V, GND, 5V, OUT3, OUT4, 5V-ENA-JMP-I, 5V-ENA-JMP-O, +5V-J1, +5V-J2, ENA, IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4, ENB
Arduino UNO
- Description: A microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, widely used for building digital devices and interactive objects.
- Pins: UNUSED, IOREF, Reset, 3.3V, 5V, GND, Vin, A0 to A5, SCL, SDA, AREF, D0 to D13
HC-05 Bluetooth Module
- Description: A Bluetooth module for wireless communication, which can be used to pair with other Bluetooth-enabled devices.
- Pins: EN, VCC, GND, TXD, RXD, STATE
12V Battery
- Description: A power source for the circuit, providing the necessary voltage to drive the motors.
- Pins: +, -
Motor and Wheels (4x)
- Description: The actuators for the vehicle, providing the necessary motion when powered.
- Pins: VCC, GND
Comments
- Description: Placeholder components for additional notes or documentation.
Wiring Details
L298N DC Motor Driver
- OUT1, OUT2 connected to Motor 1 (Left Front)
- OUT3, OUT4 connected to Motor 2 (Right Front)
- 12V connected to the positive terminal of the 12V Battery
- GND connected to the negative terminal of the 12V Battery and Arduino UNO GND
- 5V connected to Arduino UNO Vin
- ENA, IN1, IN2 connected to Arduino UNO D6, D4, D7 respectively (Left Front Motor Control)
- ENB, IN3, IN4 connected to Arduino UNO D5, D8, D9 respectively (Right Front Motor Control)
Arduino UNO
- Vin connected to L298N DC Motor Driver 5V
- GND connected to L298N DC Motor Driver GND and HC-05 GND
- D0 (RX), D1 (TX) connected to HC-05 TXD, RXD respectively
- D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9 connected to L298N DC Motor Driver IN1, ENB, ENA, IN2, IN3, IN4 respectively
HC-05 Bluetooth Module
- VCC connected to Arduino UNO 5V
- GND connected to Arduino UNO GND
- TXD connected to Arduino UNO D0 (RX)
- RXD connected to Arduino UNO D1 (TX)
12V Battery
- connected to L298N DC Motor Driver 12V
- connected to L298N DC Motor Driver GND
Motor and Wheels
- Four motors connected to L298N DC Motor Driver OUT1, OUT2, OUT3, OUT4 respectively
Documented Code
//Arduino Bluetooth Controlled Car
//Before uploading the code you have to install the necessary library
//AFMotor Library https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-motor-shield/library-install
//Now You Can Upload the Code without any problem but make sure the bt module isn't connected with Arduino while uploading code
#include <AFMotor.h>
//initial motors pin
AF_DCMotor motor1(1, MOTOR12_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor2(2, MOTOR12_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor3(3, MOTOR34_1KHZ);
AF_DCMotor motor4(4, MOTOR34_1KHZ);
char command;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Set the baud rate to your Bluetooth module.
}
void loop(){
if(Serial.available() > 0){
command = Serial.read();
Stop(); //initialize with motors stopped
//Change pin mode only if new command is different from previous.
switch(command){
case 'F':
forward();
break;
case 'B':
back();
break;
case 'L':
left();
break;
case 'R':
right();
break;
}
}
}
void forward()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255);//Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255);//Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
}
void back()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
}
void left()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
}
void right()
{
motor1.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor1.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor2.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor2.run(FORWARD); //rotate the motor clockwise
motor3.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor3.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
motor4.setSpeed(255); //Define maximum velocity
motor4.run(BACKWARD); //rotate the motor anti-clockwise
}
void Stop()
{
motor1.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor1.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
motor2.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor2.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
motor3.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor3.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
motor4.setSpeed(0); //Define minimum velocity
motor4.run(RELEASE); //stop the motor when release the button
}
This code is designed to receive Bluetooth commands to control the direction and speed of the motors. The commands 'F', 'B', 'L', and 'R' correspond to forward, backward, left, and right movements, respectively. The Stop() function is called initially to ensure the motors are stopped before receiving new commands. The AFMotor library is used to simplify the control of the DC motors through the motor driver.