
How to Use Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
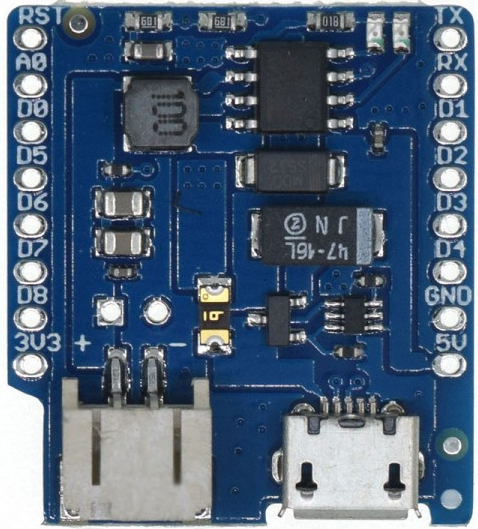
 Design with Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini in Cirkit Designer
Design with Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini is a compact and efficient battery management module designed specifically for the Wemos D1 Mini development board. This shield allows users to connect a Li-ion or LiPo battery to power the D1 Mini, making it ideal for portable and low-power IoT applications. It features integrated charging circuitry, battery level indicators, and seamless integration with the D1 Mini ecosystem.
Explore Projects Built with Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini
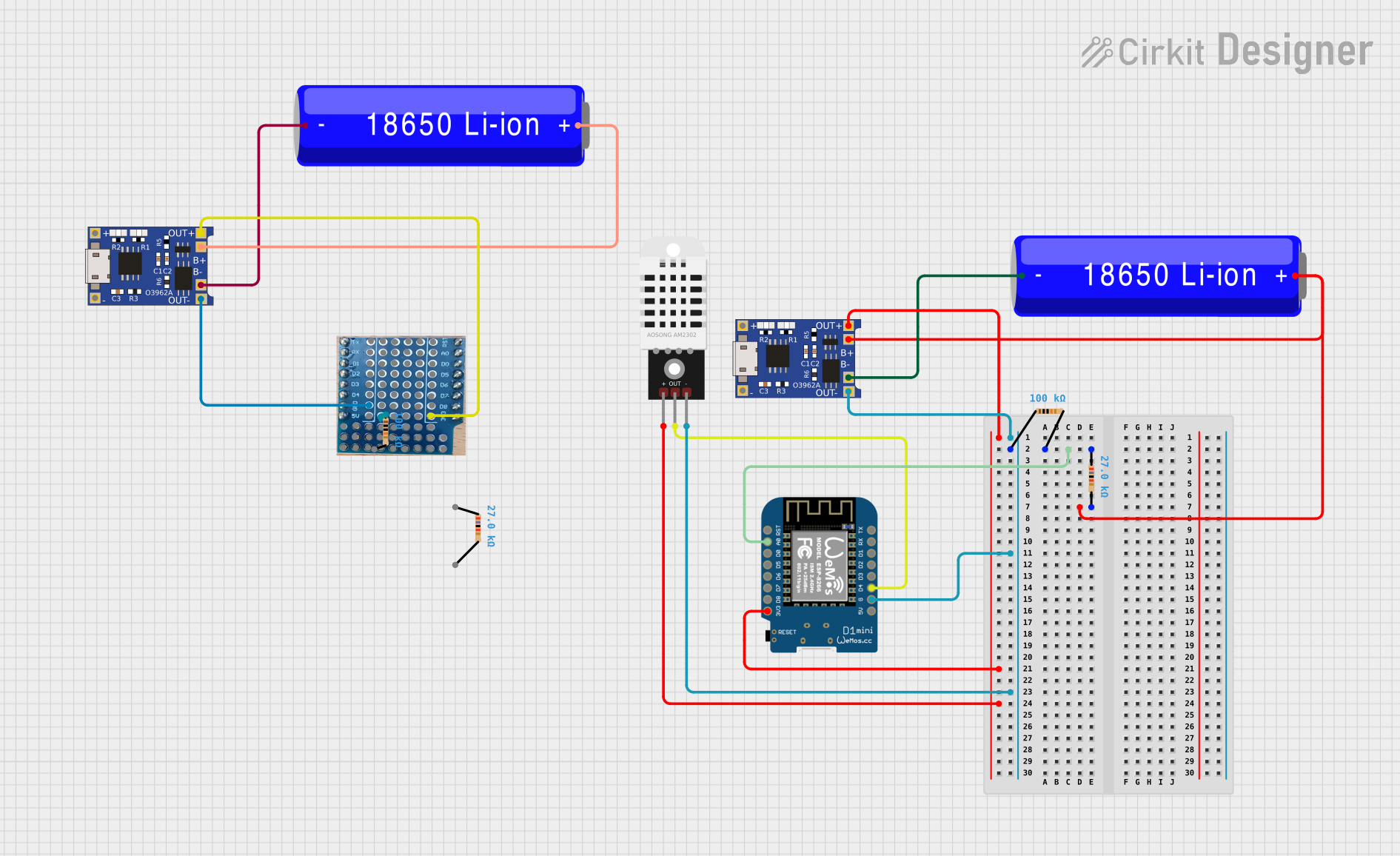
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer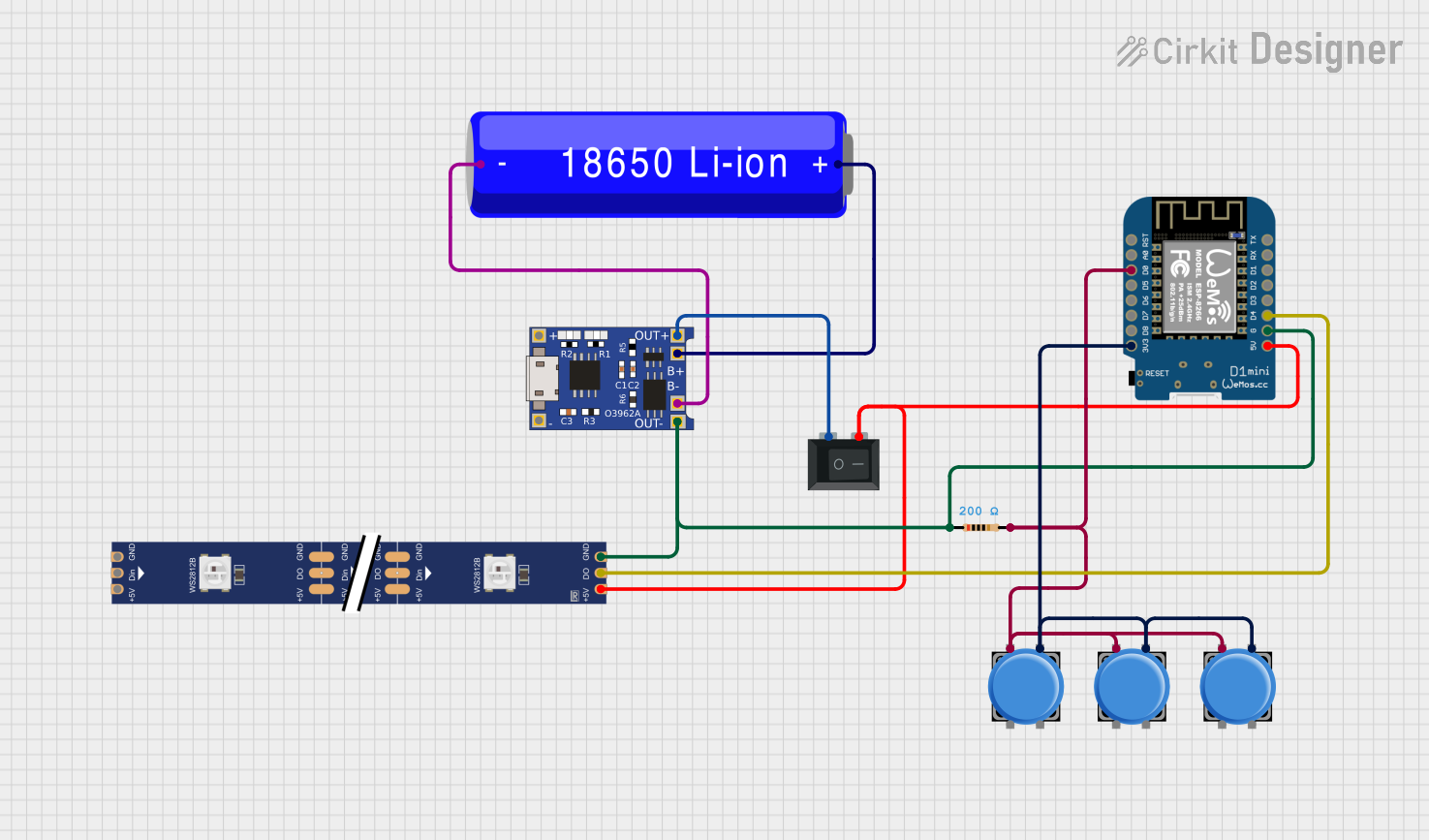
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer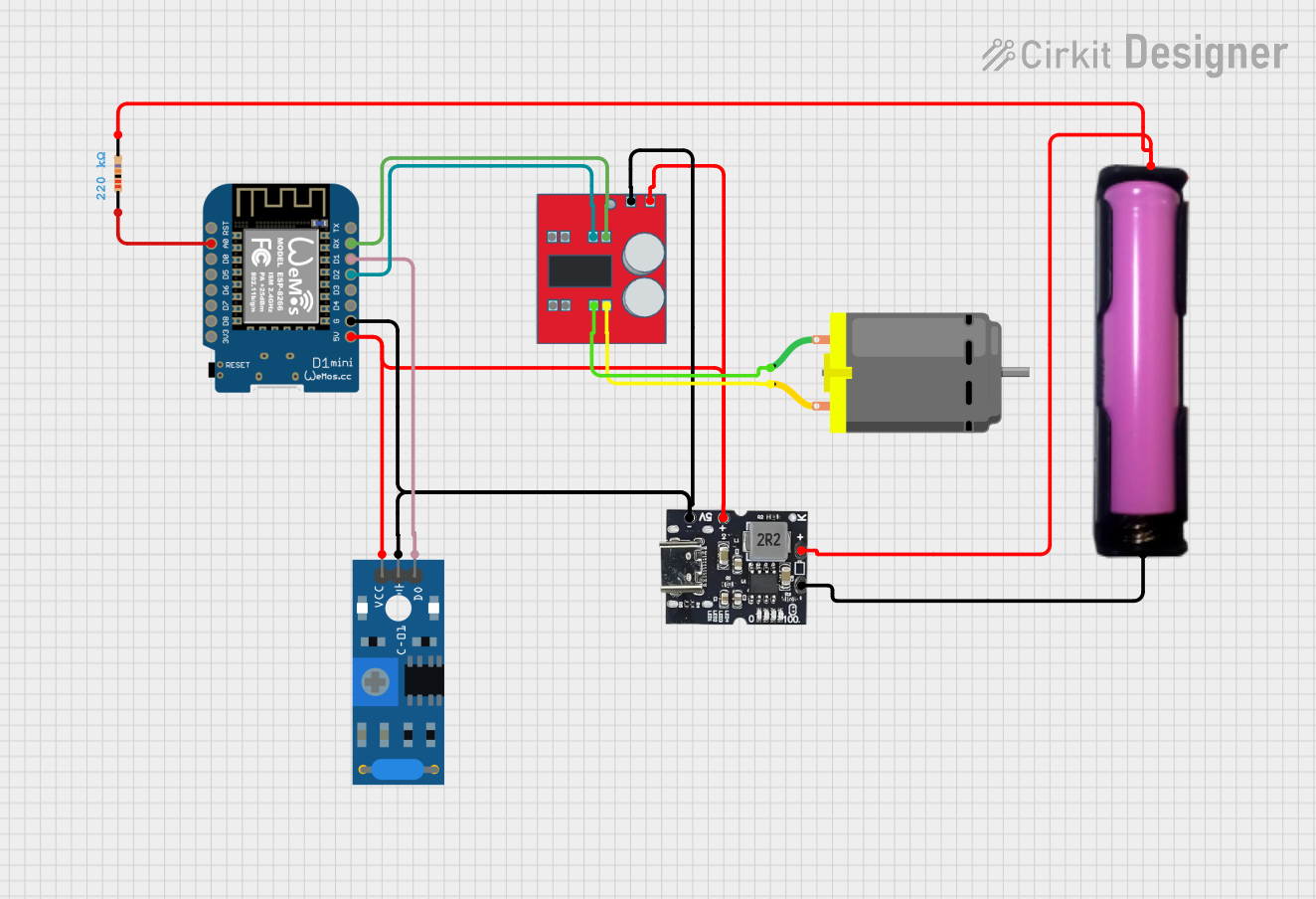
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer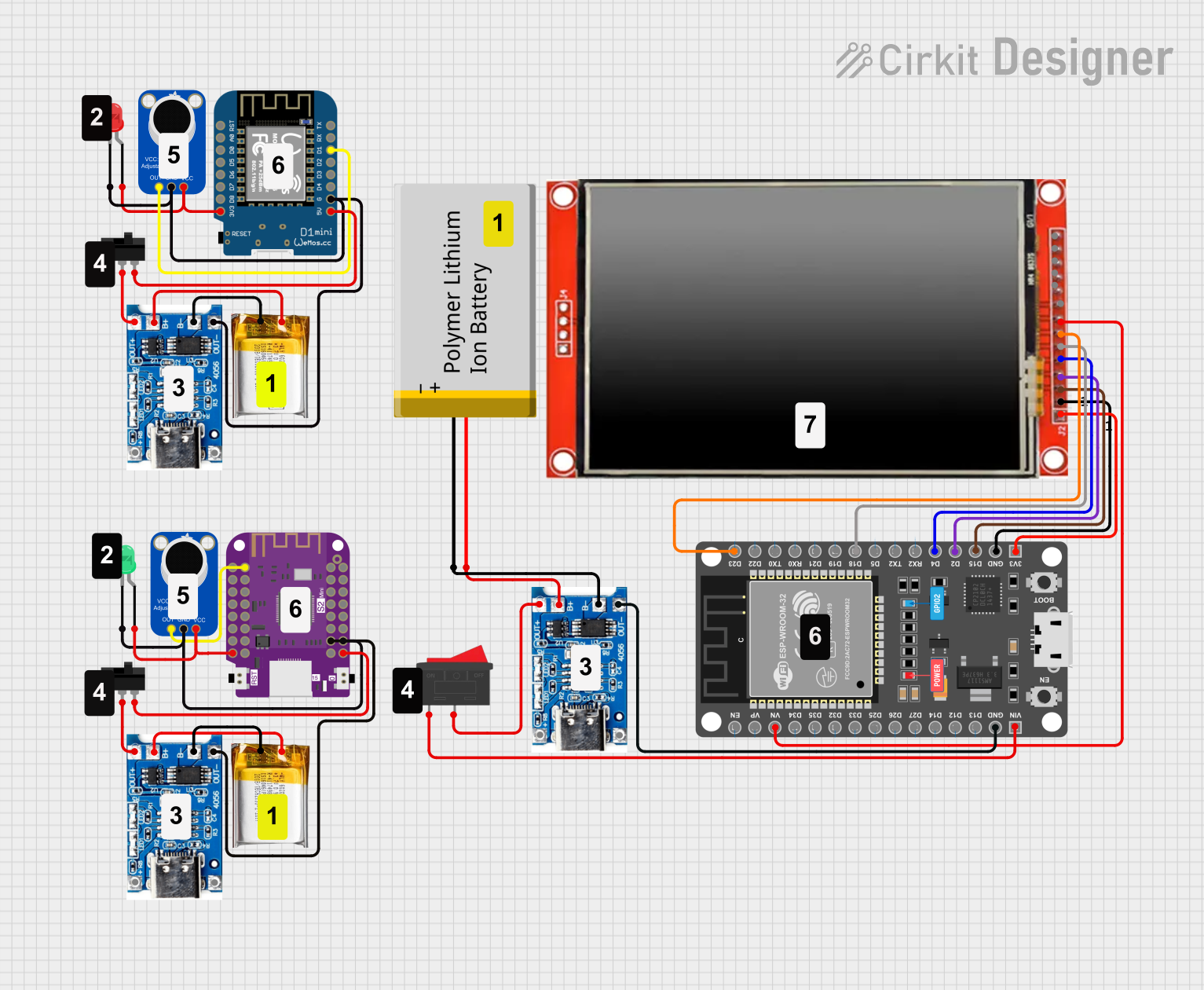
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield for D1 Mini

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Portable IoT devices
- Battery-powered sensor nodes
- Wearable electronics
- Remote monitoring systems
- Prototyping low-power wireless applications
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Wemos Li-ion Battery Shield:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage (USB) | 5V (via Micro-USB port) |
| Battery Type | Li-ion or LiPo (3.7V nominal voltage) |
| Charging Current | 500mA (default, adjustable via resistor) |
| Output Voltage | 5V (regulated) or 3.3V (via D1 Mini pins) |
| Charging Indicator LEDs | Red (charging), Blue (fully charged) |
| Dimensions | 34.2mm x 25.6mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The shield connects directly to the Wemos D1 Mini via its pin headers. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 5V | Regulated 5V output from the battery or USB input |
| 3V3 | Regulated 3.3V output (useful for powering low-voltage peripherals) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| D+ / D- | USB data lines (not typically used for battery management) |
| BAT | Direct connection to the battery's positive terminal (unregulated voltage) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Shield in a Circuit
- Connect the Battery: Attach a 3.7V Li-ion or LiPo battery to the JST connector on the shield. Ensure correct polarity to avoid damage.
- Stack the Shield: Place the shield on top of the Wemos D1 Mini, aligning the pin headers.
- Power the Shield:
- Use the Micro-USB port to charge the battery and power the D1 Mini simultaneously.
- Alternatively, the battery alone can power the D1 Mini when USB is disconnected.
- Monitor Charging: Observe the onboard LEDs:
- Red LED: Battery is charging.
- Blue LED: Battery is fully charged.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Selection: Use only 3.7V Li-ion or LiPo batteries with a JST connector. Ensure the battery has built-in protection circuitry to prevent overcharging or over-discharging.
- Charging Current Adjustment: The default charging current is 500mA. To adjust it, replace the onboard resistor labeled "R3" with a different value. Refer to the TP4056 datasheet for resistor values corresponding to desired charging currents.
- Heat Management: Avoid prolonged charging in high-temperature environments, as the shield may become warm during operation.
- Voltage Monitoring: Use the
BATpin to monitor the battery voltage in your circuit. Ensure your code accounts for the unregulated nature of this pin.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
If you are using the Wemos D1 Mini with the battery shield, you can monitor the battery voltage using the BAT pin. Below is an example sketch:
// Example code to monitor battery voltage using the BAT pin
// Connect the BAT pin to an analog input (e.g., A0) on the D1 Mini
const int BATTERY_PIN = A0; // Analog pin connected to BAT
const float VOLTAGE_DIVIDER_RATIO = 2.0; // Adjust if a voltage divider is used
const float ADC_RESOLUTION = 1023.0; // 10-bit ADC resolution
const float REFERENCE_VOLTAGE = 3.3; // Reference voltage of the D1 Mini
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
Serial.println("Battery Voltage Monitoring");
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(BATTERY_PIN); // Read the analog value from BAT pin
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / ADC_RESOLUTION) * REFERENCE_VOLTAGE * VOLTAGE_DIVIDER_RATIO;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: If you use a voltage divider to scale down the battery voltage, adjust the
VOLTAGE_DIVIDER_RATIOaccordingly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Incorrect battery connection or damaged battery.
- Solution: Verify the battery polarity and ensure the battery is functional.
Shield Overheating
- Cause: Prolonged charging at high current or high ambient temperature.
- Solution: Reduce the charging current by replacing the R3 resistor or charge in a cooler environment.
No Output Voltage
- Cause: Battery is depleted or not connected.
- Solution: Check the battery connection and charge the battery via USB.
LEDs Not Working
- Cause: Faulty LEDs or damaged charging circuitry.
- Solution: Inspect the shield for physical damage and test with a different battery.
FAQs
Can I use a different type of battery? No, the shield is designed specifically for 3.7V Li-ion or LiPo batteries. Using other types may damage the shield or the battery.
What happens if I connect both USB and battery? The shield will prioritize USB power for charging the battery and powering the D1 Mini.
Can I adjust the charging current? Yes, replace the R3 resistor with a value corresponding to your desired charging current. Refer to the TP4056 datasheet for details.
Is the shield compatible with other boards? The shield is designed for the Wemos D1 Mini but may work with other boards that share the same pinout. Verify compatibility before use.