
How to Use Arduino Mega 2560 R3: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
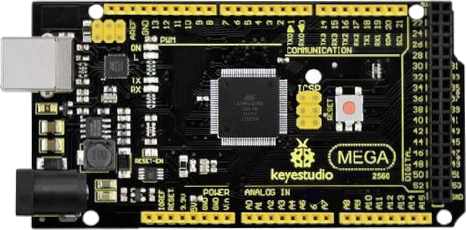
 Design with Arduino Mega 2560 R3 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Arduino Mega 2560 R3 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Arduino Mega 2560 R3 (Manufacturer Part ID: KS0002) by Keyestudio is a powerful microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It is designed for projects that require a large number of input/output connections and significant processing power. With 54 digital I/O pins, 16 analog inputs, and a USB connection for programming and power, the Mega 2560 R3 is ideal for complex applications such as robotics, home automation, and data acquisition systems.
Explore Projects Built with Arduino Mega 2560 R3
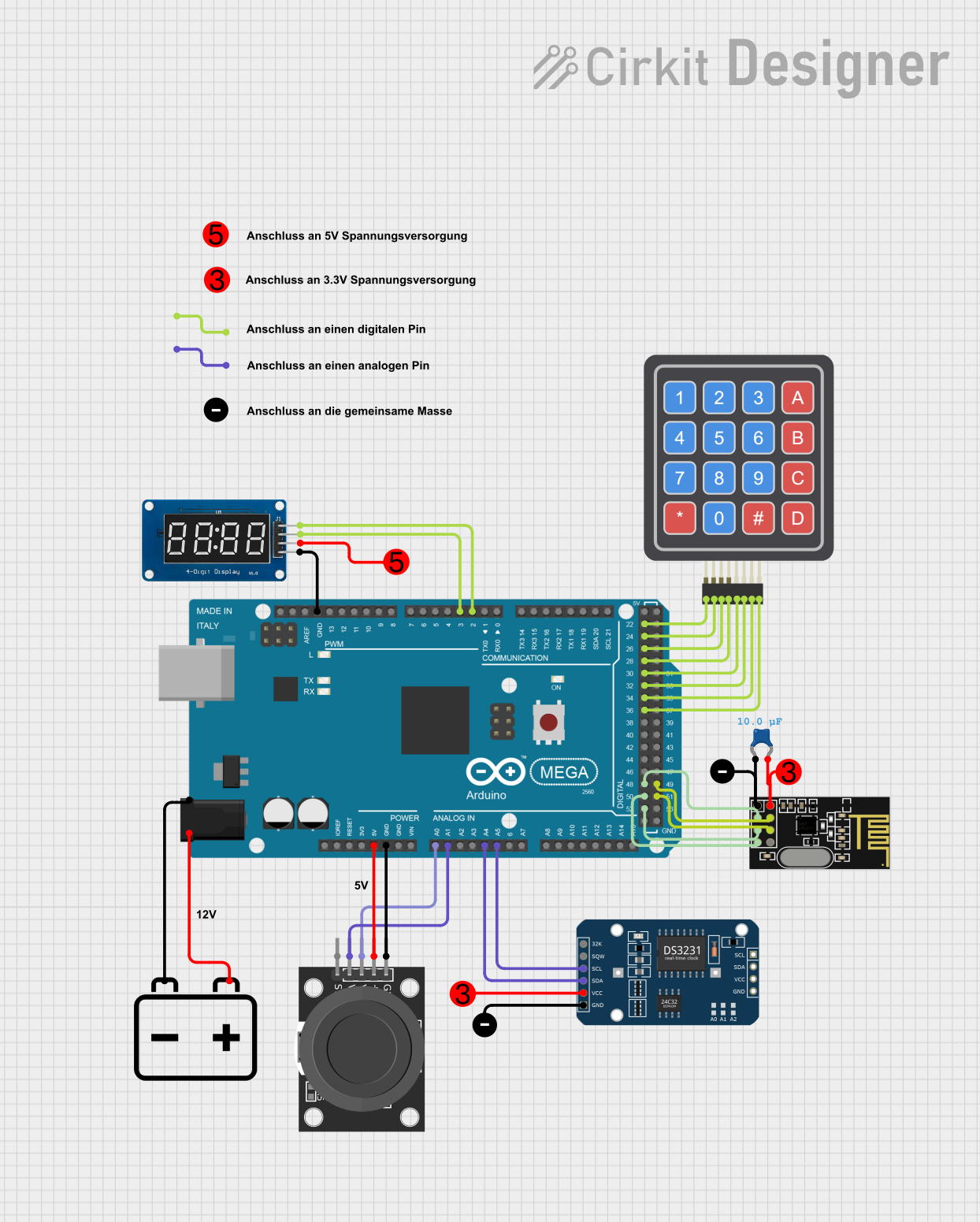
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer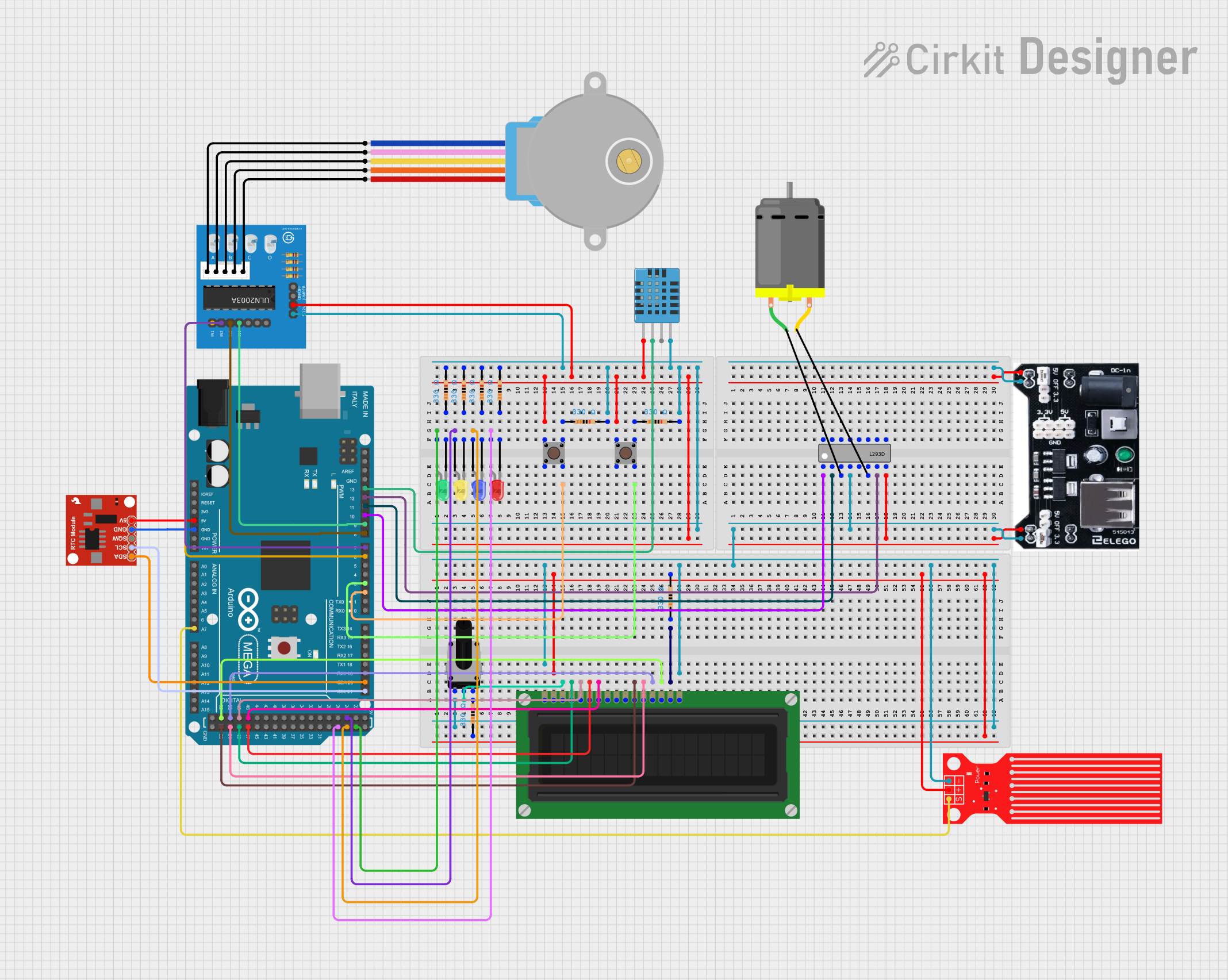
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer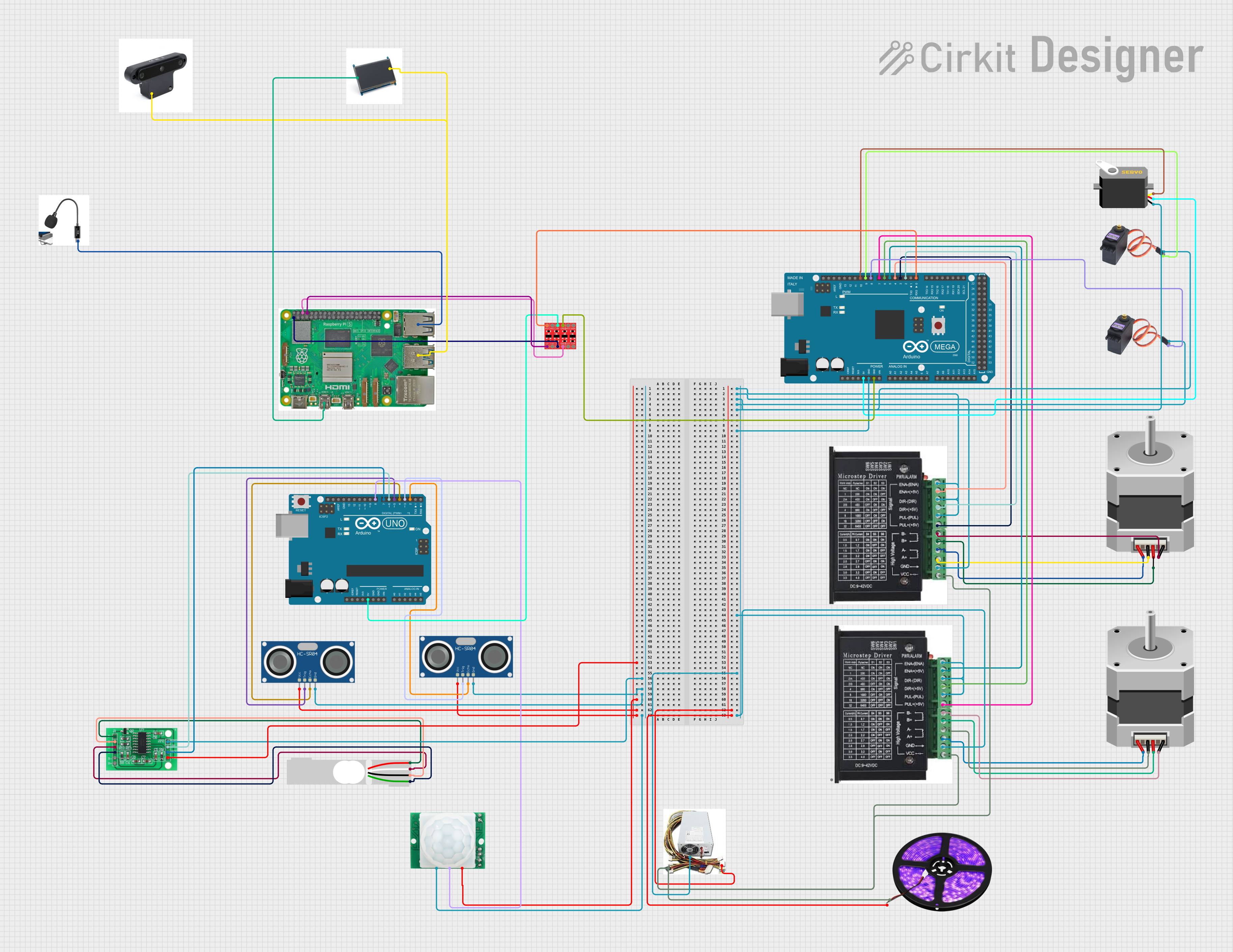
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer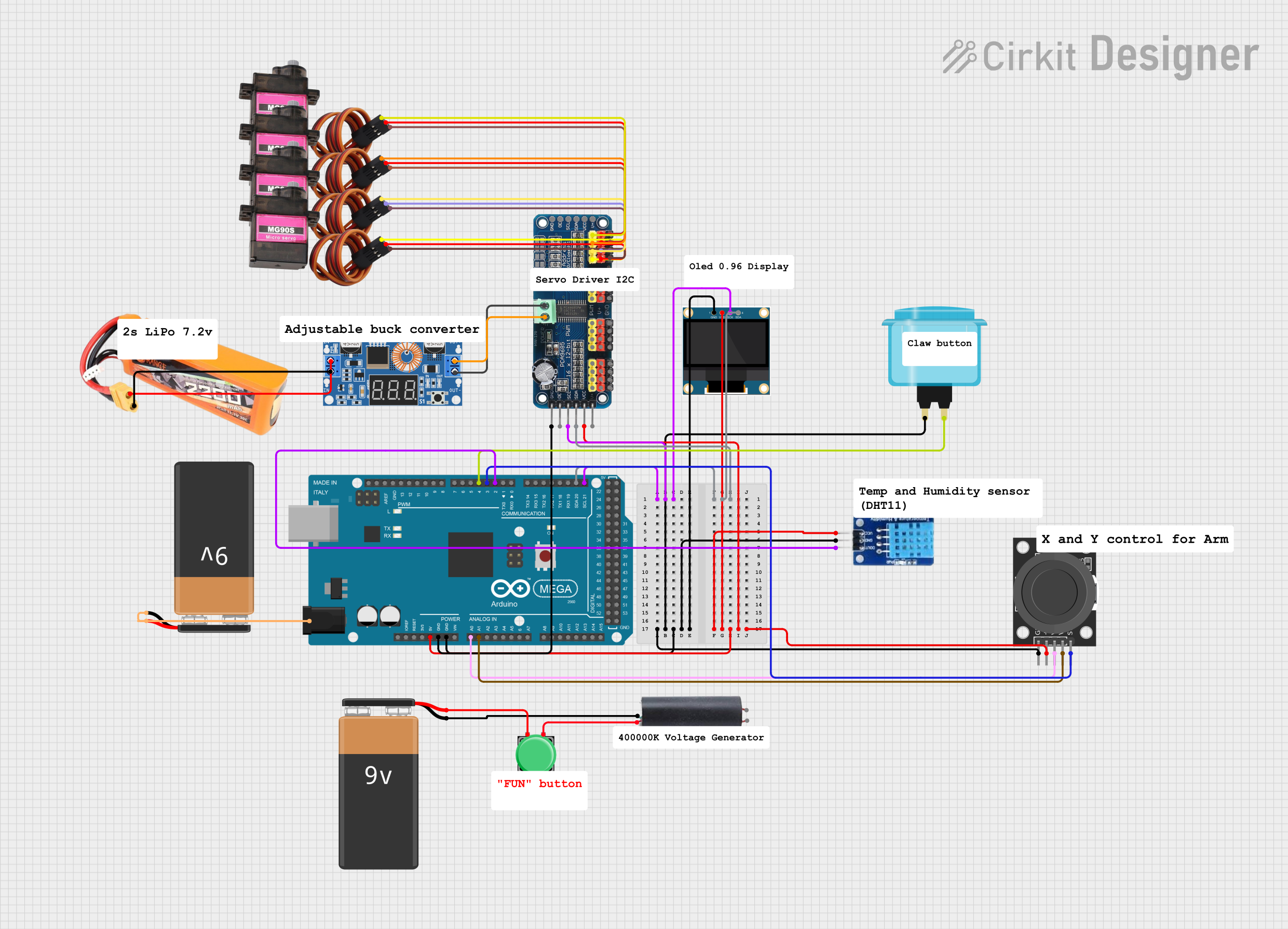
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Arduino Mega 2560 R3

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics and automation systems
- IoT (Internet of Things) projects
- Data logging and sensor networks
- Prototyping for industrial control systems
- Projects requiring multiple actuators, sensors, or displays
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Arduino Mega 2560 R3:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ATmega2560 |
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
| Input Voltage (limit) | 6-20V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 54 (15 PWM outputs) |
| Analog Input Pins | 16 |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 20 mA |
| Flash Memory | 256 KB (8 KB used by bootloader) |
| SRAM | 8 KB |
| EEPROM | 4 KB |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| USB Connection | Type-B USB |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C |
| Dimensions | 101.52 mm x 53.3 mm |
| Weight | 37 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Arduino Mega 2560 R3 features a wide array of pins for various functionalities. Below is a summary of the pin configuration:
Digital Pins
| Pin Number | Function |
|---|---|
| 0-1 | UART0 (Serial Communication) |
| 2-13 | General Digital I/O |
| 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 | PWM Outputs |
| 20-21 | I2C (SDA, SCL) |
| 50-53 | SPI (MISO, MOSI, SCK, SS) |
Analog Pins
| Pin Number | Function |
|---|---|
| A0-A15 | Analog Inputs (10-bit ADC) |
Power Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage to the board |
| 5V | Regulated 5V output |
| 3.3V | Regulated 3.3V output |
| GND | Ground |
| IOREF | Reference voltage for I/O |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Arduino Mega 2560 R3 in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to your computer using a USB Type-B cable for programming and power.
- Alternatively, use an external power supply (7-12V) via the VIN pin or the DC barrel jack.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE from the official Arduino website.
- Select "Arduino Mega 2560" as the board type in the IDE.
- Choose the correct COM port under the "Tools" menu.
- Write or load your sketch and click the upload button.
Connecting Components:
- Use the digital pins for digital sensors, actuators, or communication modules.
- Use the analog pins for sensors that output analog signals.
- Ensure proper grounding and voltage levels for all connected components.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating of 20 mA per I/O pin to prevent damage.
- Use external pull-up or pull-down resistors for stable digital input signals.
- For high-current devices, use external transistors or relays to offload the current from the board.
- Always double-check connections to avoid short circuits or incorrect wiring.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Arduino Mega 2560 R3 can communicate with an Arduino UNO via I2C. Below is an example code for setting up the Mega 2560 as an I2C master:
Code for Arduino Mega 2560 (Master)
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C as master
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(8); // Start communication with slave (address 8)
Wire.write("Hello from Mega!"); // Send data to the slave
Wire.endTransmission(); // End the transmission
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before sending again
}
Code for Arduino UNO (Slave)
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); // Initialize I2C as slave with address 8
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // Register a function to handle received data
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
// Main loop does nothing; data is handled in receiveEvent()
}
void receiveEvent(int bytes) {
while (Wire.available()) { // Check if data is available
char c = Wire.read(); // Read a byte of data
Serial.print(c); // Print the received data to the serial monitor
}
Serial.println(); // Print a newline after the message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Board Not Recognized by Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and properly connected.
- Install the necessary USB drivers for the Arduino Mega 2560 R3.
Sketch Fails to Upload:
- Verify that the correct board and COM port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Press the reset button on the board before uploading.
Unstable or Incorrect Sensor Readings:
- Check for loose connections or poor grounding.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the sensor power pins to reduce noise.
Overheating of Voltage Regulator:
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed 12V.
- Use an external power supply for high-current peripherals.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Arduino Mega 2560 R3 with 3.3V sensors?
A: Yes, but you must use a level shifter or voltage divider to step down the 5V signals to 3.3V.
Q: How do I reset the board?
A: Press the reset button on the board, or connect an external reset circuit to the RESET pin.
Q: Can I use the Mega 2560 for wireless communication?
A: Yes, you can connect wireless modules like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or LoRa via the UART, SPI, or I2C interfaces.
Q: What is the maximum length for I2C communication?
A: The maximum reliable length for I2C communication is typically around 1 meter, but this can vary depending on the pull-up resistor values and cable quality.