
How to Use Step Down Buck converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Step Down Buck converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with Step Down Buck converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Step Down Buck Converter (Generic, Part ID: 20A 300W) is a high-efficiency DC-DC converter designed to step down voltage from a higher input level to a lower output level. It is widely used in applications where devices require a stable, lower voltage supply from a higher voltage source. This converter is capable of handling up to 20A of current and delivering a maximum power output of 300W, making it suitable for high-power applications.
Explore Projects Built with Step Down Buck converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer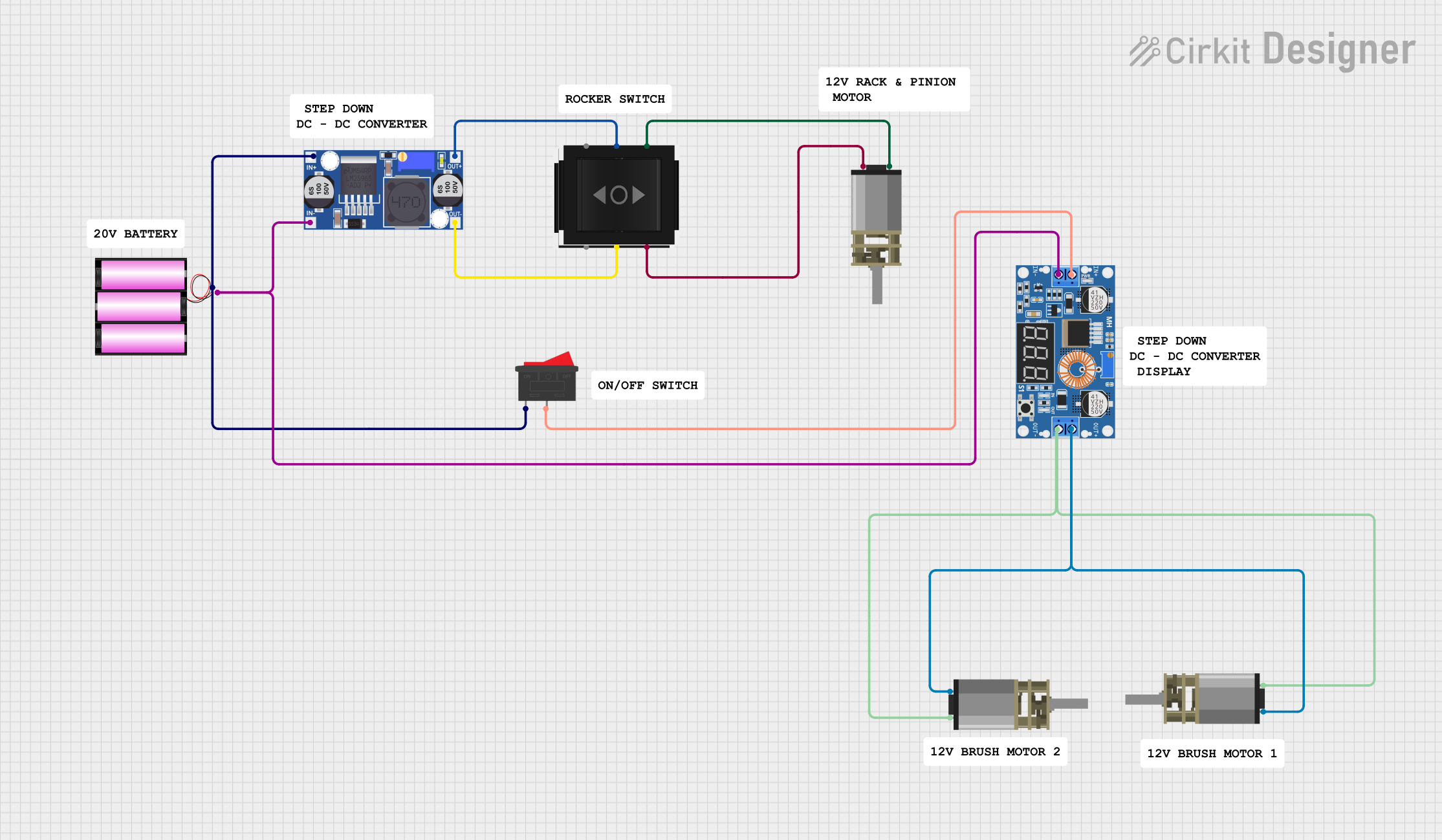
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Step Down Buck converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers, sensors, and other low-voltage devices from a high-voltage source.
- Battery charging systems.
- Solar power systems for voltage regulation.
- Automotive electronics for stepping down car battery voltage.
- LED drivers and lighting systems.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 20A 300W Step Down Buck Converter:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 6V to 40V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.2V to 36V (adjustable) |
| Maximum Output Current | 20A (with proper cooling) |
| Maximum Power Output | 300W |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 52mm x 22mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 20A 300W Step Down Buck Converter has the following input/output connections:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN+ | Positive input voltage terminal (connect to the higher voltage source). |
| VIN- | Negative input voltage terminal (connect to the ground of the voltage source). |
| VOUT+ | Positive output voltage terminal (connect to the load). |
| VOUT- | Negative output voltage terminal (connect to the ground of the load). |
| Adjust | Potentiometer to adjust the output voltage (clockwise to increase voltage). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the positive terminal of your power source to the VIN+ pin.
- Connect the ground of your power source to the VIN- pin.
- Ensure the input voltage is within the range of 6V to 40V.
Connect the Output Load:
- Connect the positive terminal of your load to the VOUT+ pin.
- Connect the ground of your load to the VOUT- pin.
Adjust the Output Voltage:
- Use the onboard potentiometer labeled "Adjust" to set the desired output voltage.
- Turn the potentiometer clockwise to increase the output voltage and counterclockwise to decrease it.
- Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage for precise adjustment.
Cooling Considerations:
- For currents above 10A, ensure proper heat dissipation by attaching a heatsink or using active cooling (e.g., a fan).
- Avoid operating the converter at maximum current for extended periods without adequate cooling.
Power On:
- Once all connections are secure, power on the input source. The converter will regulate the output voltage as per the set value.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage: Ensure the input voltage is always higher than the desired output voltage.
- Current Limitation: Do not exceed the maximum current rating of 20A to avoid damage.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of the input and output connections to prevent short circuits.
- Load Testing: Test the converter with a small load before connecting it to sensitive devices.
- Safety: Avoid touching the circuit while it is powered, as some components may become hot during operation.
Example: Using the Buck Converter with an Arduino UNO
The Step Down Buck Converter can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a 12V battery by stepping down the voltage to 5V. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code to blink an LED:
Circuit Connections:
- Connect the VIN+ pin of the converter to the positive terminal of the 12V battery.
- Connect the VIN- pin to the ground of the battery.
- Adjust the output voltage to 5V using the potentiometer.
- Connect the VOUT+ pin to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the VOUT- pin to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Arduino Code:
// Simple LED Blink Example
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Incorrect input connections or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Verify the polarity and ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.
Output Voltage Not Adjustable:
- Cause: Faulty potentiometer or incorrect adjustment.
- Solution: Check the potentiometer for damage and adjust it slowly while monitoring the output voltage.
Overheating:
- Cause: High current draw without proper cooling.
- Solution: Attach a heatsink or use a fan to improve heat dissipation.
Load Not Powering On:
- Cause: Output voltage too low or insufficient current.
- Solution: Verify the output voltage and ensure the load's current requirements are within the converter's capacity.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use this converter to charge a 12V battery?
A1: Yes, but ensure the output voltage is set slightly higher than the battery's nominal voltage (e.g., 13.8V for a 12V lead-acid battery) and monitor the charging current.
Q2: What happens if I exceed the maximum current rating?
A2: Exceeding 20A may cause overheating, damage to the converter, or trigger the overcurrent protection (if available).
Q3: Can I use this converter with a solar panel?
A3: Yes, as long as the solar panel's output voltage is within the input range of the converter (6V to 40V).
Q4: Is the converter waterproof?
A4: No, the converter is not waterproof. Use it in a dry environment or enclose it in a waterproof case for outdoor applications.