
How to Use Pixhawk 6X: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Pixhawk 6X in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pixhawk 6X in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Pixhawk 6X, manufactured by Holybro, is an advanced flight control hardware designed for drones and other unmanned vehicles. It features high processing power, multiple sensor inputs, and compatibility with various autopilot software such as PX4 and ArduPilot. The Pixhawk 6X is ideal for professional and hobbyist applications, offering reliable performance for autonomous navigation, stabilization, and control.
Explore Projects Built with Pixhawk 6X
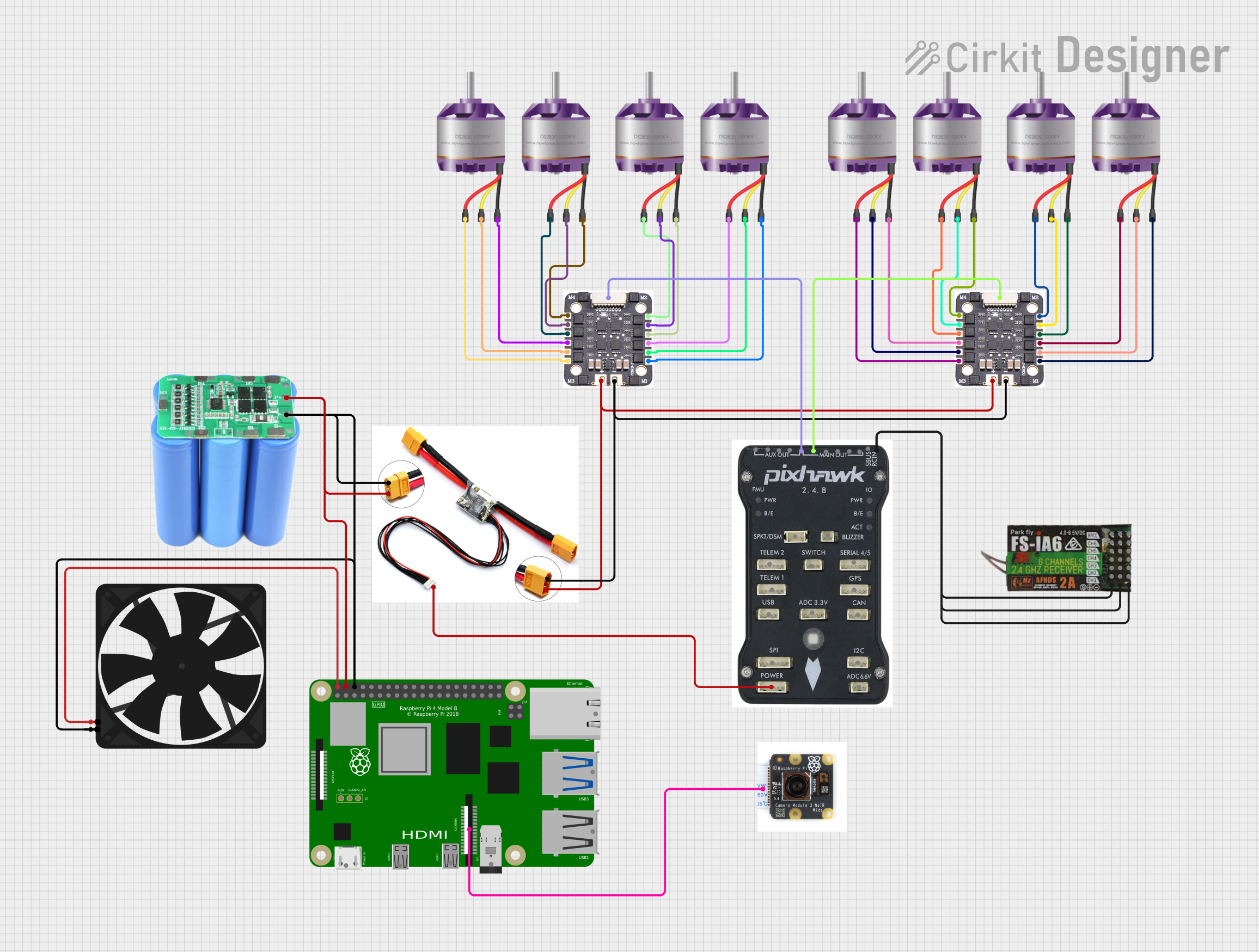
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer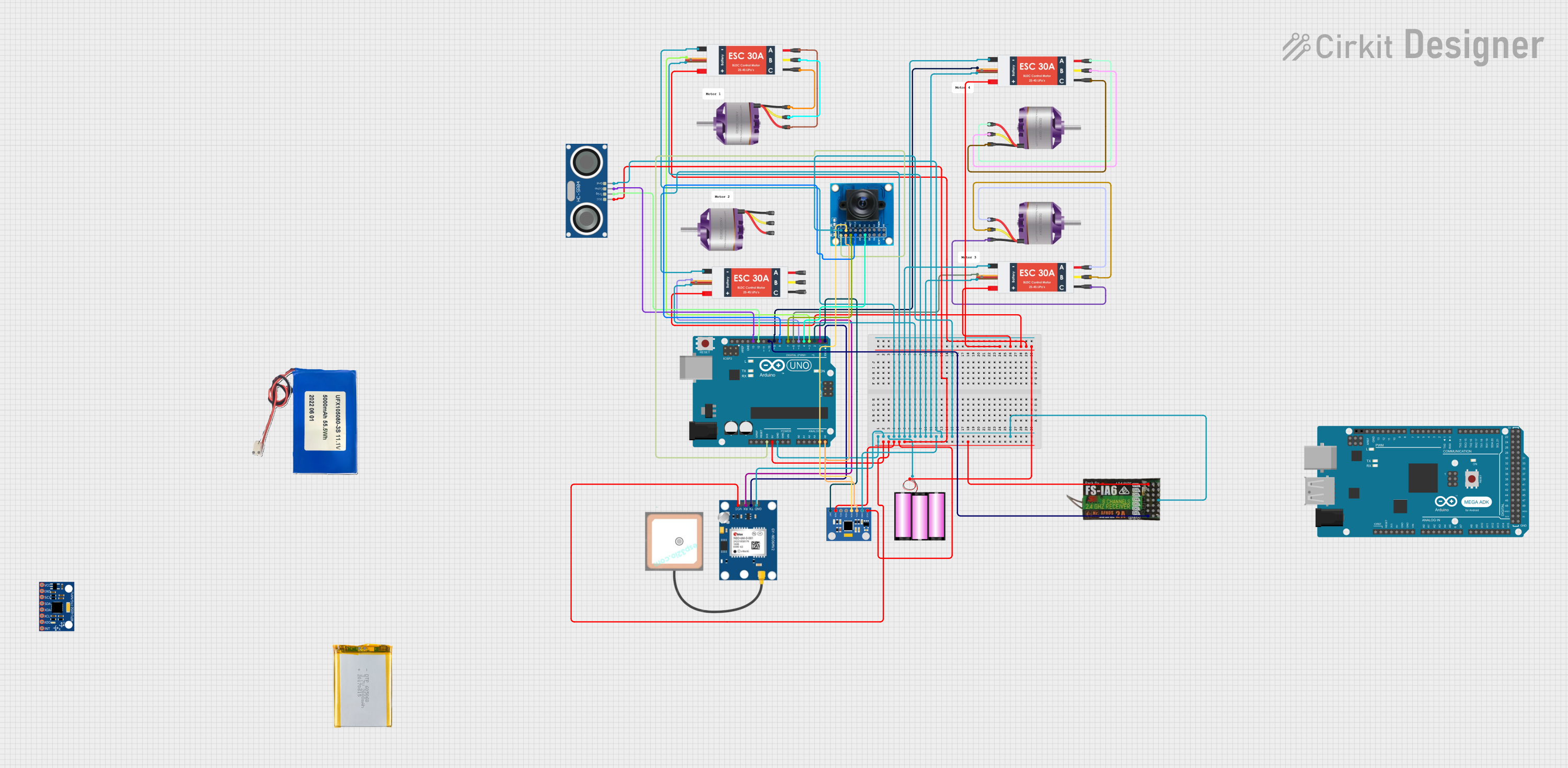
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer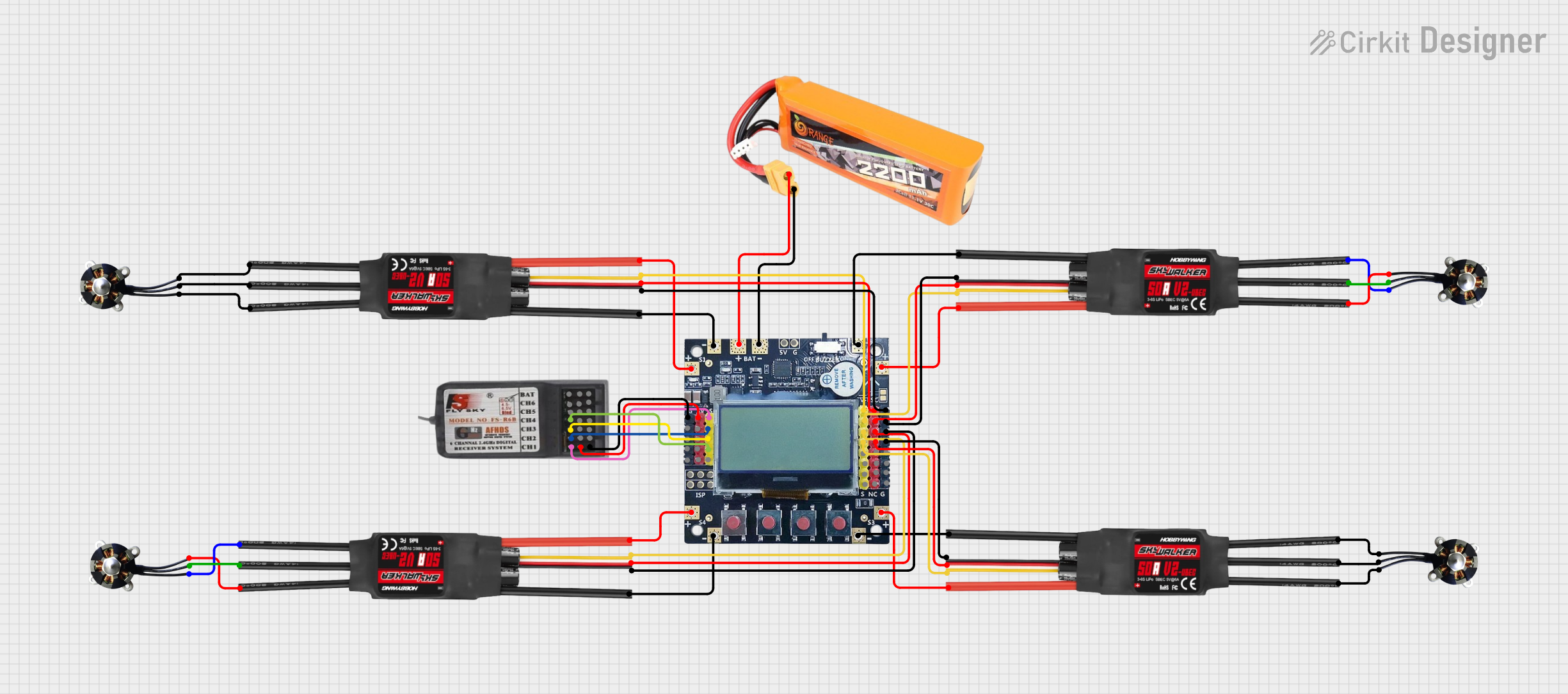
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer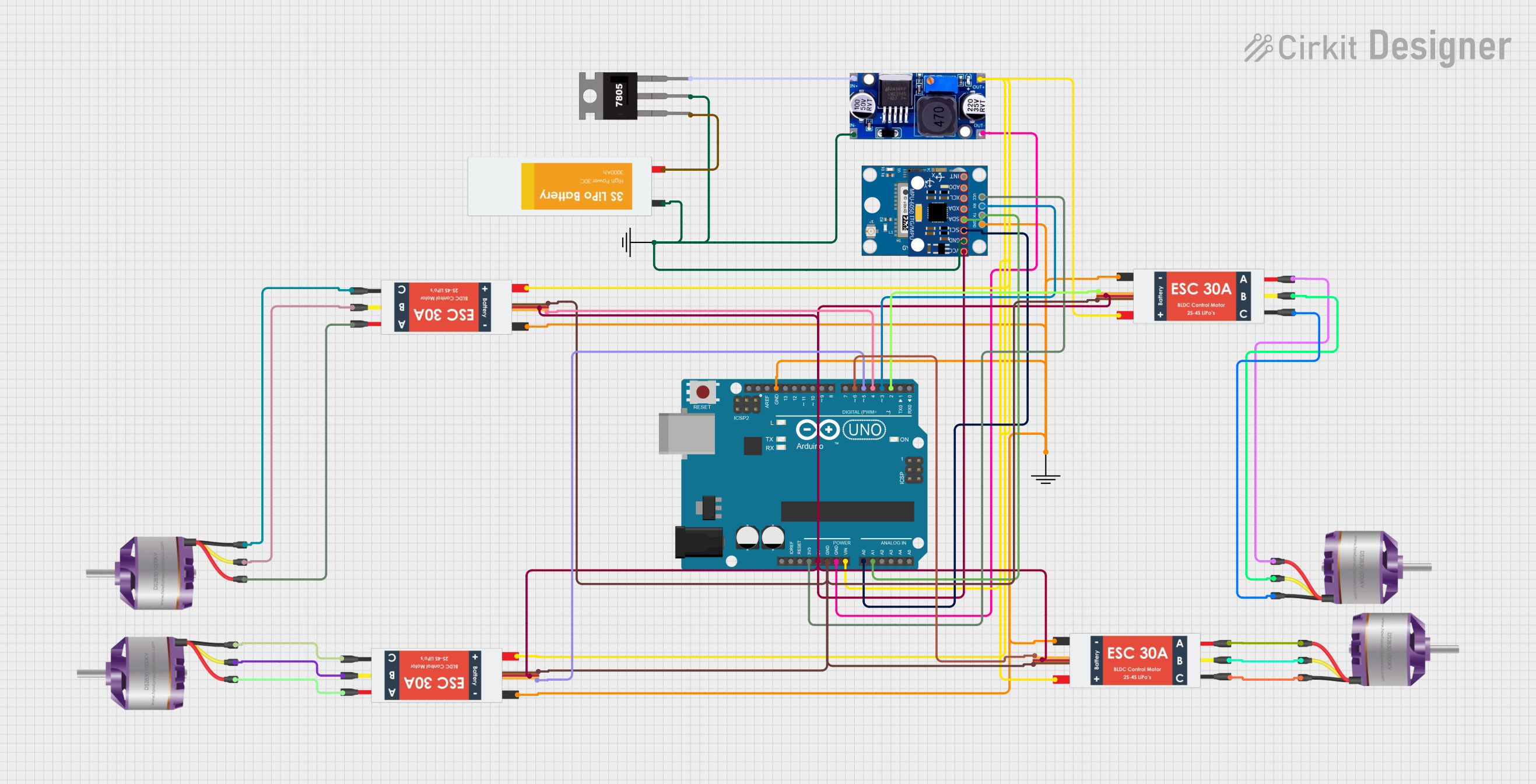
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pixhawk 6X

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Multirotor drones (quadcopters, hexacopters, etc.)
- Fixed-wing UAVs
- VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) aircraft
- Ground robots and rovers
- Marine vehicles (autonomous boats)
- Research and development in robotics and automation
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Processor | STM32H743, 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M7, 480 MHz |
| Co-Processor | STM32F100, 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M3, 24 MHz |
| IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units) | 2x ICM-42688-P (Accelerometer/Gyroscope) |
| Magnetometer | IST8310 |
| Barometer | MS5611 |
| Input Voltage Range | 4.3V to 5.4V |
| Power Consumption | ~1.5W |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, I2C, CAN, SPI, USB, DSM/SBUS, PWM |
| Dimensions | 38.5 x 55.5 x 15.5 mm |
| Weight | 15.8 g |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Pixhawk 6X features multiple ports for connecting peripherals. Below is a summary of the key pin configurations:
Power and Communication Ports
| Port Name | Pin Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| POWER1/POWER2 | Voltage input for powering the Pixhawk | Supports redundant power inputs |
| USB-C | USB interface for programming and data | Used for firmware updates and logs |
| TELEM1/TELEM2 | UART communication ports | For telemetry radios or peripherals |
| CAN1/CAN2 | CAN bus interface | For CAN-enabled devices |
Sensor and Peripheral Ports
| Port Name | Pin Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPS1/GPS2 | GPS module connection | Supports GPS and Compass modules |
| I2C | I2C communication bus | For external sensors |
| PWM OUT | PWM signal output for motors/servos | Up to 8 channels |
| AUX OUT | Auxiliary PWM outputs | For additional actuators |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter input | For voltage/current sensing |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Pixhawk 6X in a Circuit
Powering the Pixhawk 6X:
- Connect a power module to the POWER1 or POWER2 port. Ensure the input voltage is within the range of 4.3V to 5.4V.
- For redundancy, you can connect a second power source to the other power port.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Attach a GPS module to the GPS1 or GPS2 port for navigation.
- Use the TELEM1 or TELEM2 port to connect a telemetry radio for remote communication.
- Connect motors or servos to the PWM OUT ports. Ensure proper calibration of ESCs (Electronic Speed Controllers) if used.
Flashing Firmware:
- Connect the Pixhawk 6X to your computer via the USB-C port.
- Use software like QGroundControl or Mission Planner to flash the desired autopilot firmware (e.g., PX4 or ArduPilot).
Configuring the System:
- After flashing the firmware, configure the system using the ground control software.
- Calibrate sensors (IMU, magnetometer, barometer) and set up flight modes.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Redundancy: Always use redundant power sources to ensure reliability during operation.
- Vibration Isolation: Mount the Pixhawk 6X on vibration-dampening material to improve sensor accuracy.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly update the firmware to access new features and bug fixes.
- Pre-Flight Checks: Perform thorough pre-flight checks, including sensor calibration and motor testing.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Pixhawk 6X can communicate with an Arduino UNO via UART. Below is an example code snippet for reading telemetry data from the Pixhawk:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for UART communication
SoftwareSerial pixhawkSerial(10, 11); // RX = pin 10, TX = pin 11
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging via Serial Monitor
pixhawkSerial.begin(57600); // Pixhawk telemetry baud rate
Serial.println("Pixhawk-Arduino Communication Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from Pixhawk
if (pixhawkSerial.available()) {
// Read and print data from Pixhawk
char data = pixhawkSerial.read();
Serial.print(data);
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Pixhawk Not Powering On:
- Cause: Insufficient or incorrect power supply.
- Solution: Verify the input voltage is within the 4.3V to 5.4V range. Check power connections.
No GPS Signal:
- Cause: GPS module not connected or obstructed.
- Solution: Ensure the GPS module is securely connected to the GPS1 or GPS2 port. Place the GPS module in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
Telemetry Not Working:
- Cause: Incorrect baud rate or wiring.
- Solution: Verify the baud rate settings in the ground control software. Check the TELEM port connections.
Unstable Flight:
- Cause: Improper sensor calibration or vibration.
- Solution: Recalibrate all sensors and ensure the Pixhawk is mounted on vibration-dampening material.
FAQs
Q: Can the Pixhawk 6X be used with fixed-wing aircraft?
A: Yes, the Pixhawk 6X supports fixed-wing aircraft and can be configured for various flight modes.Q: What software is compatible with the Pixhawk 6X?
A: The Pixhawk 6X is compatible with PX4 and ArduPilot autopilot software.Q: How do I update the firmware?
A: Connect the Pixhawk 6X to your computer via USB-C and use QGroundControl or Mission Planner to update the firmware.Q: Can I use multiple GPS modules?
A: Yes, the Pixhawk 6X supports dual GPS modules for redundancy and improved accuracy.