
How to Use DisplaySmall: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DisplaySmall in Cirkit Designer
Design with DisplaySmall in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The DisplaySmall is a compact display module designed for applications requiring a small form factor. It is ideal for portable devices, embedded systems, and projects where space is limited but visual output is essential. This module is versatile and can display text, numbers, and simple graphics, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with DisplaySmall
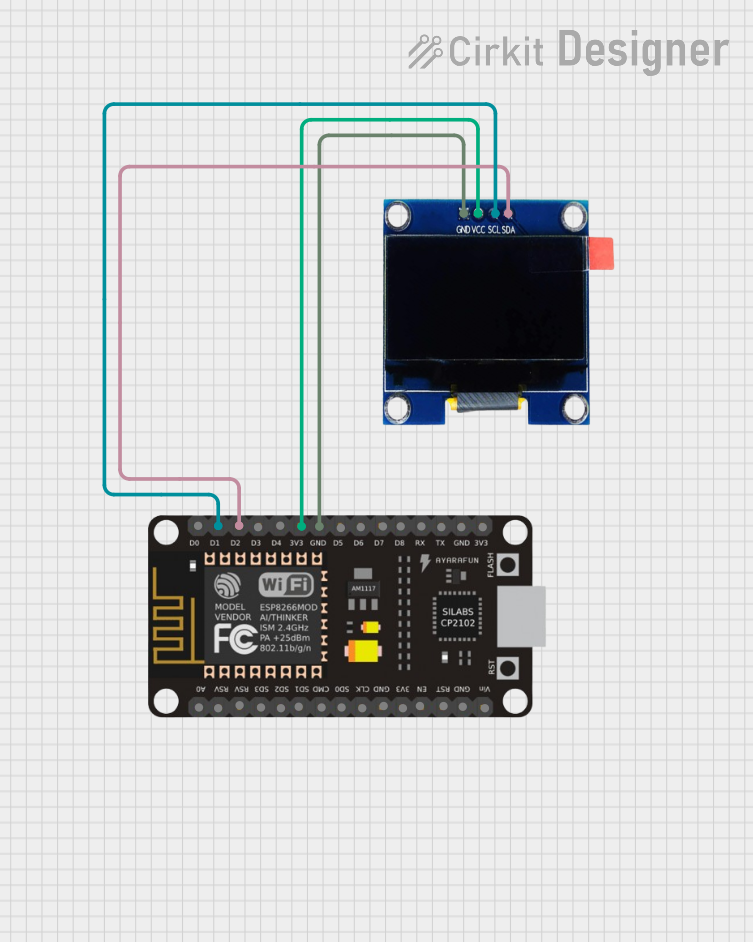
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer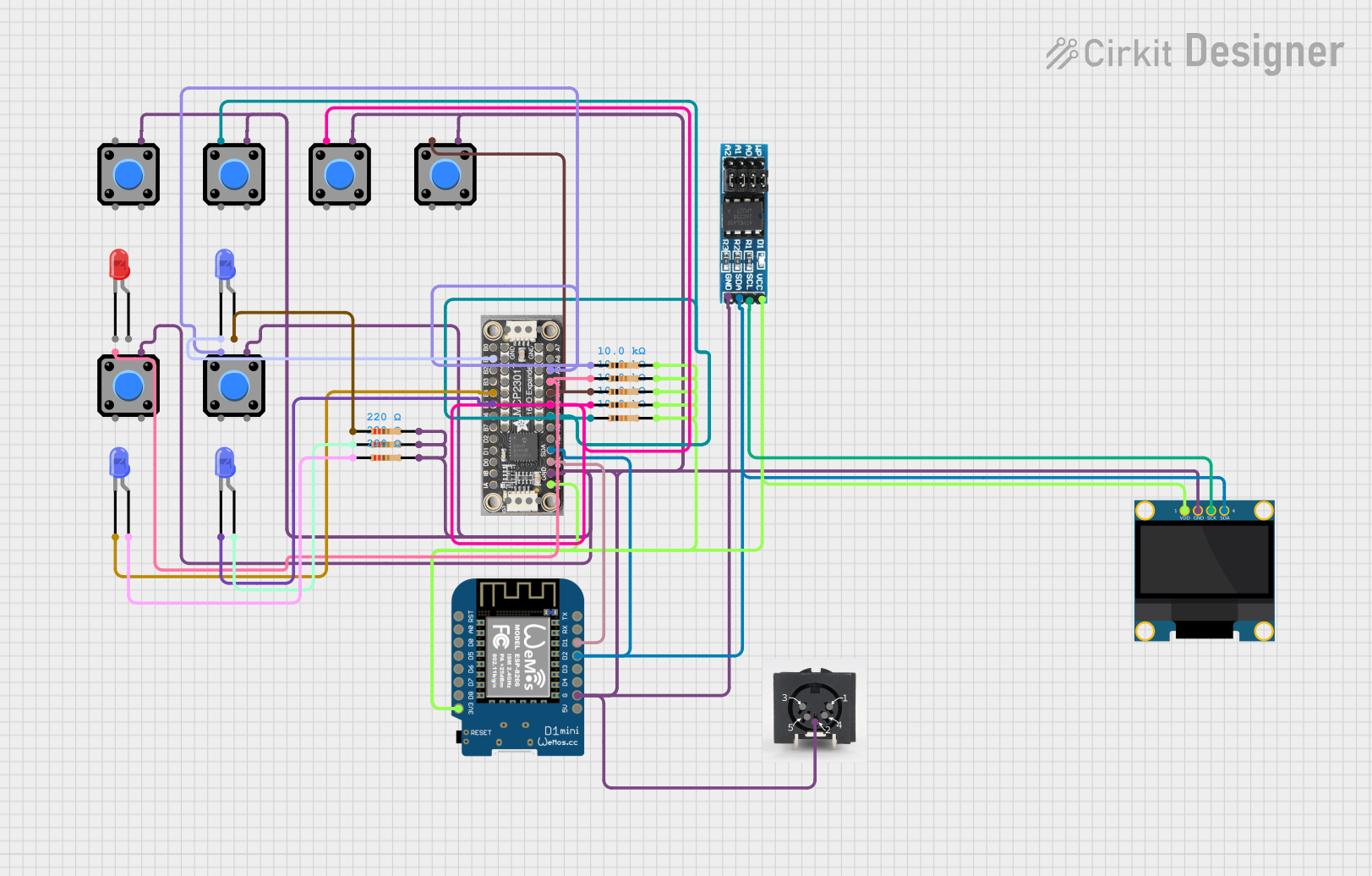
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer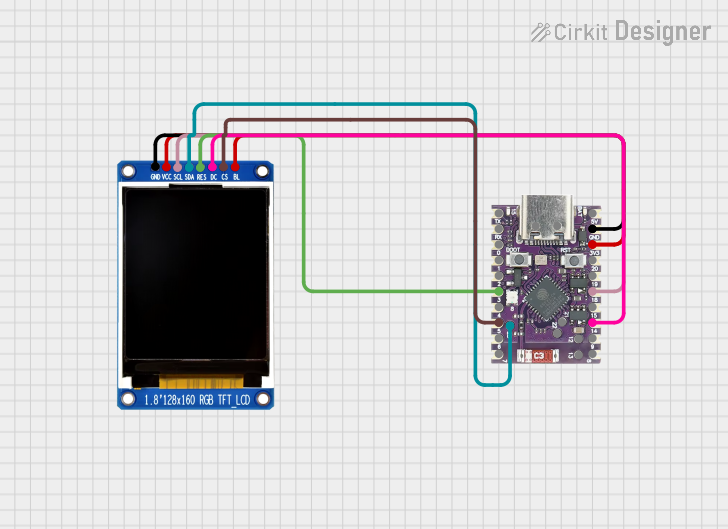
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DisplaySmall

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Portable electronic devices
- Wearable technology
- IoT (Internet of Things) projects
- Embedded systems
- Prototyping and DIY electronics
- Arduino and microcontroller-based projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the DisplaySmall module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Display Type | OLED/Monochrome |
| Resolution | 128x64 pixels |
| Interface | I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Current Consumption | ~20mA (typical) |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 15mm x 3mm |
| Viewing Angle | >160° |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DisplaySmall module has a 4-pin interface for easy integration with microcontrollers. Below is the pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the power supply. |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V. |
| 3 | SCL | Serial Clock Line for I2C communication. |
| 4 | SDA | Serial Data Line for I2C communication. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Connection: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground. - I2C Communication: Connect the
SCLandSDApins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller. For an Arduino UNO:SCLconnects to A5.SDAconnects to A4.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure that the I2C lines (SCL and SDA) have pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ to 10kΩ) if not already included on the module.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Verify that your microcontroller operates at a compatible voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- I2C Address: The default I2C address for the module is typically
0x3C. Check the datasheet or test if the address differs. - Initialization: Use a compatible library (e.g., Adafruit SSD1306 or U8g2) to initialize and control the display.
- Avoid Overheating: Operate the module within the specified temperature range to prevent damage.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the DisplaySmall module with an Arduino UNO using the Adafruit SSD1306 library:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
// Define the screen width and height
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64
// Create an instance of the display object
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, -1);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the display
if (!display.begin(SSD1306_I2C_ADDRESS, 0x3C)) {
Serial.println(F("Display initialization failed!"));
while (true); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
// Clear the display buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Display a welcome message
display.setTextSize(1); // Set text size
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE); // Set text color
display.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor position
display.println(F("Hello, DisplaySmall!"));
display.display(); // Render the text on the screen
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Display Not Turning On:
- Ensure the
VCCandGNDpins are correctly connected. - Verify the power supply voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- Ensure the
No Output on the Screen:
- Check the I2C connections (
SCLandSDA). - Confirm the I2C address matches the one in your code (default is
0x3C). - Ensure the pull-up resistors are in place if required.
- Check the I2C connections (
Flickering or Unstable Display:
- Verify the power supply is stable and sufficient.
- Check for loose connections on the I2C lines.
Library Errors:
- Ensure the Adafruit SSD1306 library is installed and up to date.
- Verify that the correct screen dimensions (128x64) are defined in the code.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage levels on the
VCCandGNDpins. - Test the I2C communication using an I2C scanner sketch to detect the module's address.
- Double-check all wiring and connections for errors or loose contacts.
- Refer to the library documentation for additional configuration options.
By following this documentation, you can successfully integrate and operate the DisplaySmall module in your projects.