
How to Use ESP32 DEVKIT V1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ESP32 DEVKIT V1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32 DEVKIT V1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32 DEVKIT V1, manufactured by Espressif, is a versatile development board built around the powerful ESP32 chip. It features integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, smart devices, and rapid prototyping. With its dual-core processor, low power consumption, and extensive GPIO options, the ESP32 DEVKIT V1 is suitable for a wide range of projects, from home automation to wearable devices.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32 DEVKIT V1
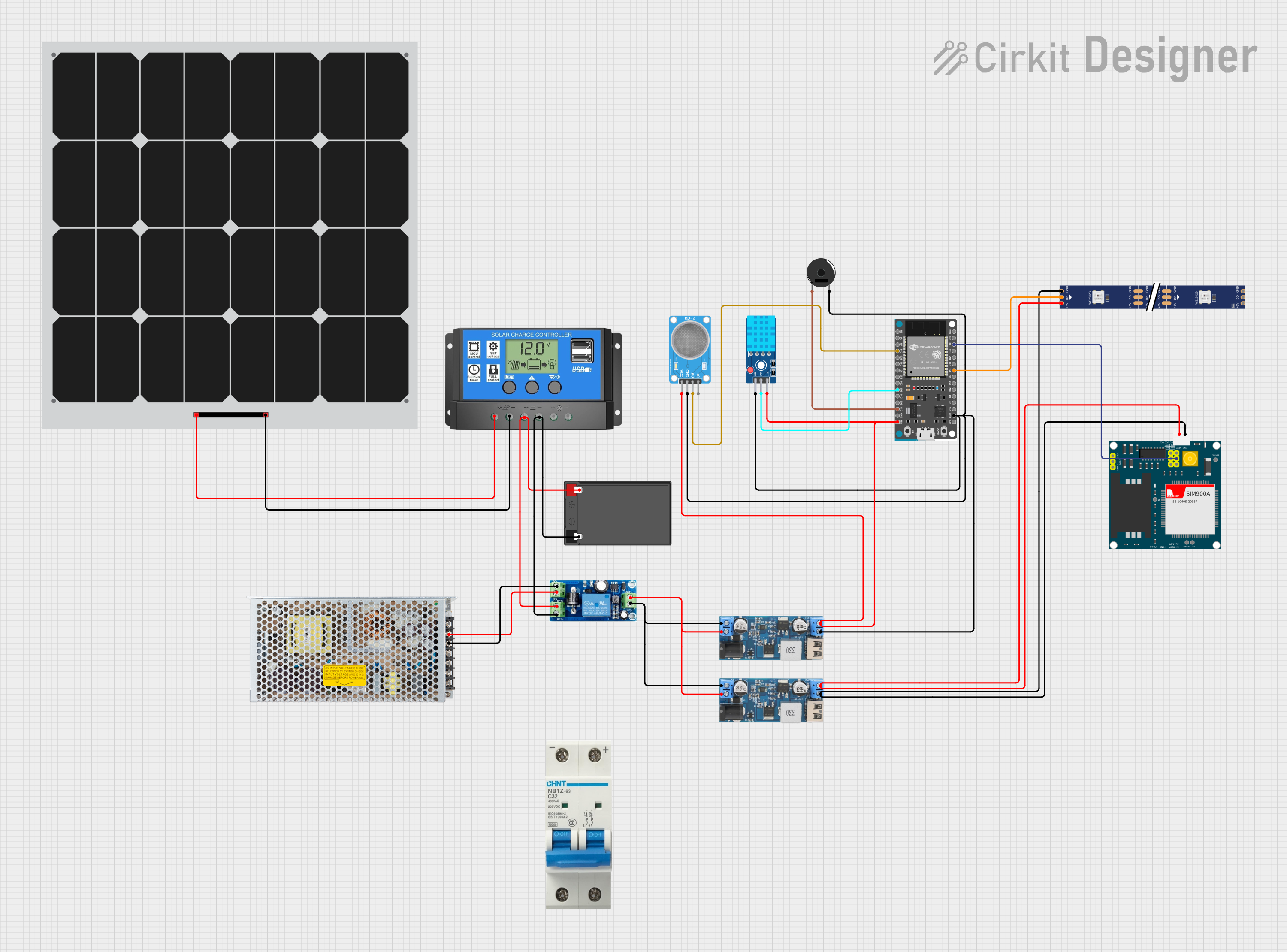
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer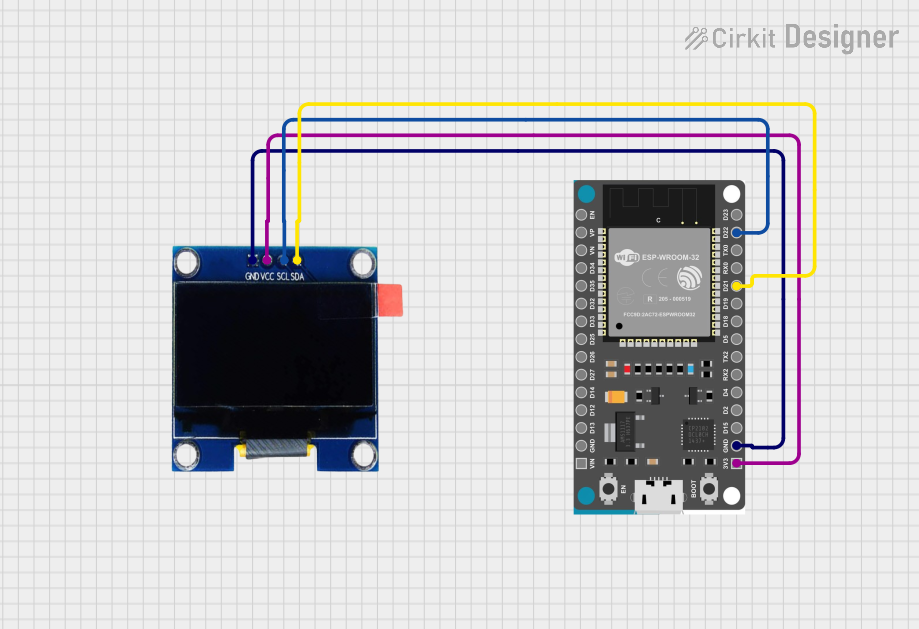
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer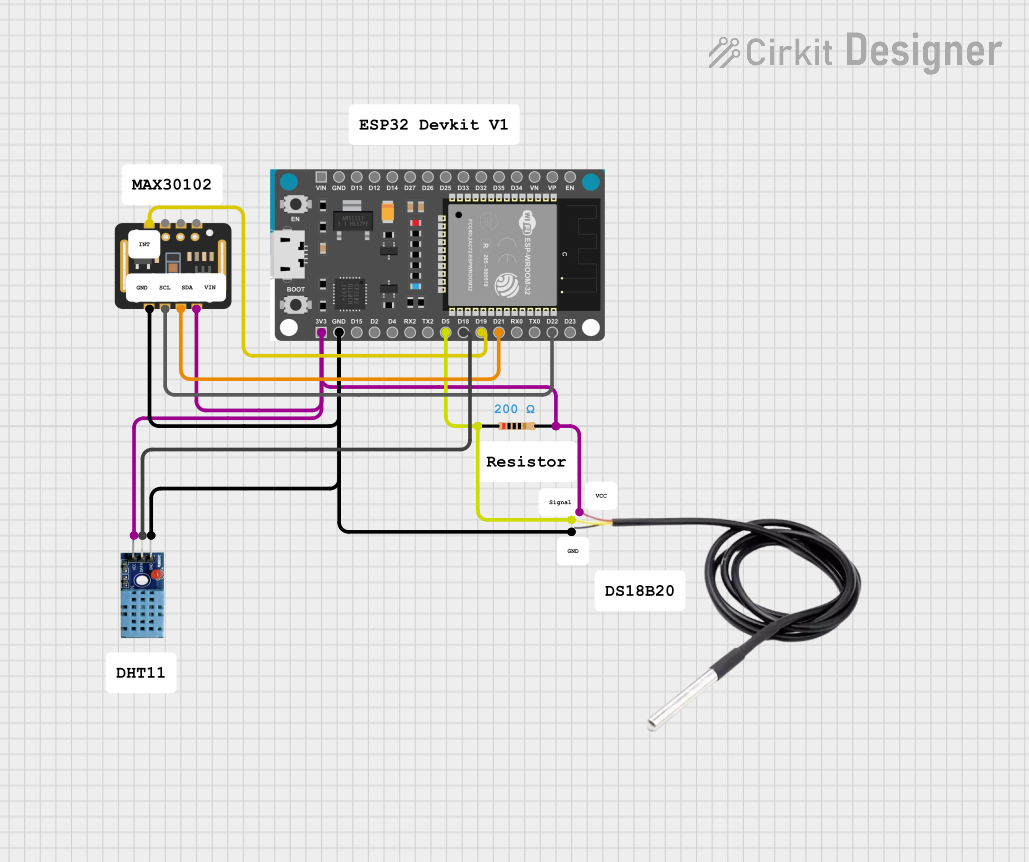
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer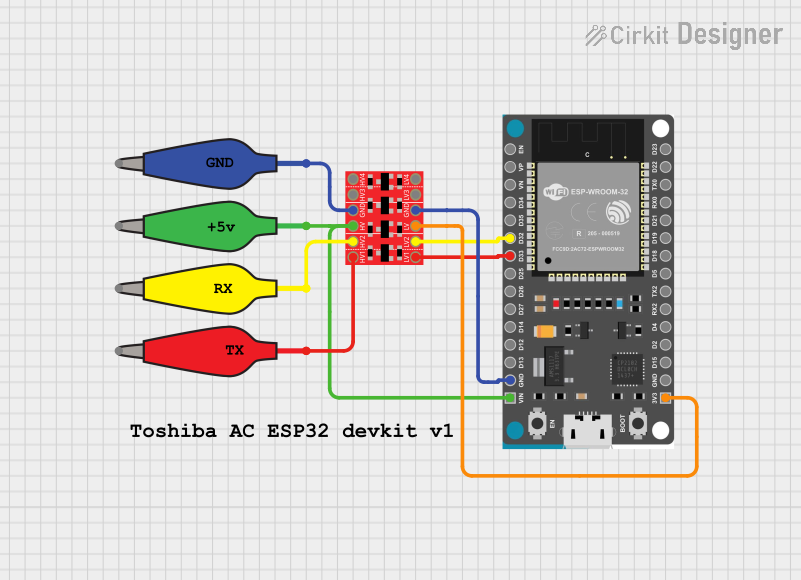
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32 DEVKIT V1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Wearable technology
- Robotics and automation
- Prototyping and educational projects
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) applications
Technical Specifications
The ESP32 DEVKIT V1 is designed to provide robust performance and flexibility. Below are its key technical specifications:
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip
- Processor: Dual-core Xtensa® 32-bit LX6 CPU, up to 240 MHz
- Wireless Connectivity: Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n and Bluetooth 4.2 (Classic + BLE)
- Flash Memory: 4 MB (varies by model)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage (via USB): 5V
- GPIO Pins: 30 (varies slightly by board version)
- ADC Channels: 18 (12-bit resolution)
- DAC Channels: 2 (8-bit resolution)
- PWM Outputs: 16
- I2C, SPI, UART: Supported
- Power Consumption: Ultra-low power consumption in deep sleep mode (~10 µA)
- Dimensions: 54 mm x 27 mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32 DEVKIT V1 features a 30-pin layout. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | EN | Enable pin. Pulling this pin low resets the chip. |
| 2 | IO0 | GPIO0. Used for boot mode selection during programming. |
| 3 | IO1 (TX0) | GPIO1. UART0 TX pin. |
| 4 | IO3 (RX0) | GPIO3. UART0 RX pin. |
| 5 | IO4 | GPIO4. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 6 | IO5 | GPIO5. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 7 | GND | Ground pin. |
| 8 | VIN | Input voltage (5V) when powering via an external source. |
| 9 | IO12 | GPIO12. Can be used as an ADC or general-purpose pin. |
| 10 | IO13 | GPIO13. Can be used as an ADC or general-purpose pin. |
| 11 | IO14 | GPIO14. Supports PWM, ADC, and general-purpose functions. |
| 12 | IO15 | GPIO15. Supports PWM, ADC, and general-purpose functions. |
| 13 | IO16 | GPIO16. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 14 | IO17 | GPIO17. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 15 | IO18 | GPIO18. SPI clock pin (SCK). |
| 16 | IO19 | GPIO19. SPI data pin (MISO). |
| 17 | IO21 | GPIO21. I2C data pin (SDA). |
| 18 | IO22 | GPIO22. I2C clock pin (SCL). |
| 19 | IO23 | GPIO23. SPI data pin (MOSI). |
| 20 | GND | Ground pin. |
| 21 | IO25 | GPIO25. DAC output or general-purpose pin. |
| 22 | IO26 | GPIO26. DAC output or general-purpose pin. |
| 23 | IO27 | GPIO27. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 24 | IO32 | GPIO32. ADC input or general-purpose pin. |
| 25 | IO33 | GPIO33. ADC input or general-purpose pin. |
| 26 | IO34 | GPIO34. ADC input (input-only pin). |
| 27 | IO35 | GPIO35. ADC input (input-only pin). |
| 28 | 3V3 | 3.3V output pin. |
| 29 | GND | Ground pin. |
| 30 | IO36 | GPIO36. ADC input (input-only pin). |
Usage Instructions
The ESP32 DEVKIT V1 is easy to use and can be programmed using the Arduino IDE or Espressif's ESP-IDF framework. Below are the steps to get started:
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to your computer via a micro-USB cable. This provides both power and a communication interface for programming.
- Alternatively, supply 5V to the VIN pin or 3.3V to the 3V3 pin for external power.
Programming the Board:
- Install the ESP32 board support package in the Arduino IDE or use the ESP-IDF framework.
- Select the correct board ("ESP32 DEVKIT V1") and port in the IDE.
- Write your code and upload it to the board.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- Ensure that the voltage levels of connected devices are compatible with the ESP32's 3.3V logic.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The ESP32 operates at 3.3V. Avoid connecting 5V signals directly to its GPIO pins to prevent damage.
- Boot Mode: To enter programming mode, ensure GPIO0 is pulled low during reset.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid unexpected resets or performance issues.
- Deep Sleep Mode: Utilize the deep sleep mode for battery-powered applications to conserve energy.
Example Code for Arduino IDE
Below is an example of how to blink an LED connected to GPIO2:
// Define the GPIO pin for the LED
const int ledPin = 2;
void setup() {
// Initialize the LED pin as an output
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED on
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Turn the LED off
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Board Not Detected in Arduino IDE:
- Ensure the correct USB driver is installed for the ESP32.
- Check that the correct COM port is selected in the IDE.
Upload Fails with "Failed to Connect" Error:
- Hold the "BOOT" button on the board while uploading the code.
- Verify that the correct board and port are selected in the IDE.
Unstable Operation or Random Resets:
- Use a stable power supply with sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Check for loose connections or short circuits.
Wi-Fi Connection Issues:
- Ensure the correct SSID and password are used in the code.
- Check for interference or weak signal strength.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to verify power supply voltages.
- Test the board with a simple sketch (e.g., blinking an LED) to confirm basic functionality.
- Update the ESP32 board package in the Arduino IDE to the latest version.
- Refer to the Espressif documentation for advanced debugging techniques.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the ESP32 DEVKIT V1 for a wide range of applications.