
How to Use Quad bit comparator: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Quad bit comparator in Cirkit Designer
Design with Quad bit comparator in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 74LS85 is a quad bit comparator manufactured by Texas Instruments (TI). It is a digital integrated circuit designed to compare two 4-bit binary numbers and determine their relationship. The comparator outputs signals indicating whether one number is greater than, less than, or equal to the other. This component is widely used in digital systems for sorting, decision-making, and arithmetic operations.
Explore Projects Built with Quad bit comparator
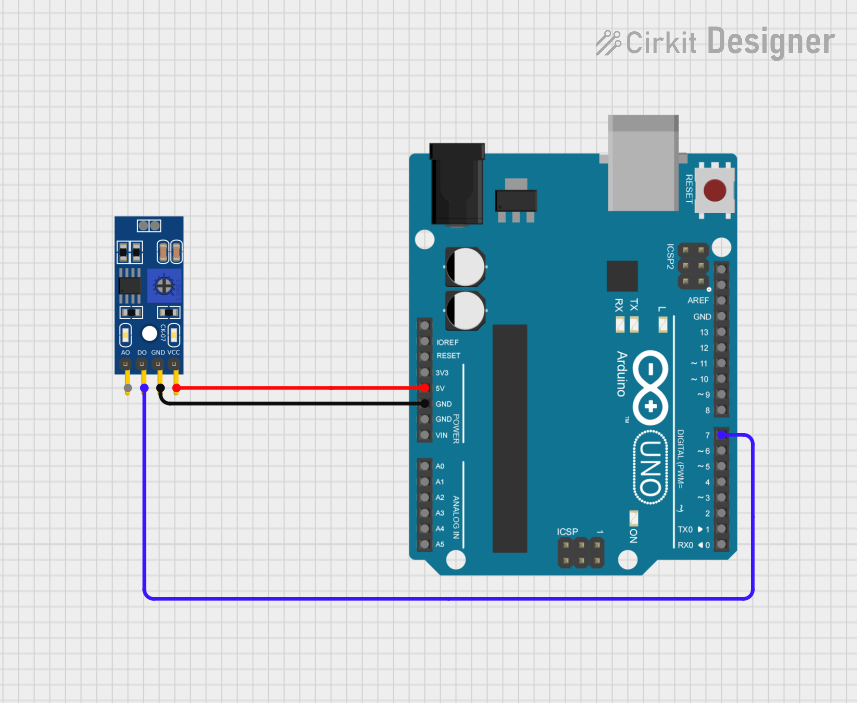
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer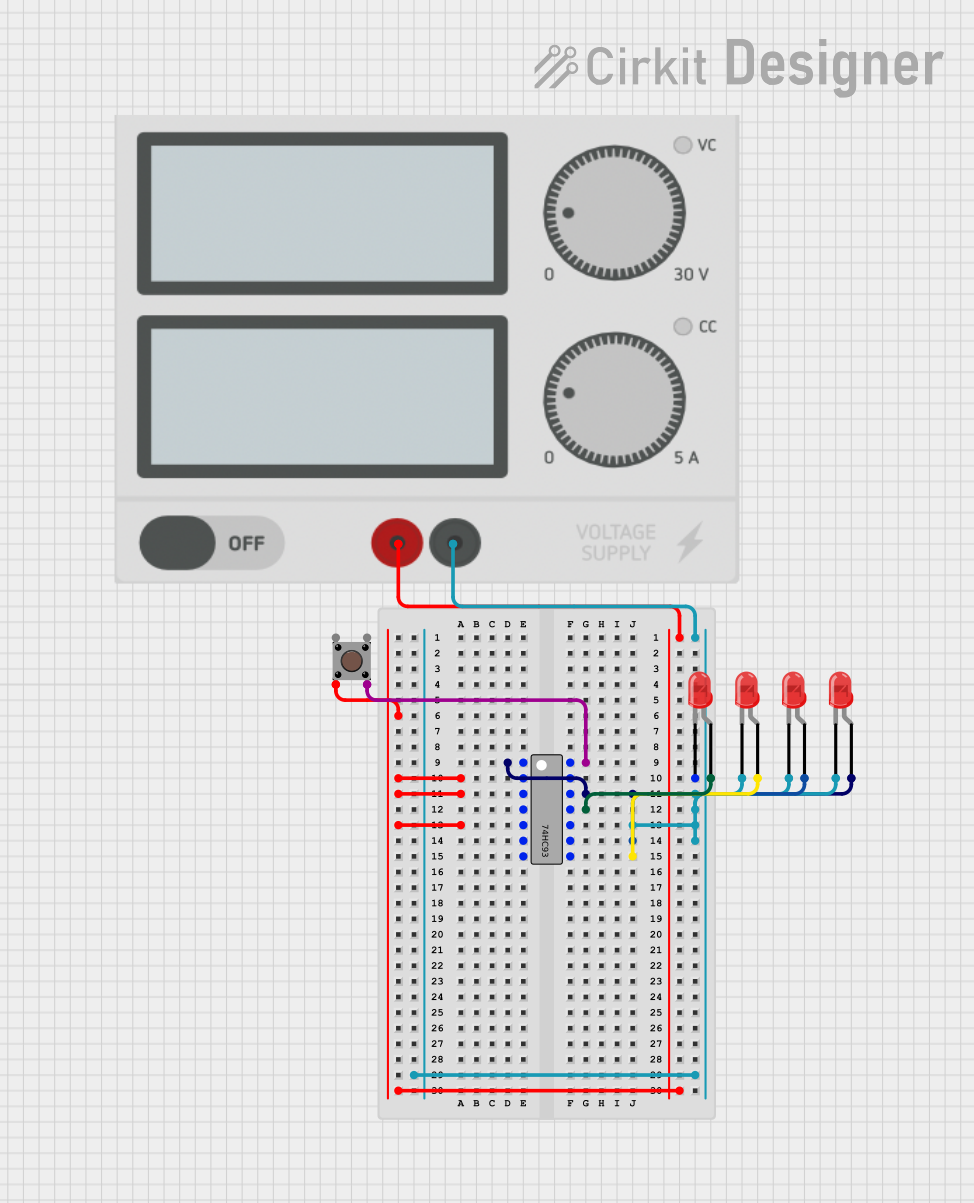
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer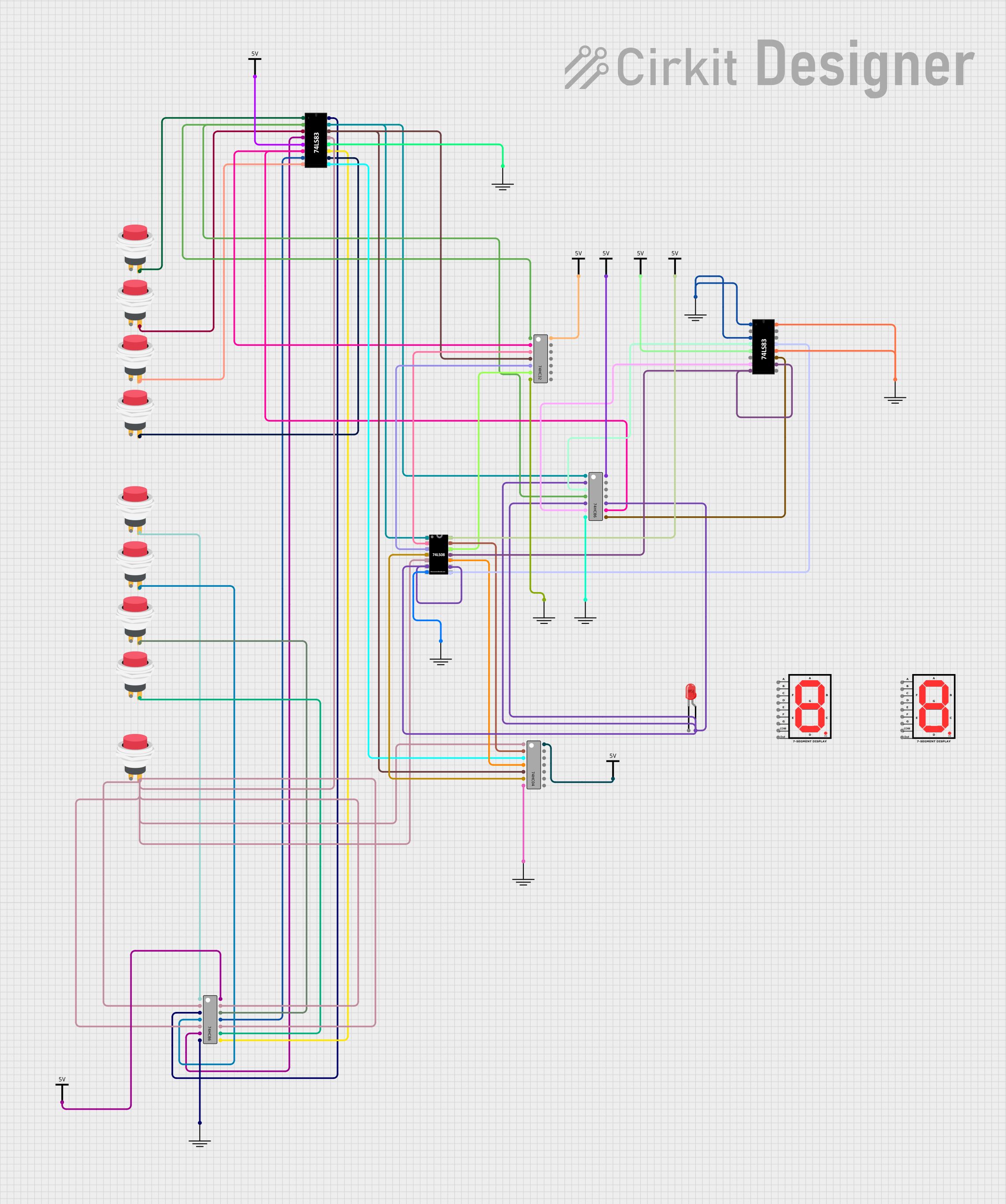
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer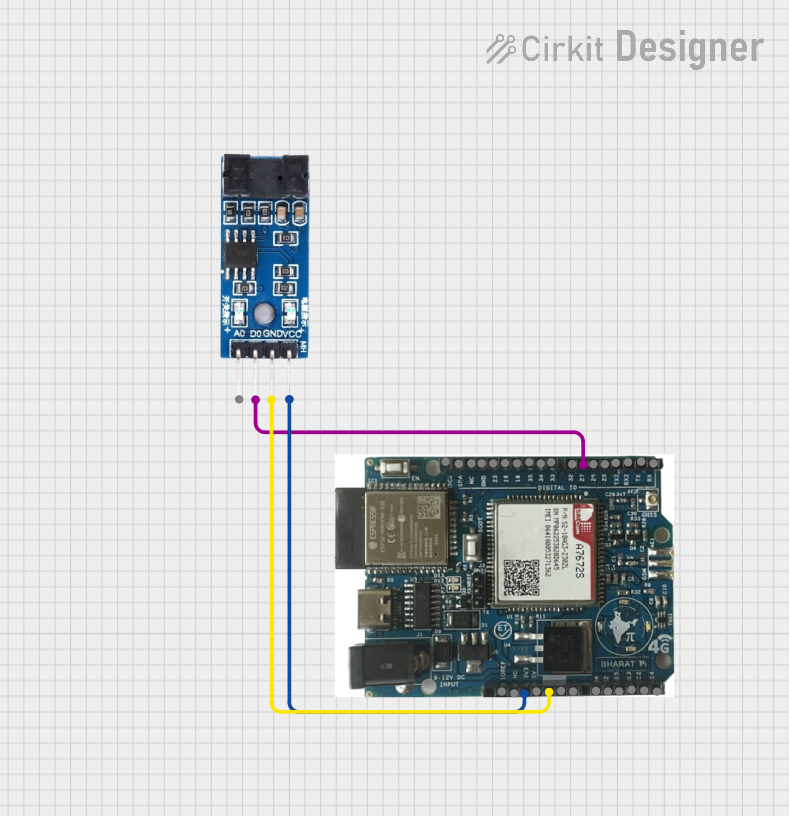
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Quad bit comparator

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Digital sorting and ranking systems
- Arithmetic and logic units (ALUs)
- Data comparison in microprocessors
- Priority encoders and decoders
- Control systems requiring binary decision-making
Technical Specifications
The 74LS85 is part of the 74LS TTL logic family, offering reliable performance and compatibility with other TTL devices. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 4.75V to 5.25V (typical 5V)
- Input High Voltage (VIH): Minimum 2V
- Input Low Voltage (VIL): Maximum 0.8V
- Output High Voltage (VOH): Minimum 2.7V
- Output Low Voltage (VOL): Maximum 0.4V
- Propagation Delay: 18ns (typical)
- Power Dissipation: 20mW (typical)
- Operating Temperature Range: 0°C to 70°C
- Package Type: DIP-16, SOIC-16
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 74LS85 comes in a 16-pin package. The pinout and descriptions are as follows:
| Pin No. | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A3 | Most significant bit (MSB) of 4-bit input A |
| 2 | B3 | Most significant bit (MSB) of 4-bit input B |
| 3 | A2 | Second most significant bit of 4-bit input A |
| 4 | B2 | Second most significant bit of 4-bit input B |
| 5 | A1 | Second least significant bit of 4-bit input A |
| 6 | B1 | Second least significant bit of 4-bit input B |
| 7 | A0 | Least significant bit (LSB) of 4-bit input A |
| 8 | GND | Ground (0V) |
| 9 | B0 | Least significant bit (LSB) of 4-bit input B |
| 10 | I(A<B) | Cascading input: A is less than B |
| 11 | I(A=B) | Cascading input: A is equal to B |
| 12 | I(A>B) | Cascading input: A is greater than B |
| 13 | O(A<B) | Output: A is less than B |
| 14 | O(A=B) | Output: A is equal to B |
| 15 | O(A>B) | Output: A is greater than B |
| 16 | Vcc | Positive supply voltage (typically +5V) |
Usage Instructions
The 74LS85 is straightforward to use in digital circuits. Below are the steps and considerations for proper usage:
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Supply:
- Connect pin 16 (Vcc) to a +5V power supply.
- Connect pin 8 (GND) to the ground of the circuit.
Input Connections:
- Connect the 4-bit binary numbers to be compared to the A (pins 1, 3, 5, 7) and B (pins 2, 4, 6, 9) inputs.
- Ensure that the binary numbers are in the correct order, with the MSB connected to A3/B3 and the LSB connected to A0/B0.
Cascading Inputs (Optional):
- For standalone operation, tie the cascading inputs (pins 10, 11, 12) to logic levels as follows:
- I(A<B) = LOW (0V)
- I(A=B) = HIGH (+5V)
- I(A>B) = LOW (0V)
- For cascading multiple comparators, connect the outputs of one comparator to the inputs of the next.
- For standalone operation, tie the cascading inputs (pins 10, 11, 12) to logic levels as follows:
Output Connections:
- The outputs (pins 13, 14, 15) will indicate the comparison result:
- O(A<B) = HIGH if A < B
- O(A=B) = HIGH if A = B
- O(A>B) = HIGH if A > B
- The outputs (pins 13, 14, 15) will indicate the comparison result:
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) near the Vcc pin to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
- Avoid leaving unused inputs floating; tie them to a defined logic level (HIGH or LOW).
- Ensure that the input voltage levels are within the specified range to prevent damage to the IC.
- If cascading multiple comparators, ensure proper timing and synchronization between stages.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The 74LS85 can be interfaced with an Arduino UNO to compare two 4-bit binary numbers. Below is an example code snippet:
// Arduino code to interface with 74LS85 Quad Bit Comparator
// This code compares two 4-bit binary numbers and reads the comparison result
// Define input pins for binary numbers A and B
const int A_pins[4] = {2, 3, 4, 5}; // A0 to A3 connected to Arduino pins 2-5
const int B_pins[4] = {6, 7, 8, 9}; // B0 to B3 connected to Arduino pins 6-9
// Define output pins for comparison results
const int O_A_less_B = 10; // O(A<B) connected to pin 10
const int O_A_equal_B = 11; // O(A=B) connected to pin 11
const int O_A_greater_B = 12; // O(A>B) connected to pin 12
void setup() {
// Set A and B pins as outputs
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(A_pins[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode(B_pins[i], OUTPUT);
}
// Set output pins as inputs
pinMode(O_A_less_B, INPUT);
pinMode(O_A_equal_B, INPUT);
pinMode(O_A_greater_B, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Example: Set binary numbers A = 5 (0101) and B = 9 (1001)
int A[4] = {1, 0, 1, 0}; // Binary representation of 5
int B[4] = {1, 0, 0, 1}; // Binary representation of 9
// Write binary numbers to the comparator
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
digitalWrite(A_pins[i], A[i]);
digitalWrite(B_pins[i], B[i]);
}
// Read comparison results
bool less = digitalRead(O_A_less_B);
bool equal = digitalRead(O_A_equal_B);
bool greater = digitalRead(O_A_greater_B);
// Print results to the serial monitor
Serial.print("A < B: ");
Serial.println(less);
Serial.print("A = B: ");
Serial.println(equal);
Serial.print("A > B: ");
Serial.println(greater);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Output:
- Ensure that the power supply is stable and within the specified range (4.75V to 5.25V).
- Verify that all inputs are connected and not left floating.
- Check for proper cascading input configuration if using multiple comparators.
Noise or Unstable Operation:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the Vcc pin to filter out noise.
- Ensure that the ground connections are solid and free of interference.
Outputs Always LOW or HIGH:
- Verify the input voltage levels and ensure they meet the TTL logic thresholds.
- Check for short circuits or incorrect wiring.
FAQs
Q: Can the 74LS85 compare numbers larger than 4 bits?
A: Yes, by cascading multiple 74LS85 ICs, you can compare numbers larger than 4 bits. Use the cascading inputs and outputs to extend the comparison.
Q: Is the 74LS85 compatible with CMOS logic?
A: The 74LS85 is a TTL device, but it can interface with CMOS logic if the voltage levels are compatible. Use level shifters if necessary.
Q: What happens if the cascading inputs are left floating?
A: Floating cascading inputs can cause unpredictable behavior. Always tie