
How to Use socket GZT80: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with socket GZT80 in Cirkit Designer
Design with socket GZT80 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Socket GZT80, manufactured by Relpol, is a versatile and reliable socket designed for connecting and securing electronic components in a variety of circuit applications. It ensures stable and durable electrical connections, making it an essential component in both prototyping and production environments. The GZT80 is particularly suited for use with relays, timers, and other modular electronic devices.
Explore Projects Built with socket GZT80
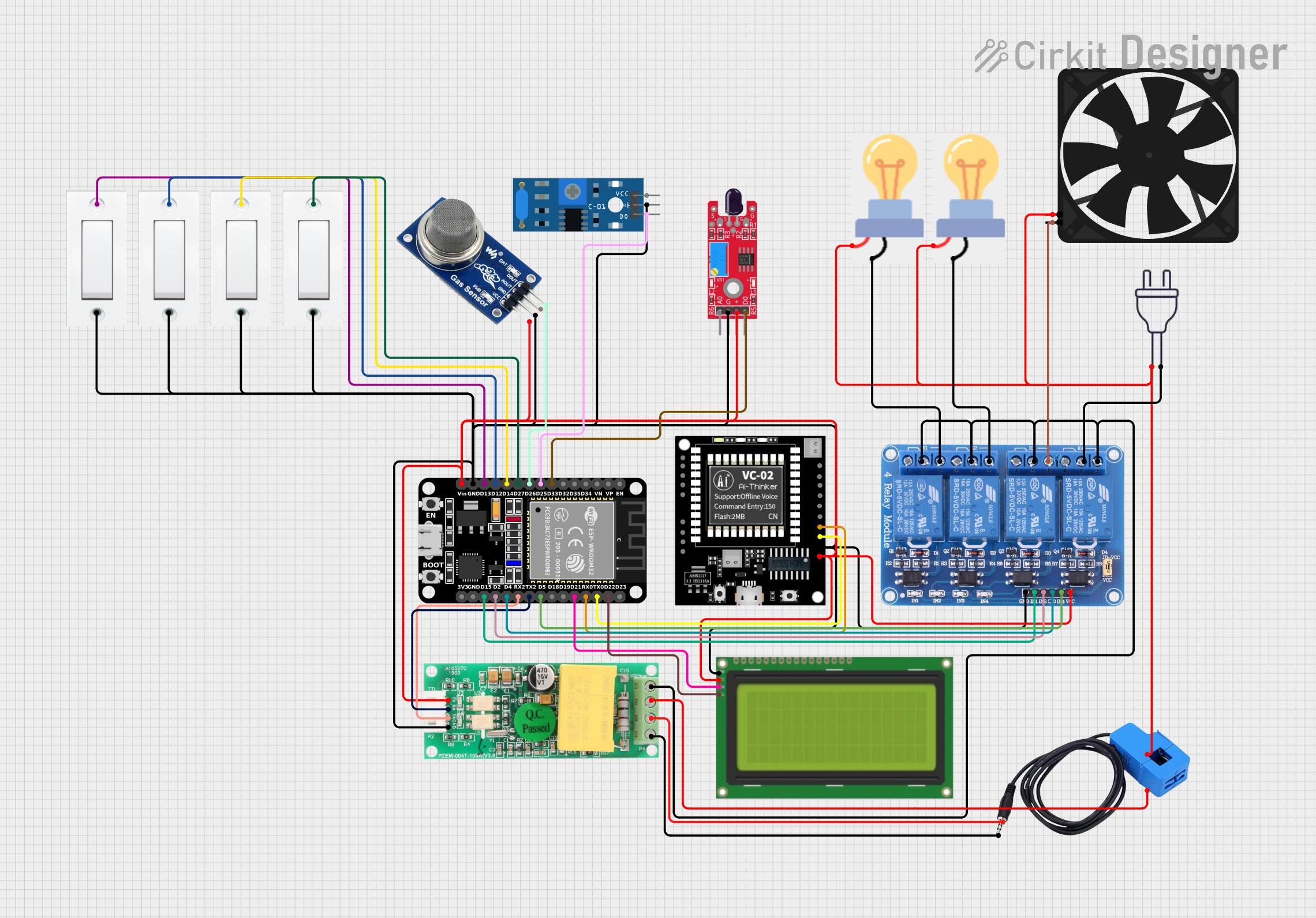
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer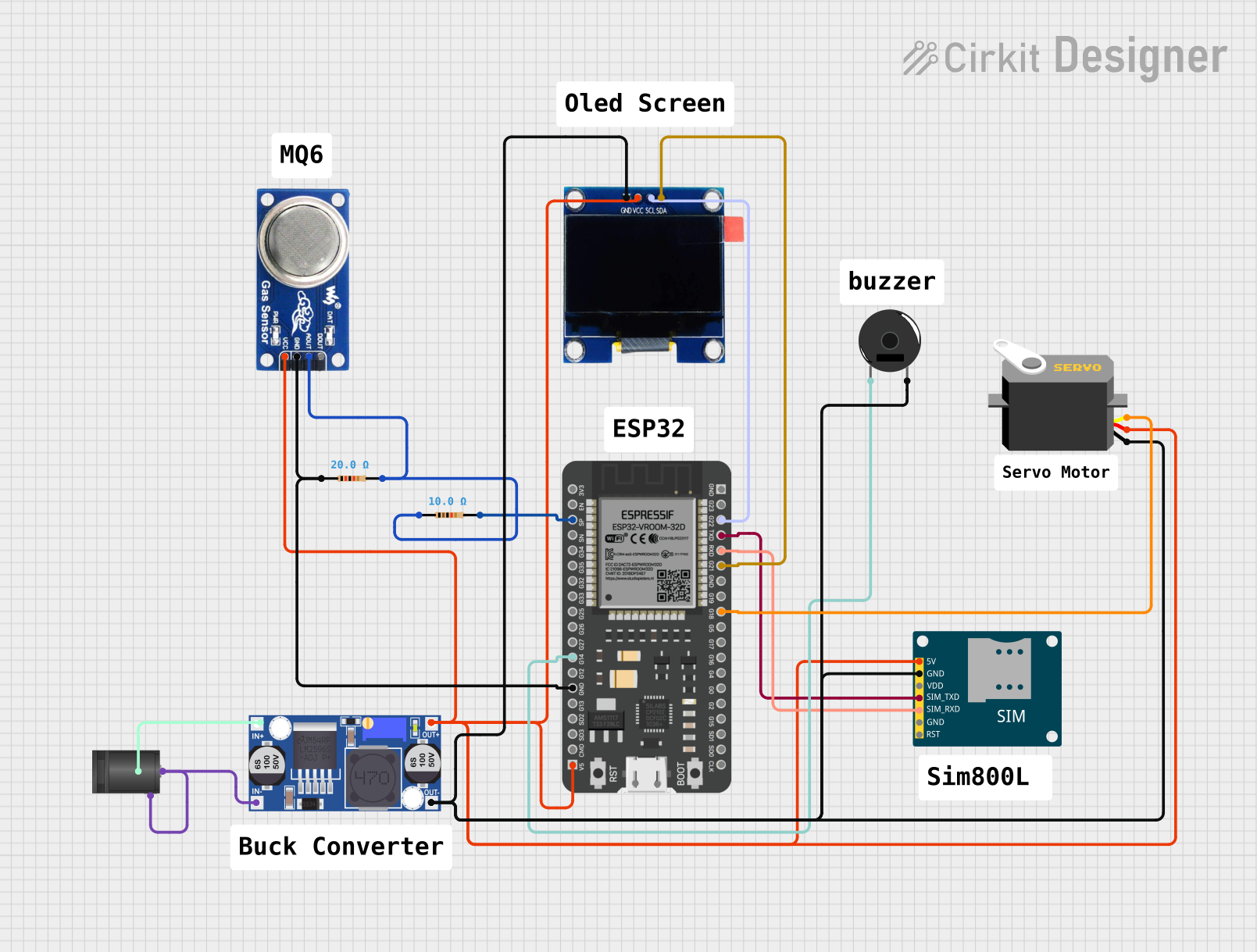
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer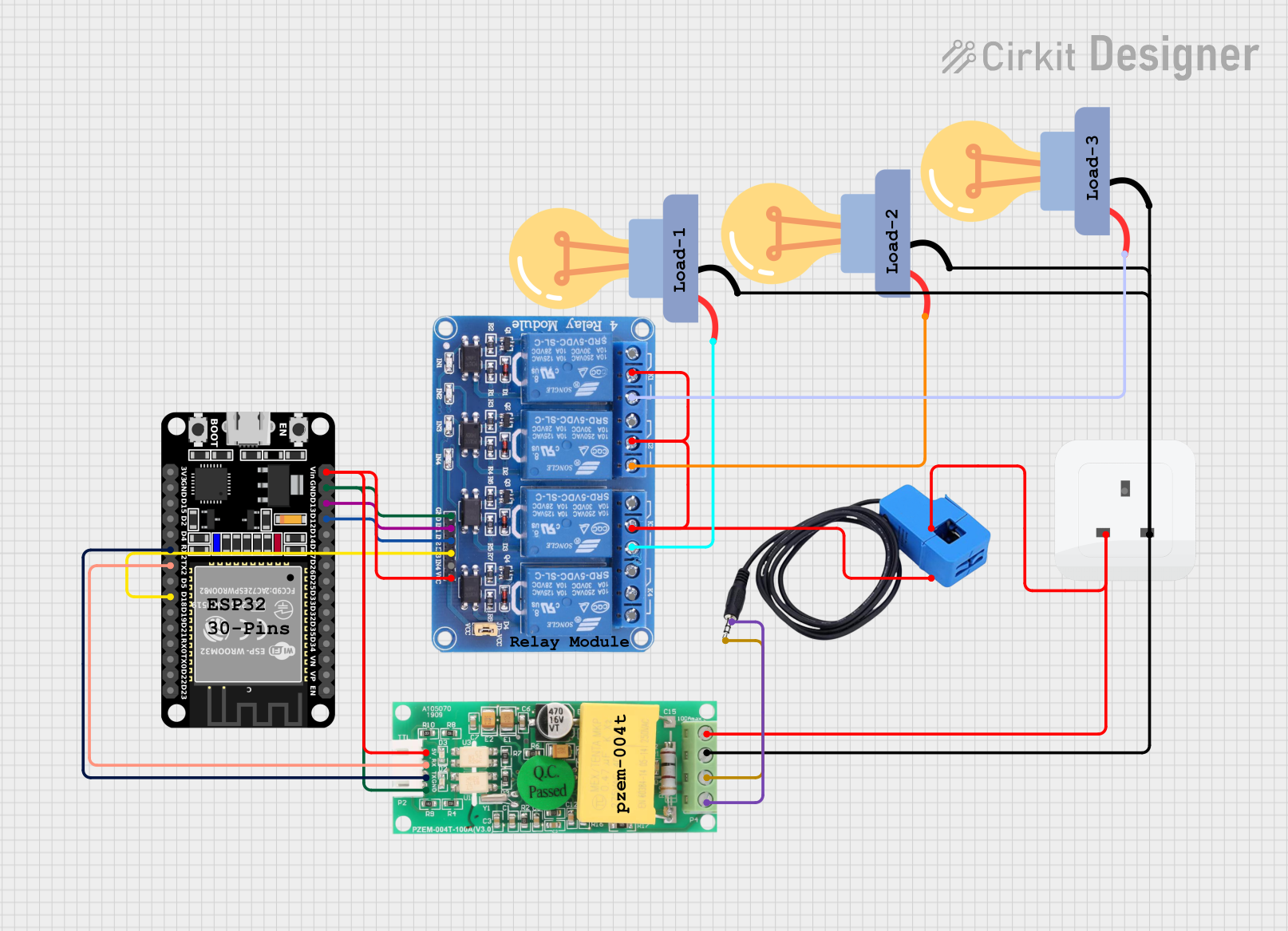
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer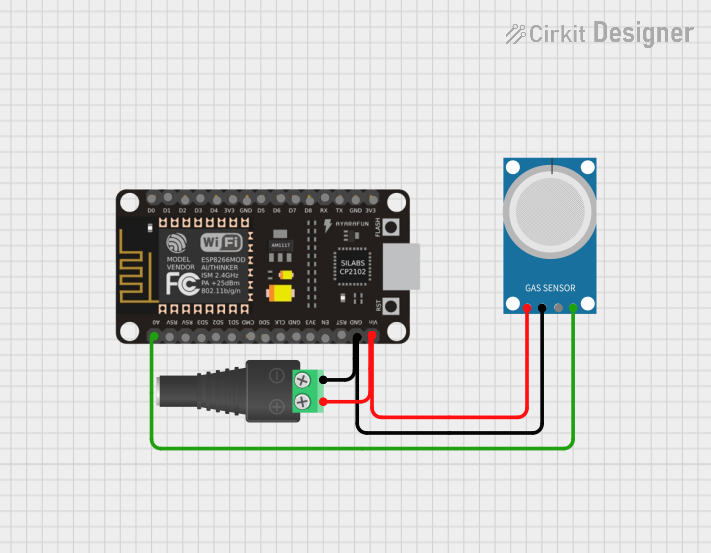
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with socket GZT80

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Relay Modules: Provides a secure base for relays in control circuits.
- Industrial Automation: Used in PLC systems and other automation setups.
- Prototyping: Ideal for testing and development of electronic circuits.
- Power Distribution: Ensures reliable connections in power management systems.
- Signal Processing: Used in circuits requiring stable signal connections.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Relpol |
| Part ID | GZT80 |
| Rated Voltage | 250V AC |
| Rated Current | 10A |
| Contact Material | Silver Alloy |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C |
| Mounting Type | DIN Rail or Panel Mount |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 78mm x 27mm x 35mm |
| Weight | 45g |
| Compliance | RoHS, CE |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GZT80 socket features a standard pin layout designed for compatibility with a wide range of relays and components. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Description | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coil Terminal 1 | Connects to one side of the relay coil |
| 2 | Coil Terminal 2 | Connects to the other side of the coil |
| 3 | Normally Closed (NC) Contact | Closed when the relay is inactive |
| 4 | Common Contact | Shared terminal for NC and NO contacts |
| 5 | Normally Open (NO) Contact | Open when the relay is inactive |
| 6 | Ground or Auxiliary Connection | Optional grounding or auxiliary use |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Socket GZT80 in a Circuit
Mounting the Socket:
- Secure the GZT80 socket onto a DIN rail or panel using the provided mounting clips or screws.
- Ensure the socket is firmly attached to prevent movement during operation.
Connecting Components:
- Insert the relay or other compatible component into the socket, aligning the pins with the corresponding terminals.
- Push the component gently but firmly until it is securely seated.
Wiring the Circuit:
- Use appropriately rated wires to connect the socket terminals to the rest of the circuit.
- Refer to the pin configuration table to ensure correct connections (e.g., coil terminals, NC/NO contacts).
Testing the Circuit:
- After wiring, test the circuit to ensure proper operation.
- Verify that the relay or component functions as expected when powered.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Do not exceed the rated voltage (250V AC) or current (10A) to avoid damage or failure.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all wires are tightly connected to the terminals to prevent loose connections.
- Environmental Conditions: Operate the socket within the specified temperature range (-40°C to +70°C) for optimal performance.
- Component Compatibility: Verify that the relay or component used is compatible with the GZT80 socket.
Example: Using the GZT80 with an Arduino UNO
The GZT80 can be used to control a relay connected to an Arduino UNO. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the relay coil terminals (pins 1 and 2) to the Arduino's digital output pin and ground, respectively.
- Wire the relay's NO and Common contacts (pins 4 and 5) to control an external load (e.g., an LED or motor).
Arduino Code
// Example code to control a relay using the GZT80 socket and Arduino UNO
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay coil
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off initially
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Turn the relay on
delay(1000); // Keep it on for 1 second
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Turn the relay off
delay(1000); // Keep it off for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Component not seating properly | Misalignment of pins | Realign the component and reinsert it |
| No electrical connection | Loose or incorrect wiring | Check and tighten all connections |
| Relay not activating | Insufficient voltage/current to the coil | Verify power supply and connections |
| Overheating of the socket | Exceeding rated current or voltage | Reduce load to within rated limits |
| Intermittent operation | Environmental factors (e.g., vibration) | Secure the socket and connections |
FAQs
Can the GZT80 be used with DC circuits?
- Yes, the GZT80 can be used with DC circuits as long as the voltage and current ratings are not exceeded.
What types of relays are compatible with the GZT80?
- The GZT80 is compatible with standard plug-in relays that match its pin configuration and electrical ratings.
How do I clean the socket contacts?
- Use a soft, dry cloth or contact cleaner to remove dirt or oxidation from the contacts. Avoid using abrasive materials.
Can the GZT80 be used outdoors?
- The GZT80 is not weatherproof. If outdoor use is required, ensure it is housed in a suitable enclosure.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the Socket GZT80 into their electronic projects and ensure reliable performance.