
How to Use INMP441 I2S Microphone Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with INMP441 I2S Microphone Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with INMP441 I2S Microphone Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The INMP441 is a digital microphone module that utilizes the I2S (Inter-IC Sound) interface for transmitting audio data. Unlike traditional analog microphones, the INMP441 outputs digital audio signals, making it ideal for modern digital audio processing systems. It features a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), low power consumption, and a compact design, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Explore Projects Built with INMP441 I2S Microphone Module
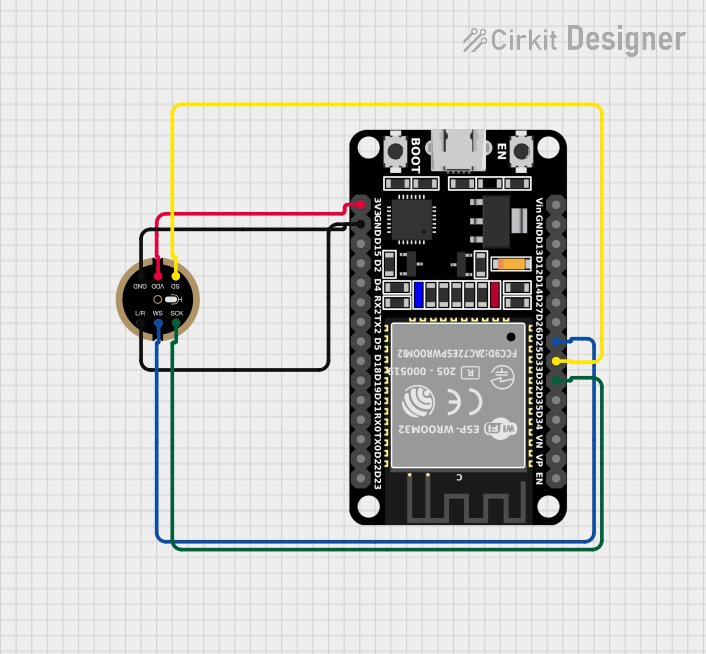
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer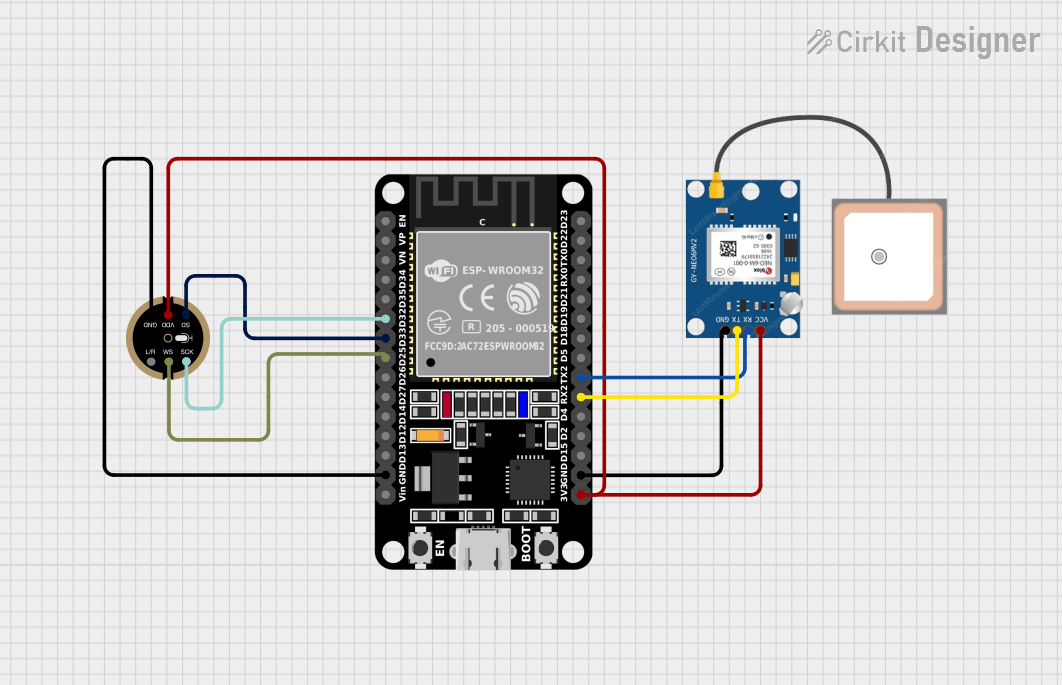
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer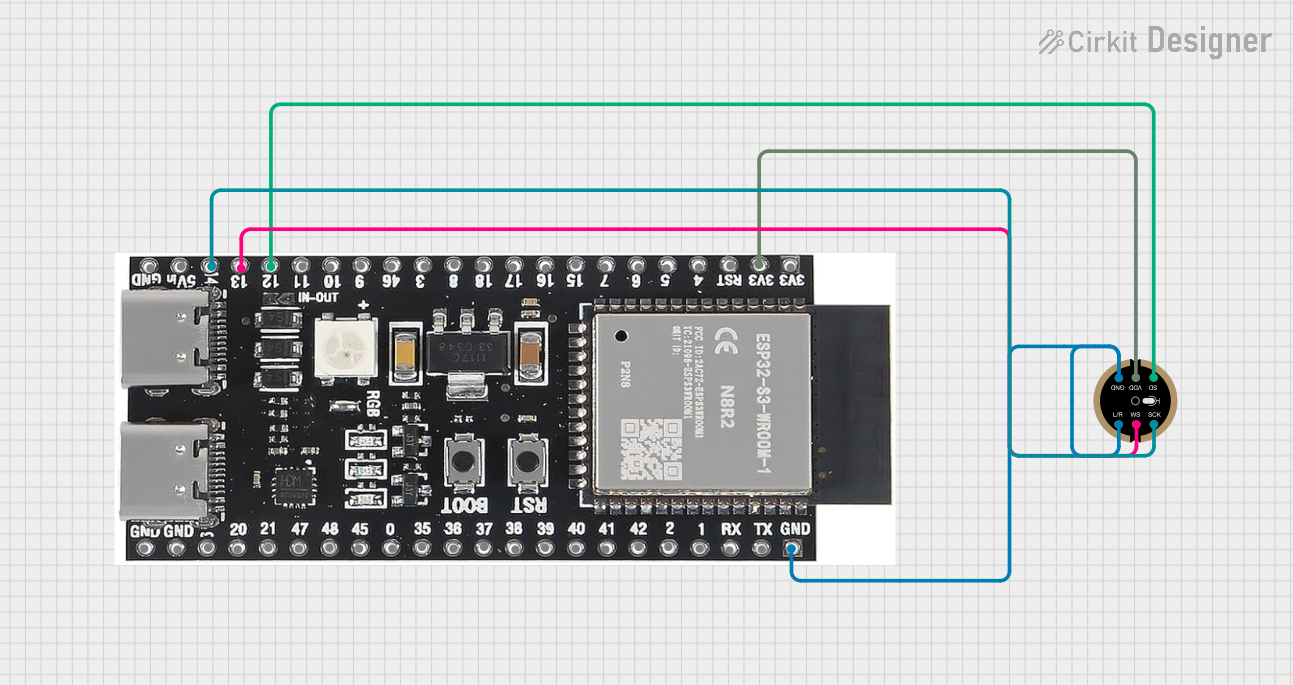
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer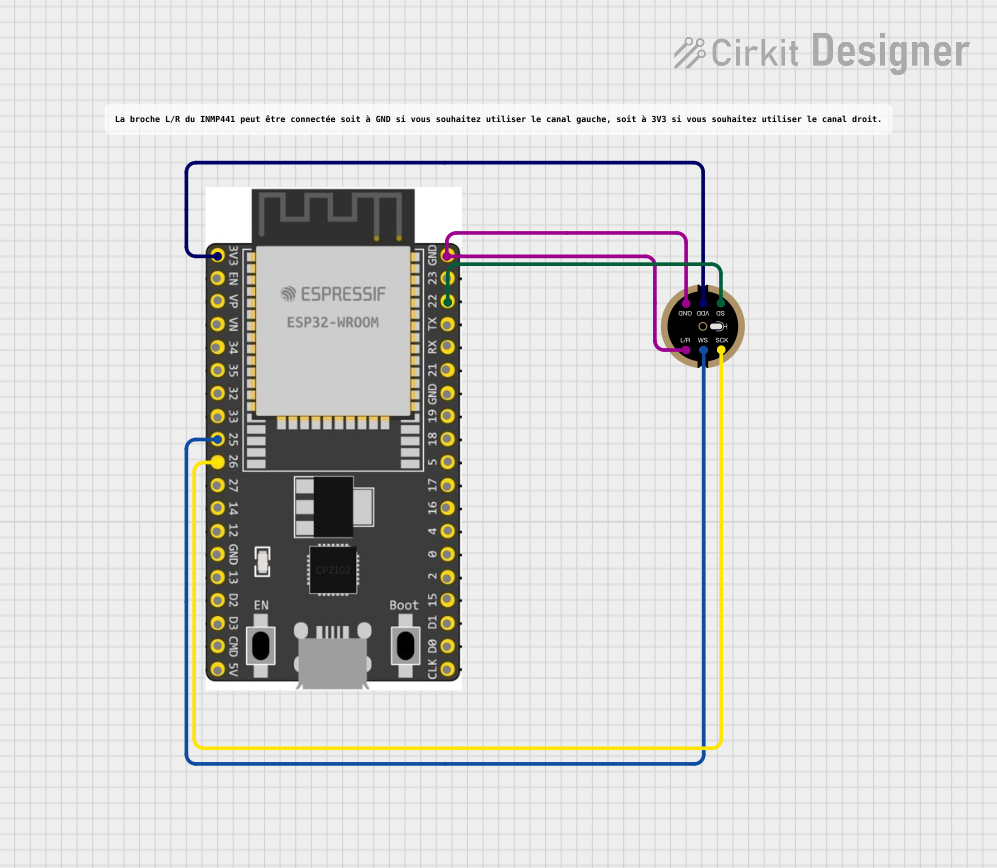
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with INMP441 I2S Microphone Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voice recognition systems (e.g., smart assistants)
- Audio recording and streaming
- IoT devices with audio input capabilities
- Digital audio processing and analysis
- Noise detection and environmental monitoring
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Interface | I2S (Inter-IC Sound) |
| Supply Voltage (VDD) | 1.8V to 3.3V |
| Current Consumption | 1.4 mA (typical) |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio | 61 dB |
| Frequency Response | 60 Hz to 15 kHz |
| Sensitivity | -26 dBFS |
| Output Format | 24-bit, I2S |
| Dimensions | 15 mm x 10 mm x 1.5 mm |
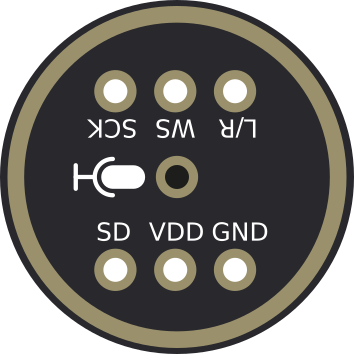
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The INMP441 module has 7 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VDD | 1 | Power supply input (1.8V to 3.3V). |
| GND | 2 | Ground connection. |
| SD | 3 | Serial data output (I2S data line). |
| SCK | 4 | Serial clock input (I2S clock line). |
| WS | 5 | Word select input (I2S left/right channel selection). |
| L/R | 6 | Left/Right channel selection pin. Connect to GND for left or VDD for right. |
| SEL | 7 | Mode selection pin (not commonly used; typically left unconnected). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the INMP441 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a 1.8V to 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- I2S Interface: Connect the SD, SCK, and WS pins to the corresponding I2S pins on your microcontroller or audio processor.
- Channel Selection: Use the L/R pin to select the microphone's audio channel:
- Connect to GND for the left channel.
- Connect to VDD for the right channel.
- Mode Selection: Leave the SEL pin unconnected unless a specific mode is required by your application.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range (1.8V to 3.3V) to avoid damaging the module.
- Use short and properly shielded wires for the I2S connections to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- The INMP441 outputs 24-bit audio data, so ensure your microcontroller or processor supports this format.
- If using multiple microphones, ensure proper synchronization of the I2S clock and word select signals.
Example: Connecting INMP441 to Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO does not natively support I2S, but you can use an external I2S interface or a compatible microcontroller like the ESP32. Below is an example of using the INMP441 with an ESP32:
Wiring Diagram
| INMP441 Pin | ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
| VDD | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SD | GPIO32 |
| SCK | GPIO14 |
| WS | GPIO15 |
| L/R | GND |
Example Code
#include <driver/i2s.h>
// I2S configuration
#define I2S_NUM I2S_NUM_0 // Use I2S port 0
#define I2S_BCK_IO 14 // Serial clock (SCK)
#define I2S_WS_IO 15 // Word select (WS)
#define I2S_DATA_IN_IO 32 // Serial data (SD)
// I2S configuration structure
void setupI2S() {
i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
.mode = i2s_mode_t(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX), // Master receive mode
.sample_rate = 16000, // Sampling rate
.bits_per_sample = I2S_BITS_PER_SAMPLE_24BIT, // 24-bit audio
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT, // Single channel (left)
.communication_format = I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S, // I2S format
.intr_alloc_flags = ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1, // Interrupt level
.dma_buf_count = 8, // Number of DMA buffers
.dma_buf_len = 64 // Buffer length
};
i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
.bck_io_num = I2S_BCK_IO, // Serial clock pin
.ws_io_num = I2S_WS_IO, // Word select pin
.data_out_num = -1, // Not used (output pin)
.data_in_num = I2S_DATA_IN_IO // Serial data input pin
};
// Install and start I2S driver
i2s_driver_install(I2S_NUM, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
i2s_set_pin(I2S_NUM, &pin_config);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
setupI2S();
Serial.println("INMP441 Microphone Initialized");
}
void loop() {
uint8_t data[128]; // Buffer to store audio data
size_t bytesRead;
// Read audio data from I2S
i2s_read(I2S_NUM, data, sizeof(data), &bytesRead, portMAX_DELAY);
// Process or transmit the audio data as needed
Serial.print("Bytes read: ");
Serial.println(bytesRead);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Audio Data Output:
- Ensure the I2S pins are correctly connected to the microcontroller.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is within the specified range (1.8V to 3.3V).
- Check the I2S configuration in your code (e.g., sample rate, bit depth).
Noise or Distorted Audio:
- Use shielded cables for the I2S connections to reduce interference.
- Ensure the microphone is not placed near high-frequency noise sources.
Microphone Not Detected:
- Verify the L/R pin configuration for the desired channel.
- Check the I2S clock and word select signals for proper synchronization.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the INMP441 with a 5V microcontroller?
A: The INMP441 requires a power supply of 1.8V to 3.3V. If your microcontroller operates at 5V, use a voltage regulator or level shifter for compatibility.
Q: Does the INMP441 support stereo audio?
A: The INMP441 is a mono microphone. However, you can use two INMP441 modules (one configured for the left channel and the other for the right channel) to achieve stereo audio.
Q: What is the maximum sampling rate supported?
A: The INMP441 supports sampling rates up to 48 kHz, depending on your I2S configuration.