
How to Use Optokobler: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Optokobler in Cirkit Designer
Design with Optokobler in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An optocoupler, also known as an opto-isolator, is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits using light waves. It typically consists of an LED (light-emitting diode) and a photodetector (such as a phototransistor) housed within a single package. When current flows through the LED, it emits light, which is detected by the photodetector, thereby enabling signal transmission while maintaining electrical isolation.
Explore Projects Built with Optokobler

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer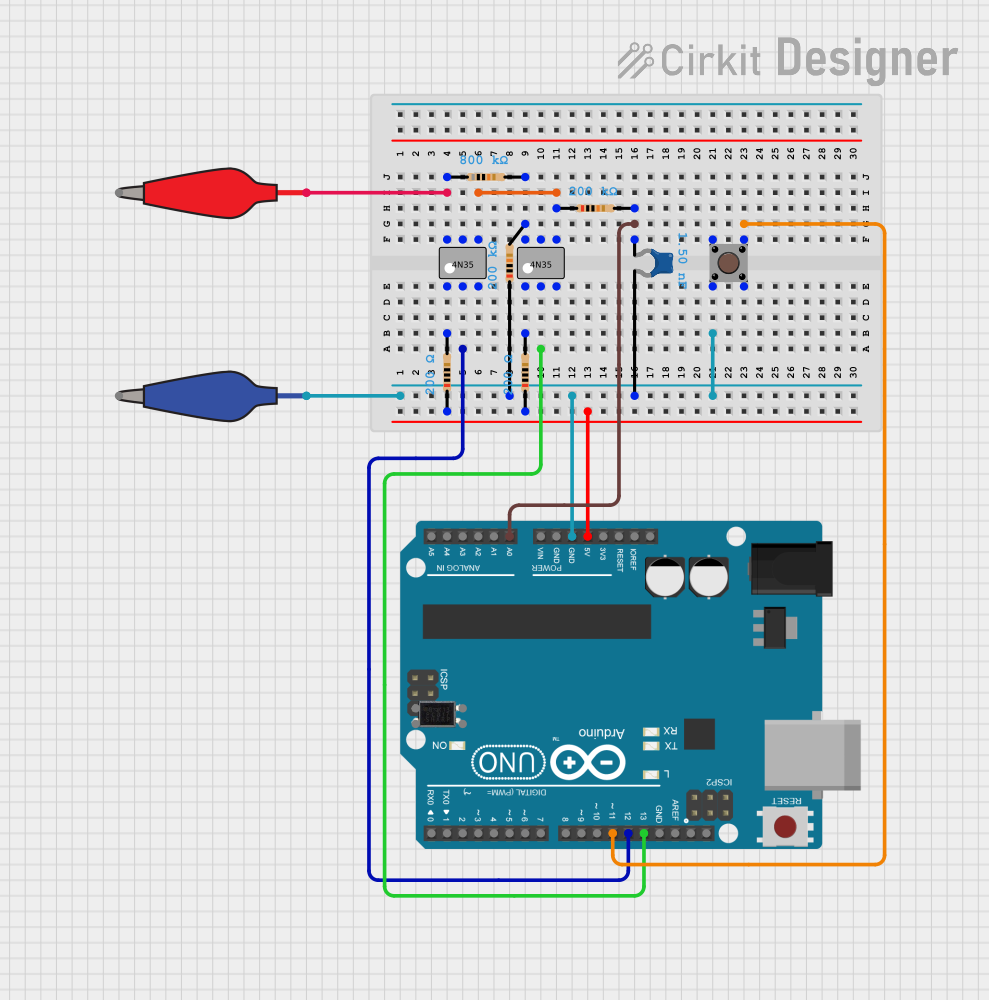
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer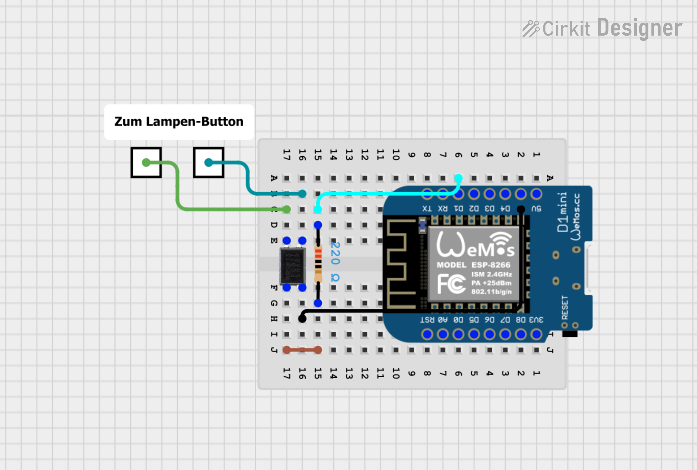
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Optokobler

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Signal Isolation: Protects sensitive components from high-voltage spikes or noise.
- Microcontroller Interfacing: Safely connects microcontrollers to high-voltage or noisy circuits.
- Switching Power Supplies: Provides feedback across isolated sections of the circuit.
- Industrial Automation: Used in motor control, relays, and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers).
- Communication Systems: Ensures signal integrity in noisy environments.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical optocoupler (e.g., 4N25, PC817). Always refer to the datasheet of the specific model you are using for precise details.
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage (LED Forward Voltage): 1.2V to 1.4V (typical)
- Input Current (LED Forward Current): 10mA to 20mA (typical)
- Output Voltage (Collector-Emitter Voltage): Up to 35V
- Output Current (Collector Current): Up to 50mA
- Isolation Voltage: 2.5kV to 5kV (depending on the model)
- Response Time: 2µs to 20µs (typical, depending on the type)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration for a common 4-pin optocoupler (e.g., PC817) is as follows:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (A) | Positive terminal of the LED (input side). |
| 2 | Cathode (K) | Negative terminal of the LED (input side). |
| 3 | Emitter (E) | Emitter of the phototransistor (output side). |
| 4 | Collector (C) | Collector of the phototransistor (output side). |
For a 6-pin optocoupler (e.g., 4N35), the additional pins may include a base pin for the phototransistor or unused pins.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Input Side (LED):
- Connect a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED to prevent damage. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's Law: [ R = \frac{V_{in} - V_f}{I_f} ] where (V_{in}) is the input voltage, (V_f) is the forward voltage of the LED, and (I_f) is the forward current.
Output Side (Phototransistor):
- Connect the collector to the positive supply voltage through a pull-up resistor.
- The emitter is typically connected to ground.
- The value of the pull-up resistor depends on the desired output current and voltage levels.
Isolation:
- Ensure that the input and output sides are electrically isolated. Do not connect their grounds directly.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Always use a resistor to limit the current through the LED.
- Voltage Ratings: Ensure the collector-emitter voltage does not exceed the maximum rating.
- Speed: For high-speed applications, choose optocouplers with faster response times.
- Temperature: Operate the optocoupler within its specified temperature range to avoid performance degradation.
Example: Connecting an Optocoupler to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a PC817 optocoupler to interface an Arduino UNO with an external circuit.
Circuit Description
- The Arduino controls the LED side of the optocoupler.
- The phototransistor side is connected to an external circuit, with a pull-up resistor to 5V.
Code Example
// Example code for using an optocoupler with Arduino UNO
// This code toggles the optocoupler LED on and off every second.
const int optoPin = 9; // Pin connected to the optocoupler LED (via a resistor)
void setup() {
pinMode(optoPin, OUTPUT); // Set the pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(optoPin, HIGH); // Turn on the optocoupler LED
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(optoPin, LOW); // Turn off the optocoupler LED
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
LED Not Lighting Up:
- Cause: Incorrect resistor value or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Recalculate the resistor value and ensure the input voltage is sufficient to drive the LED.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect pull-up resistor value or damaged phototransistor.
- Solution: Verify the pull-up resistor value and check the phototransistor's connections.
Slow Response Time:
- Cause: High capacitance or unsuitable optocoupler model.
- Solution: Use a high-speed optocoupler for faster switching applications.
Signal Distortion:
- Cause: Noise or improper grounding.
- Solution: Ensure proper grounding and use decoupling capacitors if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can an optocoupler handle AC signals?
A: Yes, but you need to use a rectifier circuit or an AC-compatible optocoupler.
Q: How do I choose the right optocoupler for my application?
A: Consider factors such as isolation voltage, response time, and current/voltage ratings.
Q: Can I use an optocoupler for PWM signals?
A: Yes, but ensure the optocoupler's response time is fast enough to handle the PWM frequency.
Q: Is it possible to use an optocoupler for bidirectional communication?
A: Standard optocouplers are unidirectional. For bidirectional communication, use specialized isolators or multiple optocouplers.
This concludes the documentation for the optocoupler. Always refer to the specific datasheet for detailed information about your component.