
How to Use Logic Level Shifter Converter Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Logic Level Shifter Converter Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with Logic Level Shifter Converter Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Logic Level Shifter Converter Module is a versatile electronic component designed to facilitate communication between devices operating at different voltage levels. It is commonly used in circuits where components with varying logic levels, such as 3.3V and 5V, need to interface seamlessly. This module ensures safe and reliable voltage translation, preventing potential damage to sensitive components.
Explore Projects Built with Logic Level Shifter Converter Module
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Logic Level Shifter Converter Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Interfacing 3.3V microcontrollers (e.g., ESP8266, ESP32) with 5V peripherals (e.g., sensors, displays).
- Enabling communication between 1.8V, 3.3V, and 5V logic systems.
- Bidirectional data transfer in I2C, SPI, UART, and GPIO applications.
- Protecting low-voltage devices from overvoltage damage.
Technical Specifications
- Voltage Levels Supported: 1.8V, 3.3V, 5V
- Number of Channels: Typically 4 bidirectional channels
- Input Voltage (High Side): 3.3V to 5V
- Input Voltage (Low Side): 1.8V to 3.3V
- Maximum Data Rate: Up to 100 kHz (I2C) or higher for other protocols
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C
- Dimensions: Varies by module, typically compact (e.g., 15mm x 20mm)
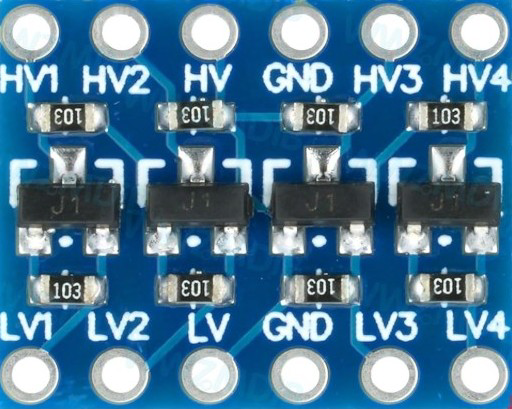
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| HV | High voltage input (e.g., 5V). Powers the high-voltage side of the module. |
| LV | Low voltage input (e.g., 3.3V). Powers the low-voltage side of the module. |
| GND | Ground connection. Common ground for both high and low voltage systems. |
| TX1, TX2, TX3, TX4 | High-voltage side data pins for bidirectional communication. |
| RX1, RX2, RX3, RX4 | Low-voltage side data pins for bidirectional communication. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power the Module:
- Connect the HV pin to the high-voltage logic level (e.g., 5V).
- Connect the LV pin to the low-voltage logic level (e.g., 3.3V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
Connect Data Lines:
- For each channel, connect the high-voltage side (e.g., TX1) to the high-voltage device.
- Connect the corresponding low-voltage side (e.g., RX1) to the low-voltage device.
Verify Connections:
- Ensure that the voltage levels on the HV and LV pins match the operating voltages of the connected devices.
- Double-check the ground connection to avoid communication issues.
Test the Circuit:
- Power on the circuit and test communication between the devices. The module will automatically handle bidirectional voltage translation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure that the HV and LV pins are powered with stable and appropriate voltage levels.
- Data Rate: For high-speed communication protocols, verify that the module supports the required data rate.
- Channel Usage: Use the correct channel pairs (e.g., TX1 ↔ RX1) for proper operation.
- Common Ground: Always connect the ground of the module to the ground of all devices in the circuit.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to use the Logic Level Shifter Converter Module to interface a 3.3V sensor with a 5V Arduino UNO.
Circuit Connections
- HV: Connect to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- LV: Connect to the sensor's 3.3V pin.
- GND: Connect to the common ground of the Arduino and the sensor.
- TX1: Connect to the Arduino's digital pin (e.g., D2).
- RX1: Connect to the sensor's data pin.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code for reading data from a 3.3V sensor using a logic level shifter
// Ensure the sensor is connected to the RX1 pin of the level shifter module
const int sensorPin = 2; // Arduino pin connected to TX1 of the level shifter
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication Between Devices:
- Cause: Incorrect voltage levels on HV or LV pins.
- Solution: Verify that the HV and LV pins are powered with the correct voltages.
Data Corruption or Loss:
- Cause: High data rate exceeding the module's capability.
- Solution: Reduce the communication speed or use a module rated for higher speeds.
Module Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Check the wiring and ensure the module is not overloaded.
Unstable Operation:
- Cause: Missing or poor ground connection.
- Solution: Ensure a solid ground connection between all devices.
FAQs
Q: Can this module handle analog signals?
A: No, the module is designed for digital signals only. Use a dedicated level shifter for analog signals.Q: How many channels can I use simultaneously?
A: Most modules support 4 bidirectional channels, but check your specific module's datasheet.Q: Can I use this module with I2C communication?
A: Yes, the module supports bidirectional I2C communication. Connect the SDA and SCL lines to separate channels.Q: Is it safe to connect 1.8V devices to this module?
A: Yes, as long as the LV pin is powered with 1.8V, the module can safely interface with 1.8V devices.