
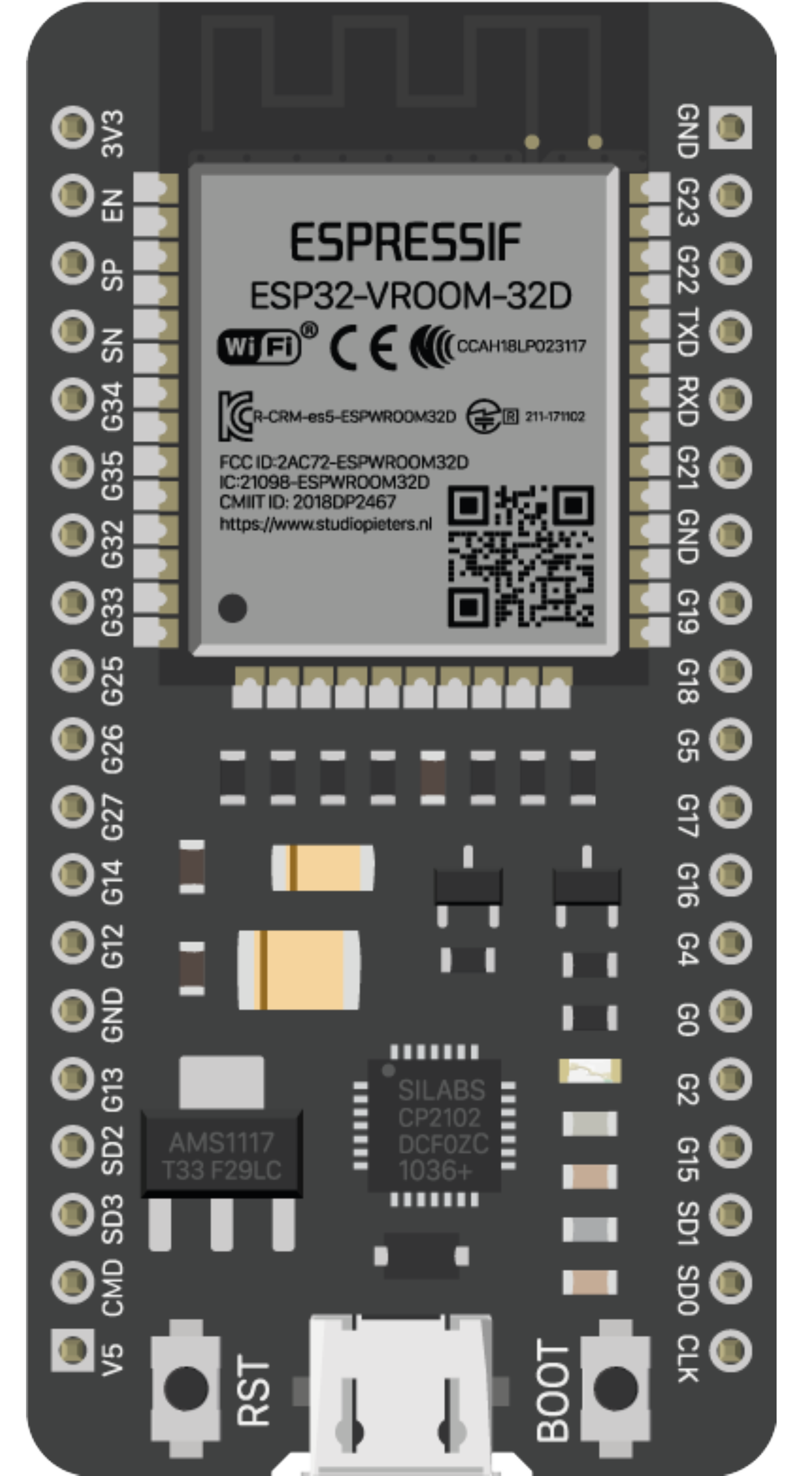
How to Use ESP32 - 38 pins: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with ESP32 - 38 pins in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32 - 38 pins in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32 is a versatile system on a chip (SoC) that has been designed for a wide range of Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It integrates Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, making it ideal for smart home devices, wearable electronics, and various wireless sensors. With its 38 pins, the ESP32 offers a significant number of GPIOs for interfacing with different peripherals and sensors.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32 - 38 pins
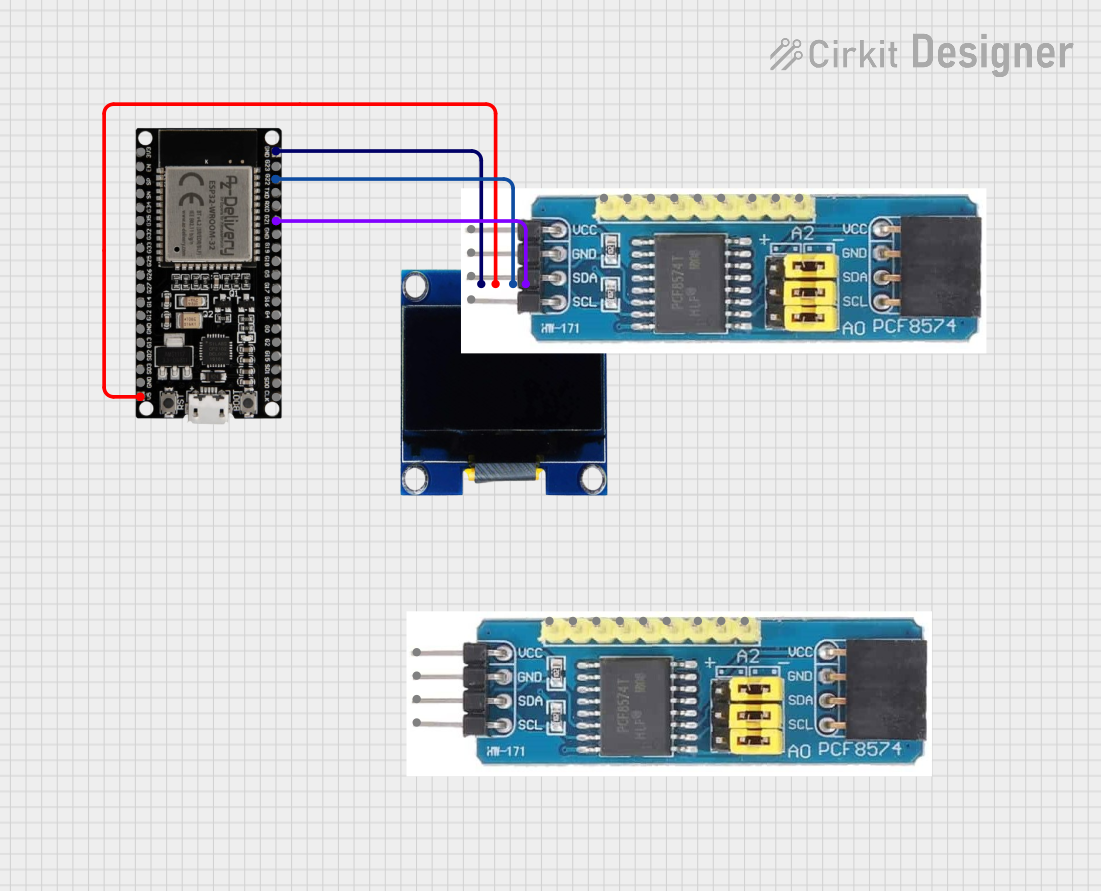
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer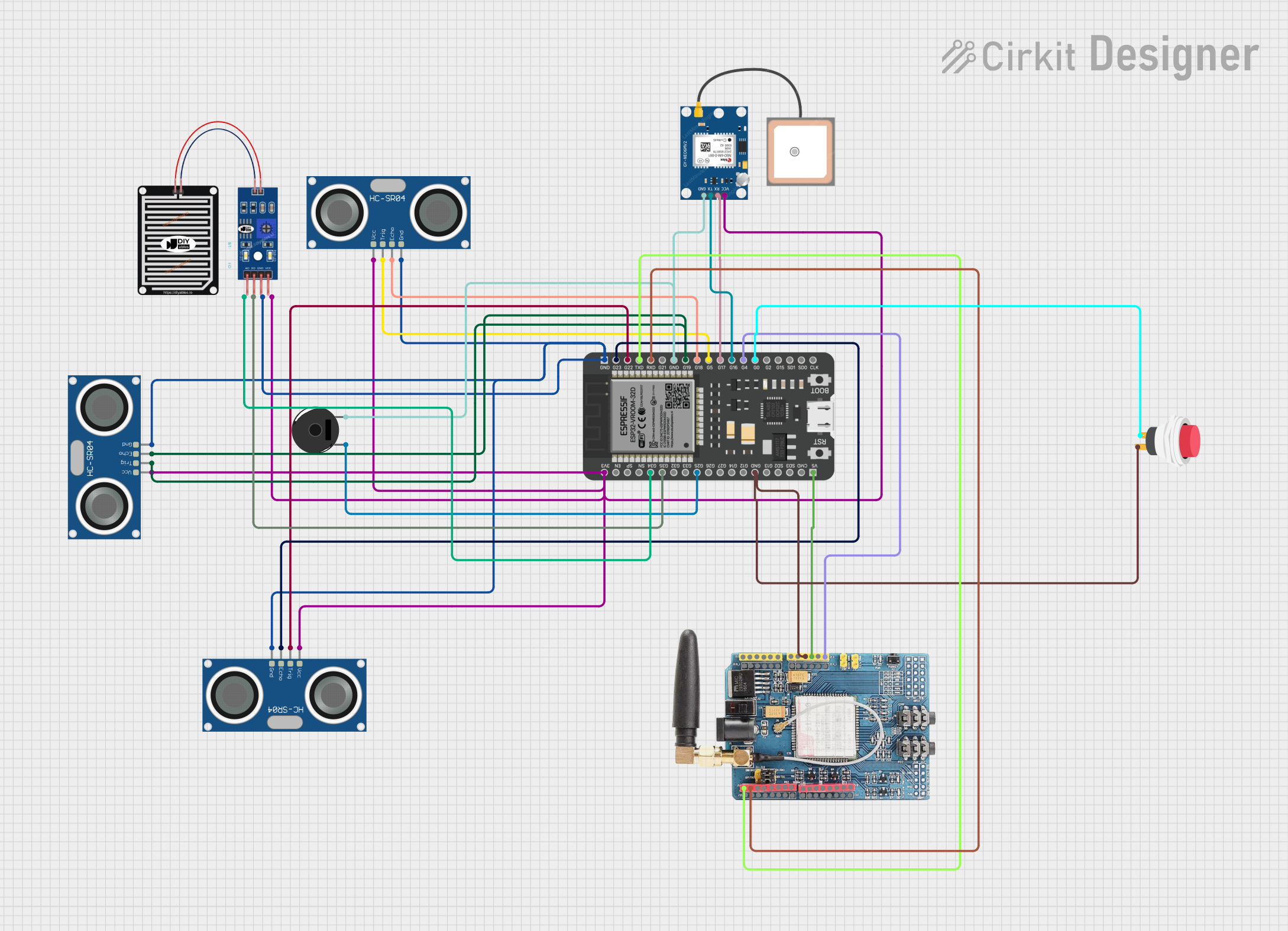
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer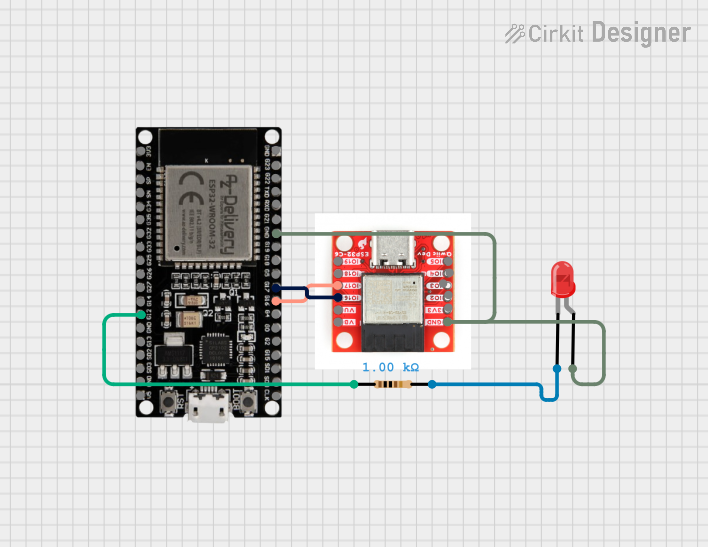
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer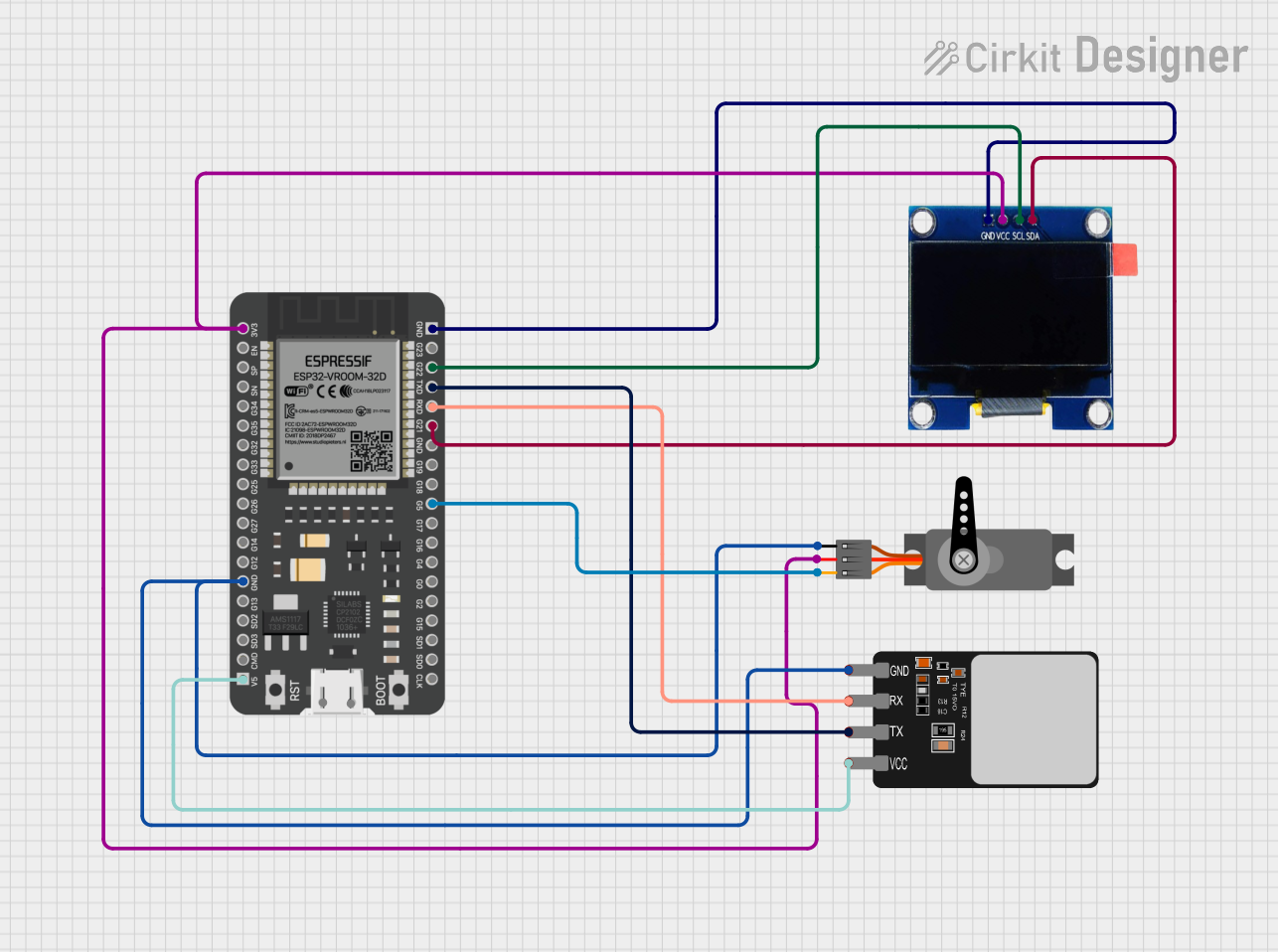
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32 - 38 pins

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smart Home Devices (e.g., smart lights, thermostats)
- Wearable Electronics
- Wireless Sensor Networks
- IoT Prototyping
- Robotics
- DIY Projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: Tensilica Xtensa LX6 dual-core processor
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage (recommended): 5V
- Input Voltage (limit): 6-12V
- Digital I/O Pins: 34 (GPIOs)
- Analog Input Pins: 18 (ADC channels)
- Analog Output Pins: 2 (DAC channels)
- Flash Memory: 4MB
- SRAM: 520 KB
- Clock Speed: 240MHz
- Wi-Fi: 802.11 b/g/n
- Bluetooth: v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V Power Supply |
| 4-5 | EN | Chip Enable. Active high. |
| 6-7 | VP, VN | ADC0, ADC1 - Sensor Voltage Pins |
| 8-21 | GPIO1 - GPIO14 | General Purpose Input/Output Pins |
| 22-23 | TX0, RX0 | UART0 - Serial Communication Pins |
| 24-25 | GPIO15, GPIO2 | Additional GPIOs |
| 26-27 | TX2, RX2 | UART2 - Additional Serial Communication Pins |
| 28-29 | GPIO4, GPIO0 | Additional GPIOs |
| 30-31 | GPIO16, GPIO17 | Additional GPIOs |
| 32-33 | GPIO5, GPIO18 | Additional GPIOs |
| 34-35 | GPIO19, GPIO21 | Additional GPIOs |
| 36-37 | GPIO3, GPIO1 | Additional GPIOs |
| 38 | VIN | Input Voltage for Battery or External Power |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the ESP32:
- Connect the 3V3 pin to a 3.3V supply, or VIN to a 5V supply.
- Ensure that the ground pins (GND) are connected to the common ground of your circuit.
Programming the ESP32:
- Use a micro USB cable to connect the ESP32 to your computer.
- Select the appropriate board and port in the Arduino IDE.
Interfacing with Peripherals:
- Connect sensors or actuators to the GPIO pins.
- Use the ADC pins for analog input and DAC pins for analog output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Do not exceed the recommended voltage levels on any pin to prevent damage.
- GPIO pins can be configured as input or output, with various pull-up/pull-down options.
- Some pins have specific functions (e.g., bootstrapping pins) that should be considered during design.
- Ensure that the antenna area is clear of metal components to avoid signal interference.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
#include <WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "your_SSID";
const char* password = "your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Connect to Wi-Fi
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi...");
}
Serial.println("Connected to WiFi");
}
void loop() {
// Put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Failure to Connect to Wi-Fi:
- Ensure the SSID and password are correct.
- Check the signal strength and distance from the router.
ESP32 Not Recognized by Computer:
- Install the CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers.
- Try a different USB cable or port.
Unexpected Resets or Behavior:
- Check for adequate power supply and stable voltage.
- Ensure that GPIO pins are not overloaded.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use serial output to debug and track down issues in your code.
- Make sure to have the latest version of the ESP32 board definitions installed in the Arduino IDE.
- Consult the ESP32 datasheet for detailed information on pin functions and limitations.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the ESP32 with a battery? A: Yes, you can power the ESP32 with a battery connected to the VIN pin.
Q: How do I put the ESP32 into deep sleep mode?
A: Use the esp_deep_sleep_start() function after configuring the wake-up source.
Q: Is it possible to use Bluetooth and Wi-Fi simultaneously? A: Yes, the ESP32 can use both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi at the same time, but it may affect performance.
Q: What is the maximum current that GPIO pins can source/sink? A: Each GPIO can source or sink up to 12 mA.
Q: How can I update the firmware on the ESP32? A: Firmware can be updated using the esptool.py utility or through the Arduino IDE.