
How to Use Single Channel Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
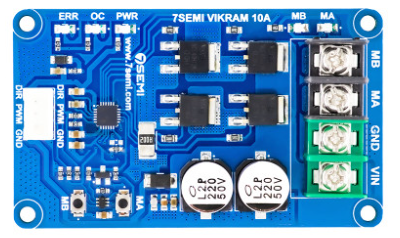
 Design with Single Channel Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with Single Channel Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Single Channel Motor Driver is a versatile electronic component designed to control the direction and speed of a single DC motor. By regulating the voltage and current supplied to the motor, this device enables precise motor control, making it an essential component in robotics, automation, and other motor-driven applications.
Explore Projects Built with Single Channel Motor Driver
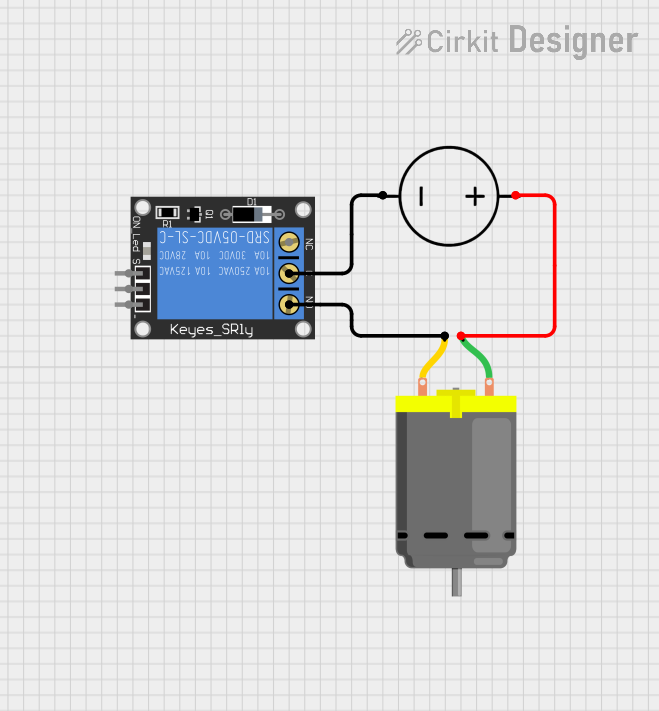
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer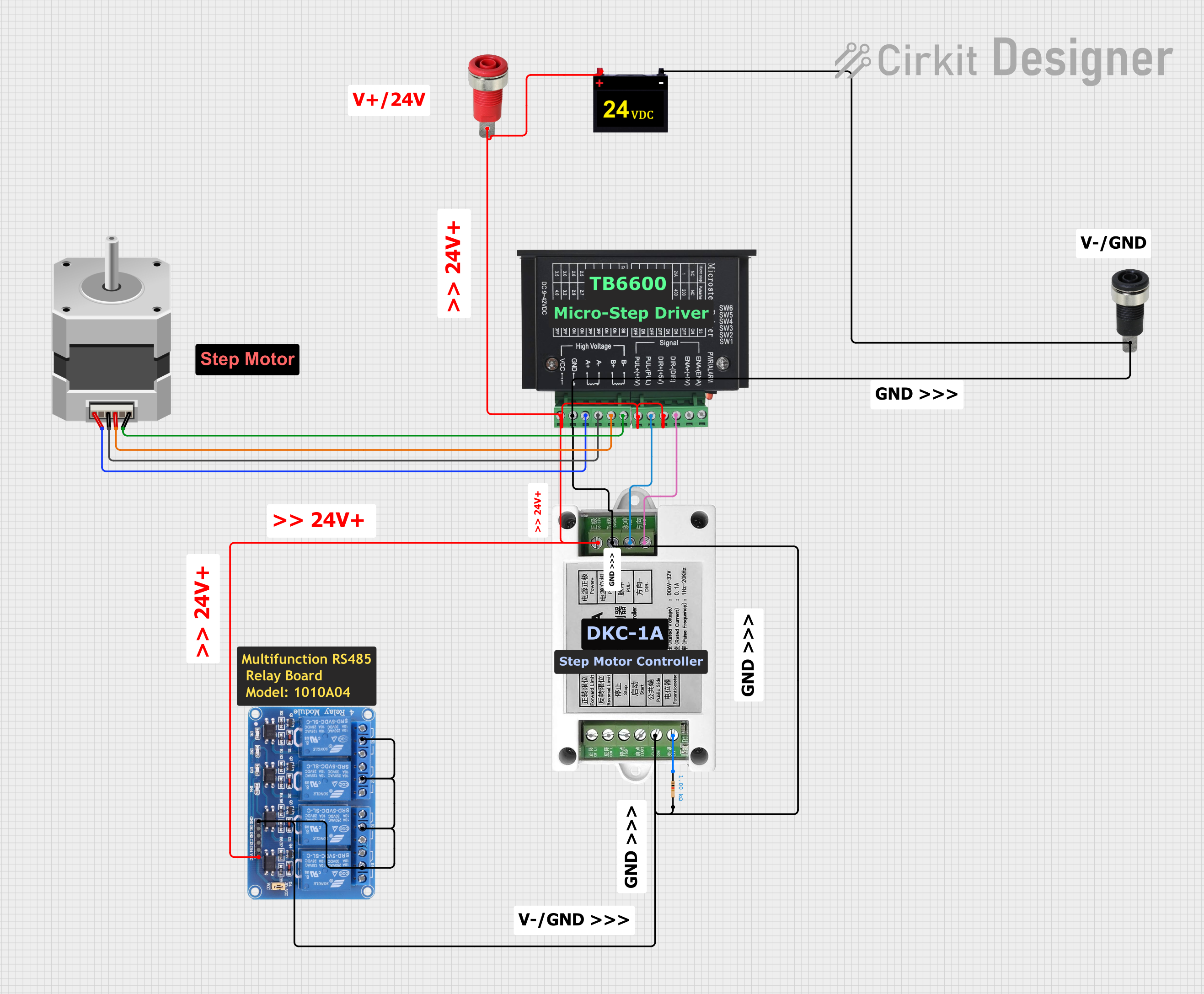
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer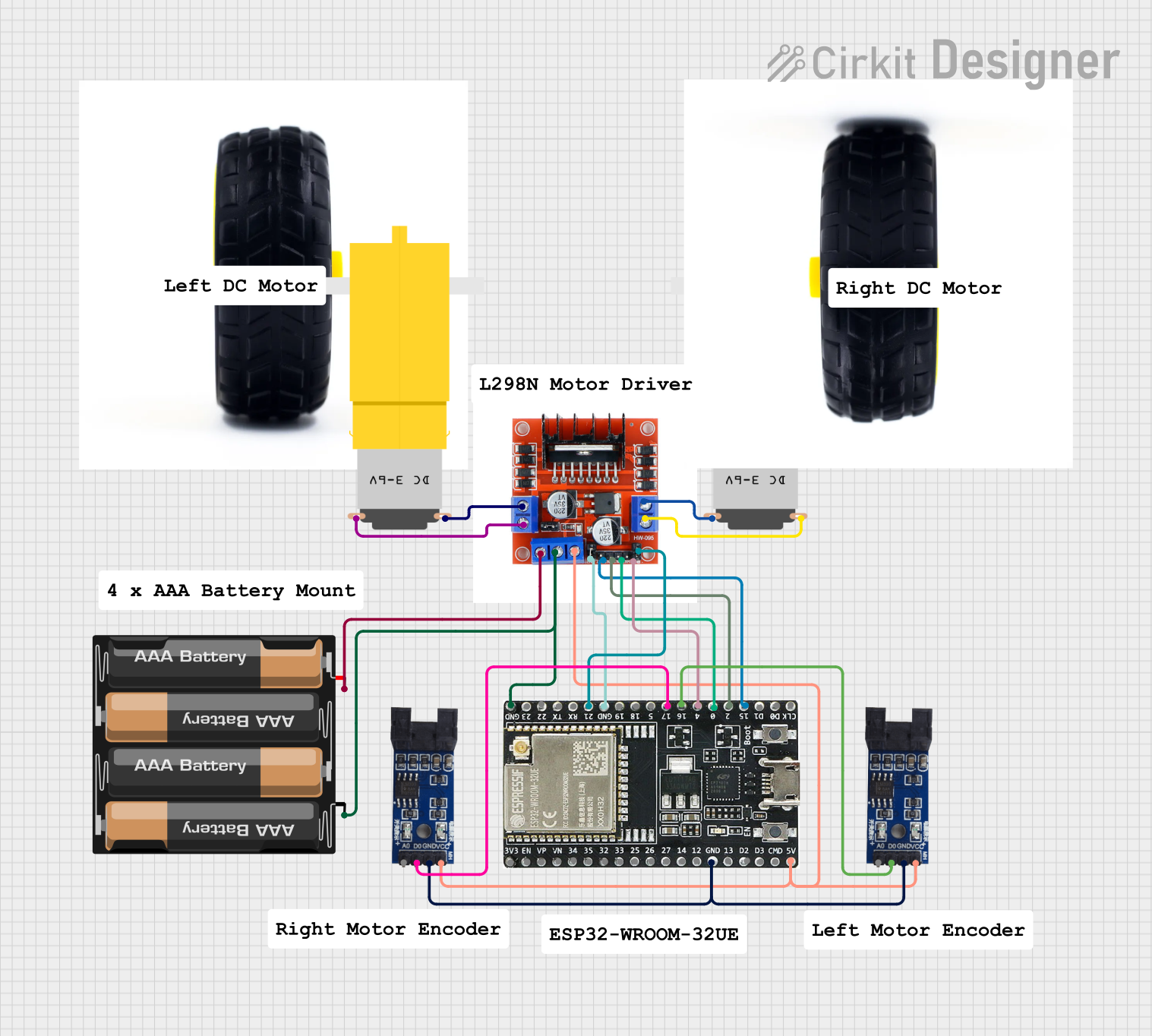
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Single Channel Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Controlling wheels or robotic arms
- Automation systems: Conveyor belts, fans, or pumps
- Remote-controlled vehicles
- DIY electronics projects involving DC motors
- Educational projects for learning motor control
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical Single Channel Motor Driver. Specifications may vary slightly depending on the specific model.
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 5V to 30V (varies by model)
- Output Current: Up to 2A (continuous), 3A (peak)
- Control Logic Voltage: 3.3V or 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- PWM Frequency: Up to 20 kHz
- Motor Type Supported: Brushed DC motors
- Protection Features: Overcurrent, thermal shutdown, and reverse polarity protection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Single Channel Motor Driver typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input for the motor driver (5V to 30V). |
| GND | Ground connection. |
| IN1 | Input pin to control motor direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
| IN2 | Input pin to control motor direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
| EN (Enable) | PWM input to control motor speed (connect to a PWM-capable pin on a microcontroller). |
| OUT1 | Output pin connected to one terminal of the motor. |
| OUT2 | Output pin connected to the other terminal of the motor. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a power source that matches the motor's voltage requirements. Ensure the GND pin is connected to the ground of the power source and the microcontroller.
- Motor Connections: Connect the motor terminals to the OUT1 and OUT2 pins.
- Control Pins:
- Use the IN1 and IN2 pins to set the motor's direction:
- IN1 = HIGH, IN2 = LOW: Motor rotates in one direction.
- IN1 = LOW, IN2 = HIGH: Motor rotates in the opposite direction.
- IN1 = LOW, IN2 = LOW: Motor stops.
- Use the EN pin to control the motor's speed by providing a PWM signal from a microcontroller.
- Use the IN1 and IN2 pins to set the motor's direction:
- Microcontroller Integration: Connect the control pins (IN1, IN2, and EN) to the appropriate GPIO pins on your microcontroller.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the motor's requirements and does not exceed the driver's maximum voltage rating.
- Heat Dissipation: If the motor driver gets hot during operation, consider adding a heat sink or improving ventilation.
- Current Limits: Do not exceed the driver's maximum current rating to avoid damage.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Add capacitors near the VCC and GND pins to reduce noise and voltage spikes.
Example: Using with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a DC motor using a Single Channel Motor Driver and an Arduino UNO.
// Define motor driver pins
const int IN1 = 9; // Motor direction control pin 1
const int IN2 = 8; // Motor direction control pin 2
const int EN = 10; // Motor speed control (PWM) pin
void setup() {
// Set motor driver pins as outputs
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(EN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction at 50% speed
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 HIGH
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(EN, 128); // Set speed to 50% (128 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(EN, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction at full speed
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); // Set IN2 HIGH
analogWrite(EN, 255); // Set speed to 100% (255 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(EN, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Spinning:
- Check the power supply connections and ensure the voltage matches the motor's requirements.
- Verify that the IN1, IN2, and EN pins are receiving the correct signals from the microcontroller.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Swap the connections of the motor terminals to OUT1 and OUT2, or adjust the logic levels on IN1 and IN2.
Motor Driver Overheating:
- Ensure the motor's current draw does not exceed the driver's maximum current rating.
- Add a heat sink or improve ventilation around the driver.
PWM Signal Not Controlling Speed:
- Confirm that the EN pin is connected to a PWM-capable pin on the microcontroller.
- Check the PWM frequency and duty cycle settings in your code.
FAQs
Can I use this driver with a stepper motor? No, this driver is designed for brushed DC motors. Use a dedicated stepper motor driver for stepper motors.
What happens if I reverse the power supply polarity? Most motor drivers include reverse polarity protection, but it is best to double-check the datasheet for your specific model.
Can I control the motor without a microcontroller? Yes, you can use manual switches or a potentiometer to control the IN1, IN2, and EN pins, but a microcontroller provides more precise control.
This concludes the documentation for the Single Channel Motor Driver.