
How to Use TP4057 1A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
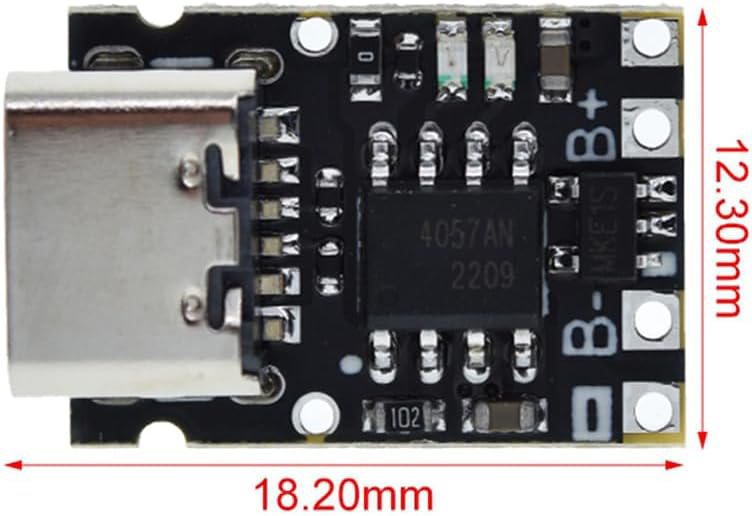
 Design with TP4057 1A in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4057 1A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4057 is a highly integrated lithium-ion battery charger IC designed to provide a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile. It is capable of charging single-cell lithium-ion batteries with a maximum charging current of 1A. The TP4057 is a compact and efficient solution for battery charging applications, requiring minimal external components. Its built-in safety features, such as thermal regulation and overvoltage protection, make it a reliable choice for portable electronics.
Explore Projects Built with TP4057 1A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer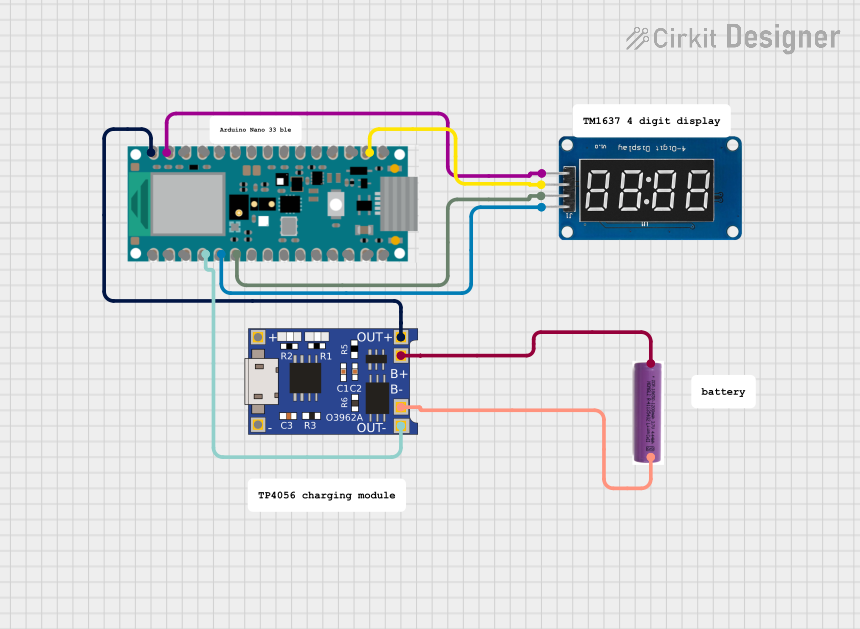
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer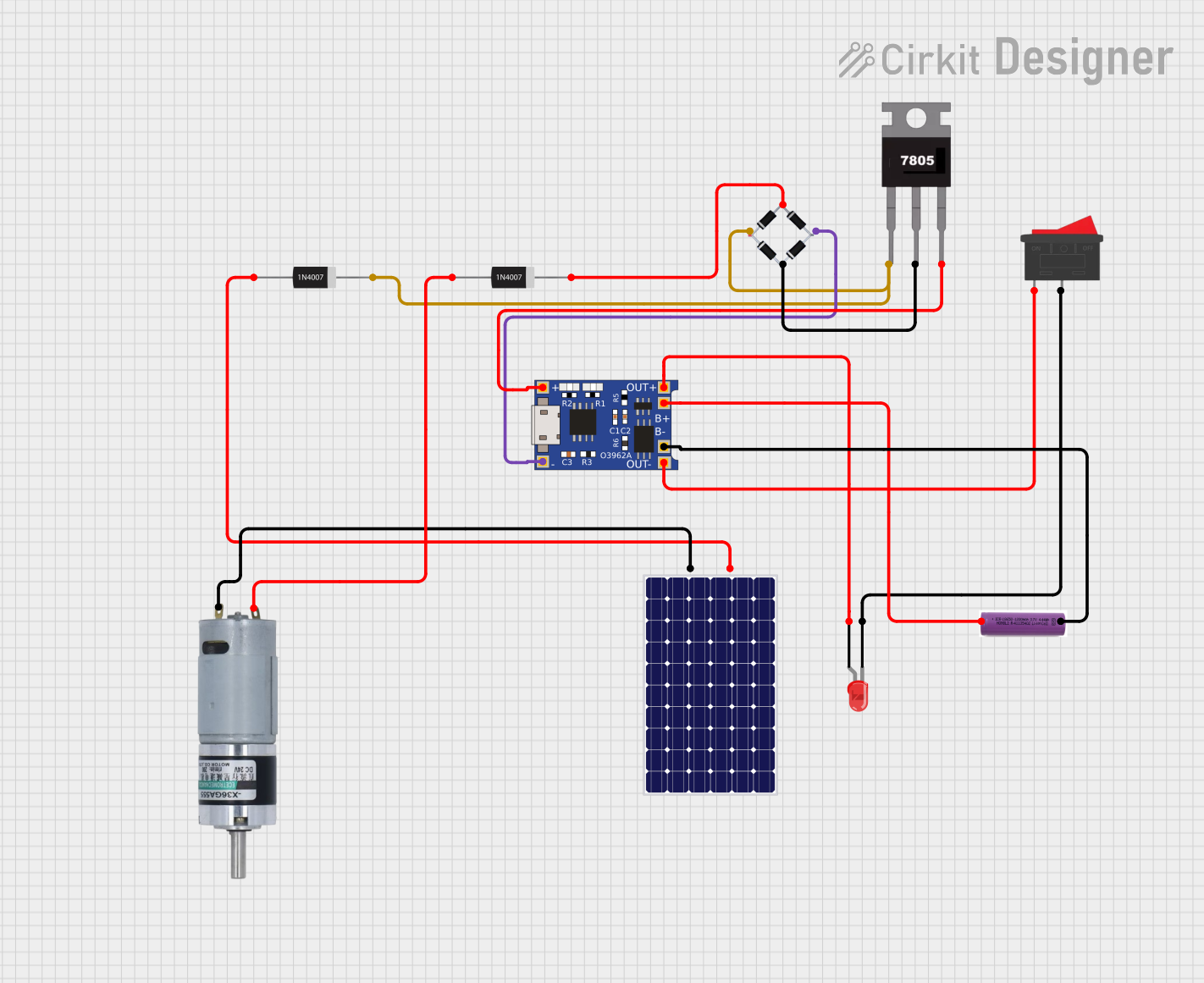
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4057 1A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Smartphones and tablets
- Wearable devices
- Power banks
- Portable medical equipment
- Wireless peripherals (e.g., headphones, mice, keyboards)
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.0V to 8.0V |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A |
| Standby Current | < 25µA |
| Thermal Regulation | 120°C (typical) |
| Battery Overvoltage Limit | 4.35V |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | SOT-23-5 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4057 is typically available in a 5-pin SOT-23 package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BAT | Battery connection pin. Connect directly to the positive terminal of the battery. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the system ground. |
| 3 | VCC | Input supply voltage. Connect to a DC source (4.0V to 8.0V). |
| 4 | PROG | Programming pin. Connect a resistor to set the charging current. |
| 5 | STAT | Status indicator pin. Open-drain output for charging status (e.g., LED). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4057 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a DC power source with a voltage between 4.0V and 8.0V. Ensure the power source can supply sufficient current for the charging process.
- Battery Connection: Connect the BAT pin directly to the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery. The negative terminal of the battery should be connected to GND.
- Programming Charging Current: Use a resistor (RPROG) connected between the PROG pin and GND to set the charging current. The charging current (ICHG) can be calculated using the formula: [ I_{CHG} = \frac{1000}{R_{PROG}} ] For example, to set a charging current of 1A, use a 1kΩ resistor.
- Status Indicator: Connect an LED with a current-limiting resistor to the STAT pin to monitor the charging status:
- LED ON: Charging in progress.
- LED OFF: Charging complete or no battery connected.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Thermal Management: Ensure proper heat dissipation, as the TP4057 regulates its charging current to prevent overheating.
- Input Voltage: Avoid exceeding the maximum input voltage of 8.0V to prevent damage to the IC.
- Battery Safety: Use the TP4057 only with single-cell lithium-ion batteries. Do not use it for multi-cell configurations.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place a 1µF ceramic capacitor close to the VCC pin to stabilize the input voltage and reduce noise.
Example: Using TP4057 with Arduino UNO
The TP4057 can be used in conjunction with an Arduino UNO to monitor the charging status. Below is an example code snippet:
// TP4057 Status Monitoring with Arduino UNO
// Connect the STAT pin of TP4057 to Arduino digital pin 2
const int statPin = 2; // TP4057 STAT pin connected to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Onboard LED for status indication
void setup() {
pinMode(statPin, INPUT); // Set STAT pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set onboard LED as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int chargingStatus = digitalRead(statPin); // Read the STAT pin
if (chargingStatus == LOW) {
// Charging in progress (STAT pin LOW)
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on onboard LED
Serial.println("Battery is charging...");
} else {
// Charging complete or no battery connected (STAT pin HIGH)
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off onboard LED
Serial.println("Charging complete or no battery connected.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Charging Current Detected
- Cause: Incorrect RPROG resistor value or poor connection.
- Solution: Verify the RPROG resistor value and ensure proper connections.
Overheating of the IC
- Cause: Insufficient heat dissipation or high ambient temperature.
- Solution: Improve thermal management by adding a heatsink or increasing airflow.
STAT Pin Not Functioning
- Cause: Faulty connection or damaged IC.
- Solution: Check the wiring and replace the IC if necessary.
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Input voltage too low or battery voltage too high.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the 4.0V to 8.0V range and the battery voltage is below 4.2V.
FAQs
Q1: Can the TP4057 charge batteries with capacities greater than 1000mAh?
A1: Yes, the TP4057 can charge larger capacity batteries, but the charging current should not exceed 1A. Adjust the RPROG resistor accordingly.
Q2: Is it safe to leave the battery connected to the TP4057 after charging is complete?
A2: Yes, the TP4057 automatically terminates charging and enters a low-power standby mode when the battery is fully charged.
Q3: Can I use the TP4057 with a solar panel as the input source?
A3: Yes, as long as the solar panel provides a stable voltage within the 4.0V to 8.0V range. Use a capacitor to stabilize the input voltage.
Q4: What happens if the input voltage exceeds 8.0V?
A4: Exceeding 8.0V can damage the IC. Use a voltage regulator or zener diode to protect the TP4057.