
How to Use PowerBoost 1000 Basic Pad Terminal: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
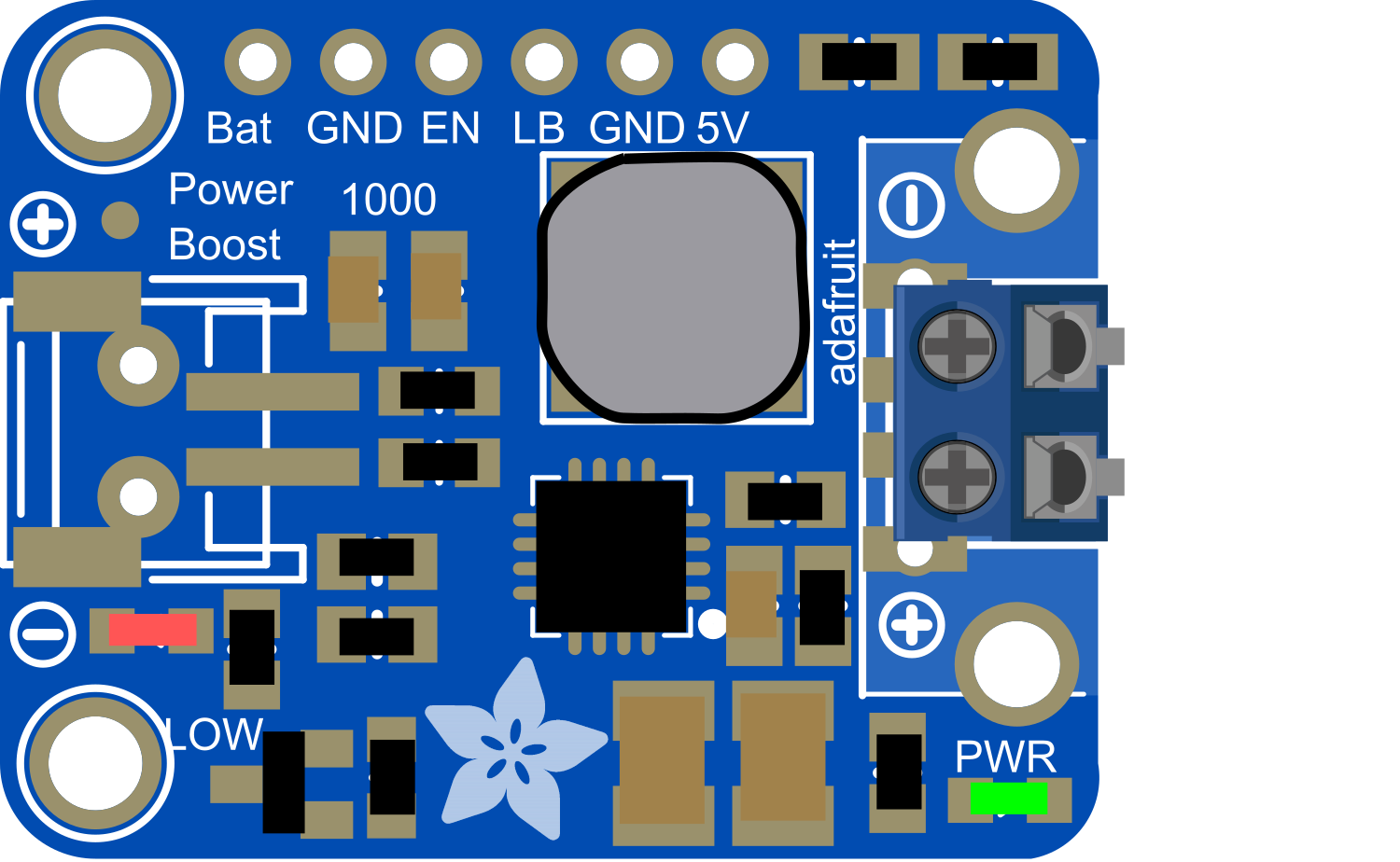
 Design with PowerBoost 1000 Basic Pad Terminal in Cirkit Designer
Design with PowerBoost 1000 Basic Pad Terminal in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PowerBoost 1000 Basic is a versatile and efficient power supply module designed to provide a stable 5V output from a single lithium polymer (LiPo) battery. It is an ideal solution for portable electronics, wearables, and projects that require a rechargeable power source. With its built-in charging circuit, users can easily recharge the battery without the need for a separate charger. The pad terminals on the PowerBoost 1000 Basic facilitate easy soldering, making it a convenient choice for DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with PowerBoost 1000 Basic Pad Terminal

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer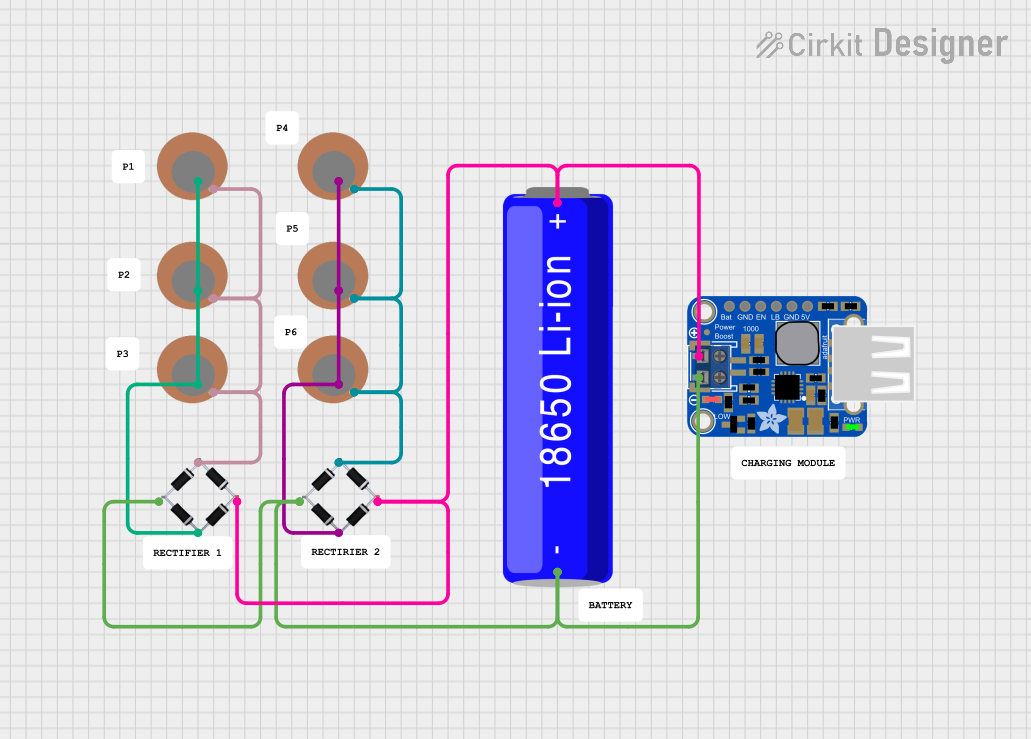
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer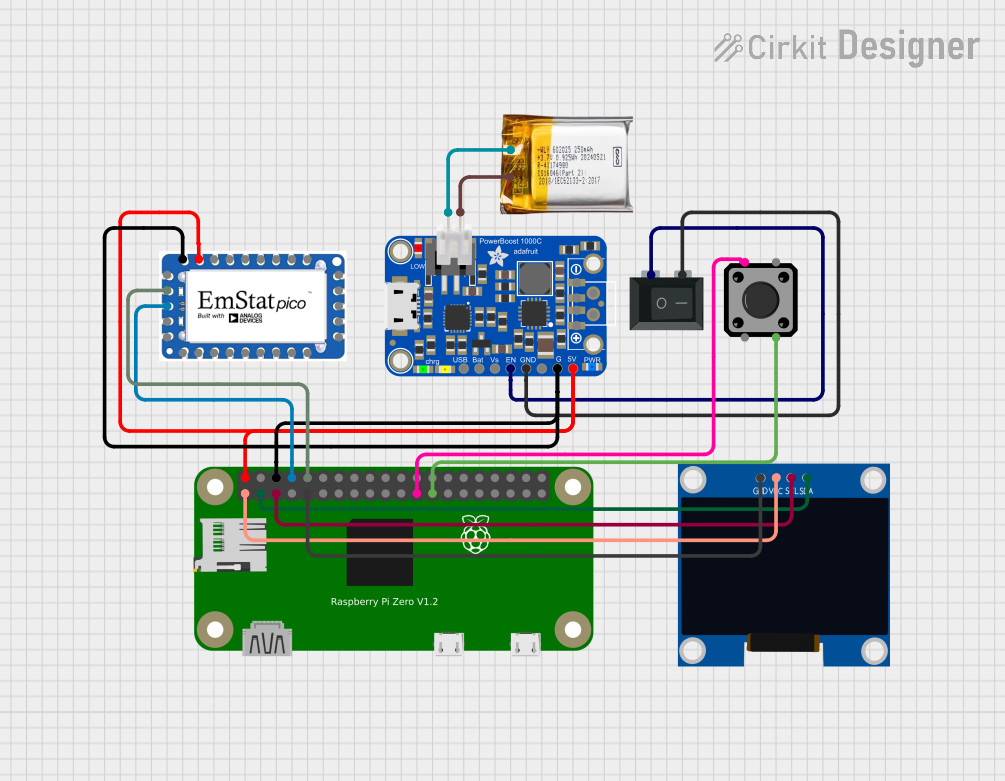
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer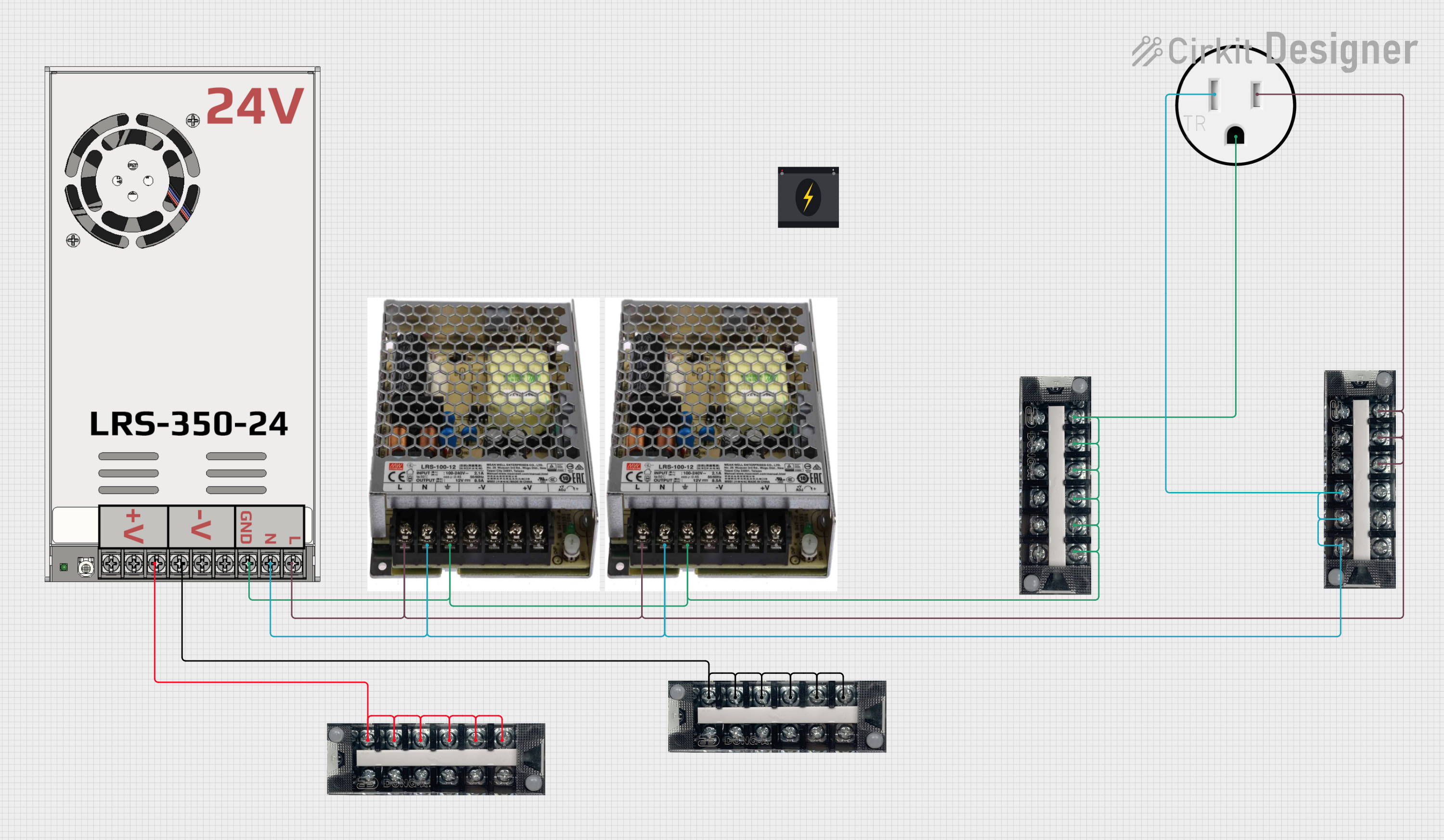
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PowerBoost 1000 Basic Pad Terminal

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Portable USB chargers
- Wearable electronics
- Battery-powered Raspberry Pi projects
- Mobile robotics
- DIY electronics projects requiring a 5V power supply
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage: 3.7V nominal (LiPo battery)
- Output Voltage: 5V regulated output
- Maximum Output Current: 1A
- Charging Current: Up to 1000mA
- Efficiency: 90% typical at full load
- Low Battery Indicator: Yes
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BAT | Battery input terminal for LiPo battery connection |
| GND | Ground connection |
| 5V | Regulated 5V output |
| EN | Enable pin for turning the module on/off |
| USB | USB power output, can be used to charge devices |
| LBO | Low Battery Output, goes low when the battery is low |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Solder the positive terminal of the LiPo battery to the
BATpad. - Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the
GNDpad.
- Solder the positive terminal of the LiPo battery to the
Drawing Power:
- Connect your device's power input to the
5VandGNDpads for a regulated 5V supply.
- Connect your device's power input to the
Charging the Battery:
- Connect a 5V source to the
USBpad to charge the connected LiPo battery.
- Connect a 5V source to the
Enabling/Disabling Power Output:
- Connect the
ENpad toGNDto disable the 5V output. - Leave the
ENpad floating to enable the 5V output.
- Connect the
Monitoring Battery Status:
- Connect an LED or a digital input of a microcontroller to the
LBOpad to monitor the battery status.
- Connect an LED or a digital input of a microcontroller to the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the LiPo battery voltage does not exceed the module's input voltage range.
- Do not short-circuit the output terminals.
- Avoid placing the module in a high-temperature environment to prevent overheating.
- When soldering, be careful not to overheat the pad terminals.
- Always disconnect the battery when not in use to prevent over-discharge.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Output Voltage:
- Check if the battery is charged and properly connected.
- Ensure the
ENpad is not inadvertently connected toGND.
Battery Not Charging:
- Verify that the 5V source is connected to the
USBpad and is supplying power. - Check for any loose connections or cold solder joints.
- Verify that the 5V source is connected to the
Low Battery Indicator Always On:
- Ensure the battery is fully charged.
- If the issue persists, the battery may be damaged and need replacement.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check all connections and solder joints for continuity.
- Use a multimeter to verify the input and output voltages.
- If the module becomes hot, disconnect it immediately and check for any issues with the circuit or battery.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the PowerBoost 1000 Basic to power a Raspberry Pi? A: Yes, the PowerBoost 1000 Basic can power a Raspberry Pi as it provides a stable 5V output.
Q: How do I know when the battery is fully charged? A: The module does not have a dedicated charge indicator. You will need to monitor the battery voltage or use an external charging indicator circuit.
Q: Is it possible to increase the charging current? A: The charging current is set to a maximum of 1000mA and should not be increased to ensure the safety and longevity of the battery.
Q: Can I use the PowerBoost 1000 Basic with batteries other than LiPo? A: The PowerBoost 1000 Basic is specifically designed for LiPo batteries. Using other types of batteries is not recommended and may damage the module.
For any further assistance or technical support, please contact the manufacturer or visit the official product forum.