
How to Use Pmod MicroSD (SDIO): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
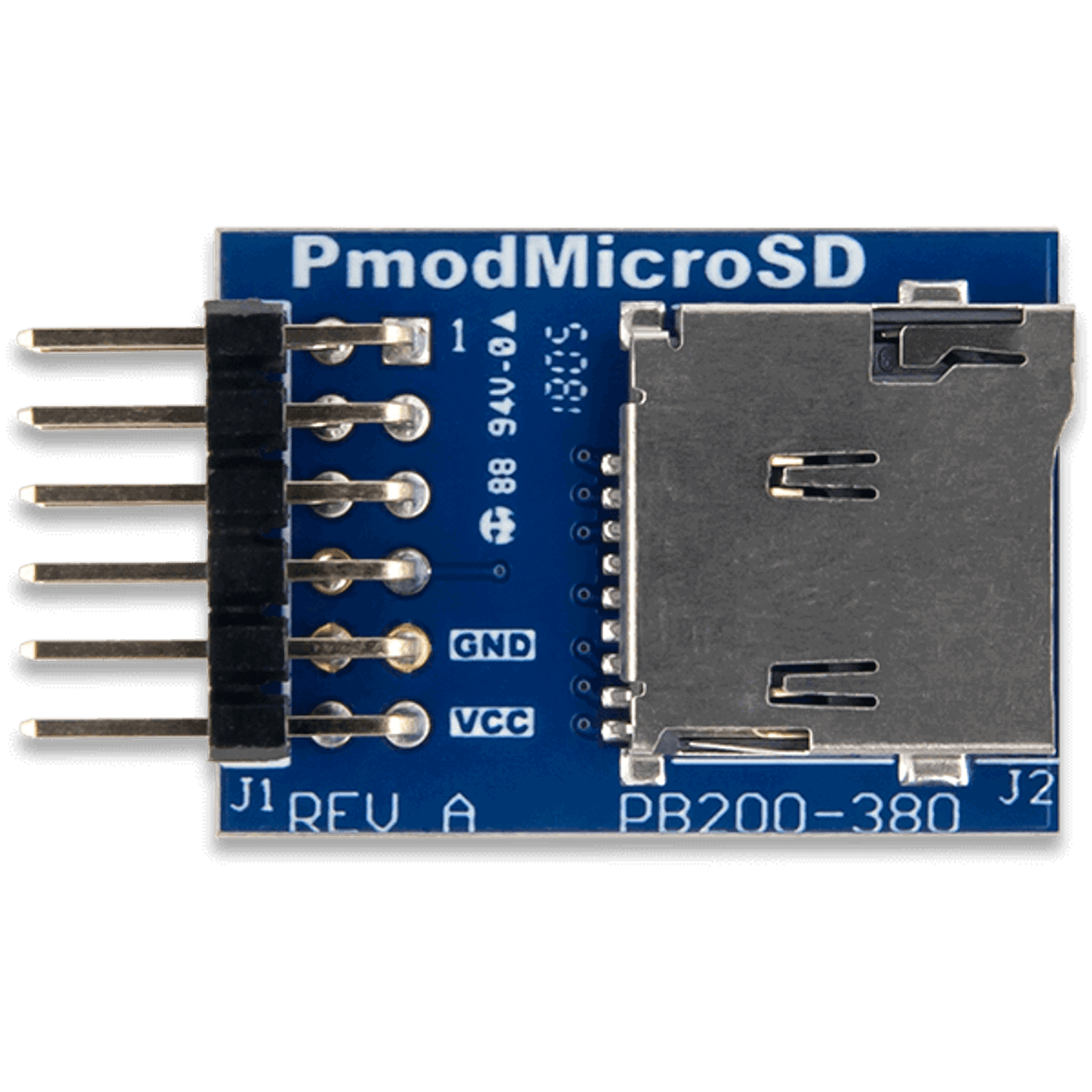
 Design with Pmod MicroSD (SDIO) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pmod MicroSD (SDIO) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Pmod MicroSD (SDIO), manufactured by Digilent (Part ID: 1286-1200-ND), is a versatile Pmod interface module designed to enable the connection of a MicroSD card to embedded systems. It utilizes the SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) protocol for high-speed data storage and retrieval, making it an ideal solution for applications requiring compact and reliable data storage.
Explore Projects Built with Pmod MicroSD (SDIO)
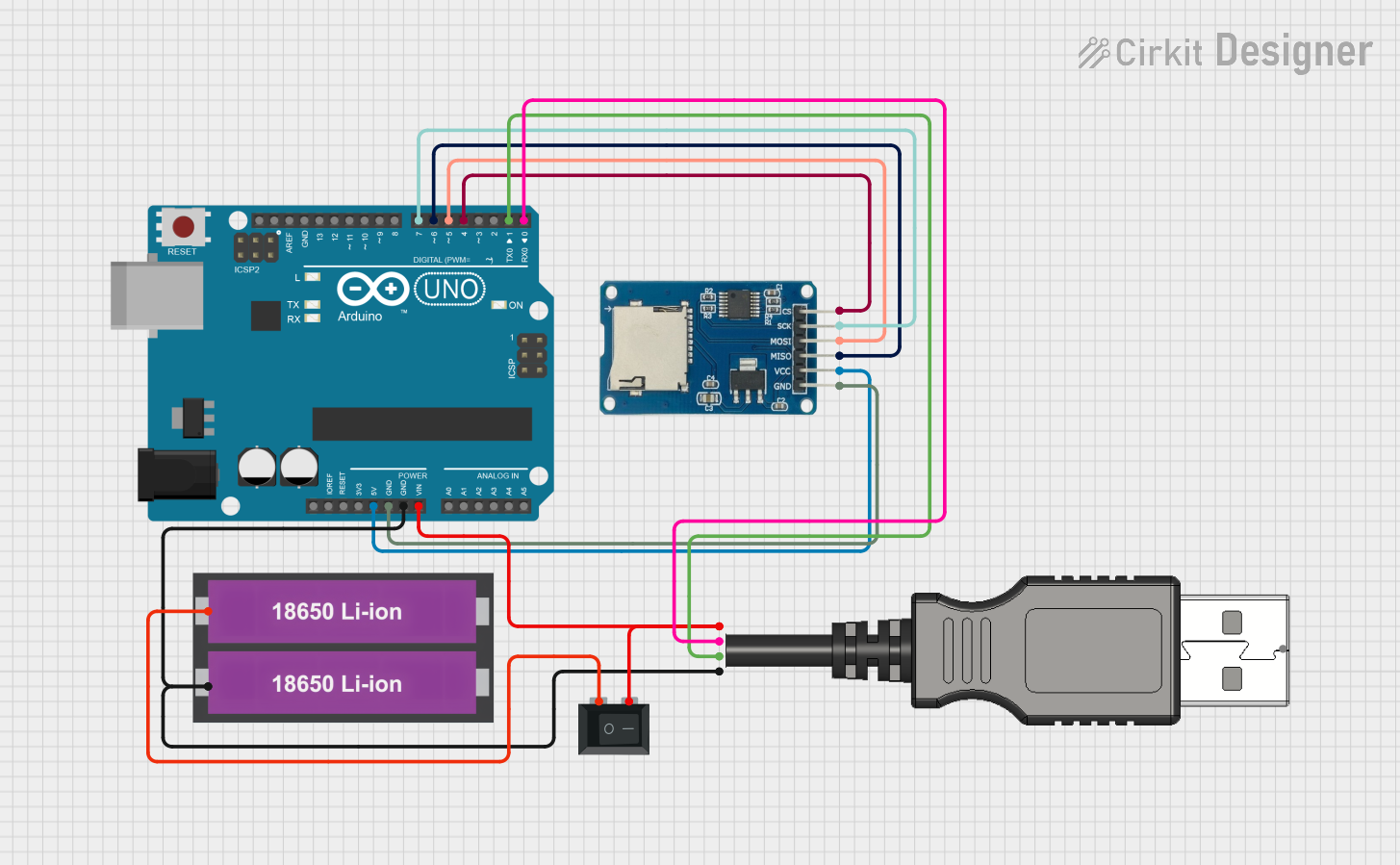
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer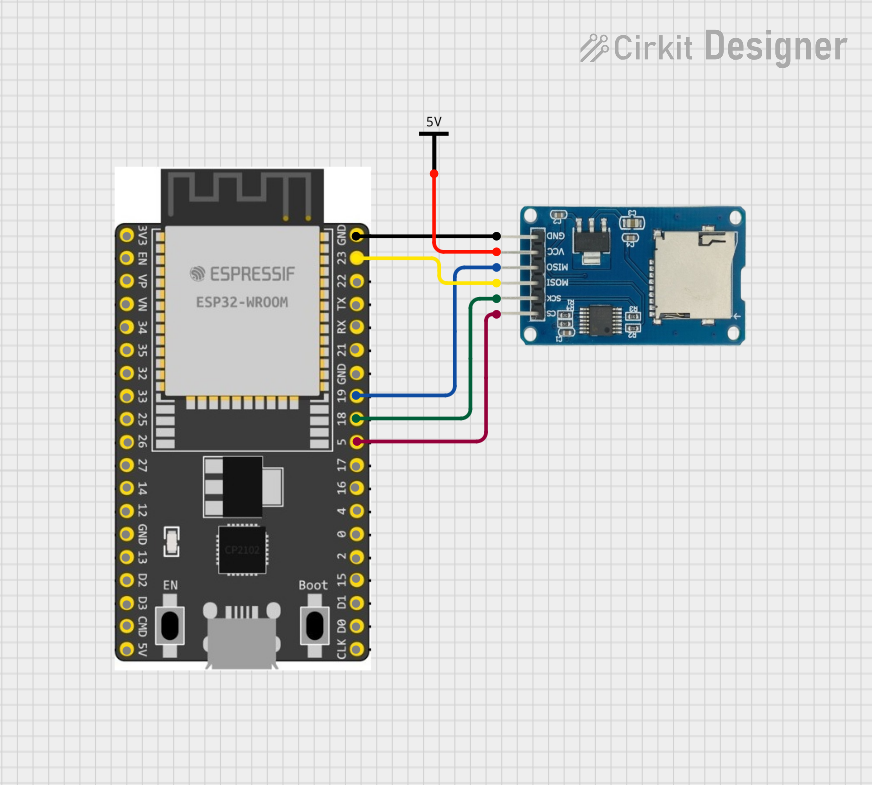
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer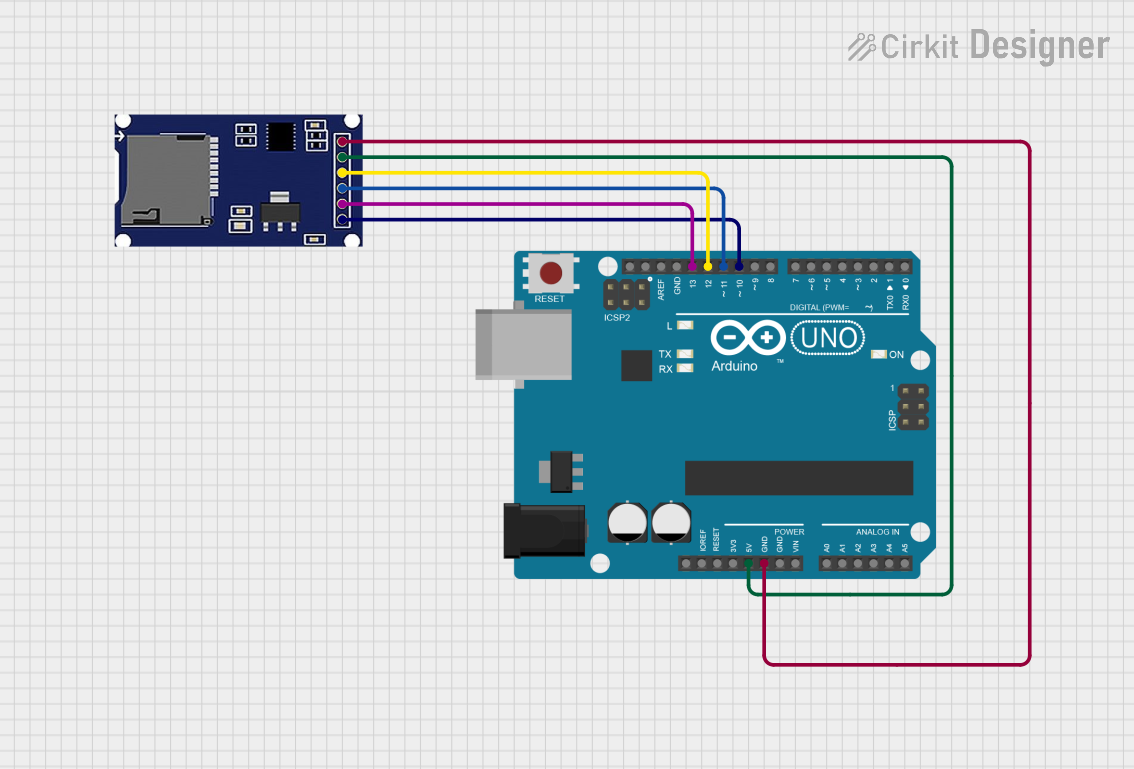
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pmod MicroSD (SDIO)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Data logging in embedded systems
- Storing configuration files or firmware updates
- Multimedia storage for audio, video, or image files
- Applications requiring portable and removable storage solutions
- Prototyping and development of SDIO-based systems
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Pmod MicroSD (SDIO):
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Interface Protocol | SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Maximum Clock Speed | 25 MHz |
| MicroSD Card Support | Standard and High-Capacity (SDHC) |
| Connector Type | 6-pin Pmod |
| Dimensions | 0.8" × 1.3" (20.32 mm × 33.02 mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Pmod MicroSD (SDIO) uses a 6-pin interface. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SD_CLK | Clock signal for SDIO communication |
| 2 | SD_CMD | Command line for SDIO communication |
| 3 | SD_DAT0 | Data line 0 (used for data transfer) |
| 4 | SD_DAT1 | Data line 1 (used in 4-bit mode) |
| 5 | SD_DAT2 | Data line 2 (used in 4-bit mode) |
| 6 | SD_DAT3 | Data line 3 (used in 4-bit mode) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Pmod MicroSD (SDIO) in a Circuit
Connect the Pmod MicroSD to a Host Controller:
- Use a 6-pin Pmod connector to interface the module with a microcontroller or FPGA.
- Ensure the host controller supports the SDIO protocol and operates at 3.3V logic levels.
Insert a MicroSD Card:
- Insert a compatible MicroSD card (standard or SDHC) into the slot on the Pmod MicroSD module.
Initialize the SDIO Interface:
- Configure the host controller to initialize the SDIO interface.
- Set the clock speed (up to 25 MHz) and ensure proper communication settings.
Read and Write Data:
- Use the SDIO protocol to send commands and transfer data to/from the MicroSD card.
- Ensure proper file system management (e.g., FAT32) for data storage and retrieval.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: The Pmod MicroSD operates at 3.3V. Ensure the host controller's I/O pins are also 3.3V compatible to avoid damage.
- Clock Speed: Do not exceed the maximum clock speed of 25 MHz to ensure reliable communication.
- File System: Format the MicroSD card with a compatible file system (e.g., FAT16 or FAT32) before use.
- ESD Protection: Handle the module and MicroSD card with care to prevent electrostatic discharge damage.
Example: Using Pmod MicroSD with Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO does not natively support SDIO but can interface with the Pmod MicroSD using SPI mode. Below is an example code snippet for interfacing the Pmod MicroSD with an Arduino UNO using the SD library:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// Define the chip select pin for the Pmod MicroSD
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // Wait for the serial port to connect
}
Serial.println("Initializing SD card...");
// Initialize the SD card
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("SD card initialization failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("SD card initialized successfully.");
// Create a test file and write data to it
File dataFile = SD.open("test.txt", FILE_WRITE);
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.println("Hello, Pmod MicroSD!");
dataFile.close();
Serial.println("Data written to test.txt.");
} else {
Serial.println("Error opening test.txt for writing.");
}
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Notes:
- Connect the Pmod MicroSD to the Arduino UNO using an SPI-to-Pmod adapter.
- Ensure the
chipSelectpin matches the wiring configuration.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
SD Card Initialization Fails:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or incompatible SD card.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the SD card is formatted with FAT16 or FAT32.
Data Corruption:
- Cause: Exceeding the maximum clock speed or improper file system handling.
- Solution: Ensure the clock speed is within the specified range and use a reliable file system library.
Module Not Detected:
- Cause: Voltage mismatch or damaged module.
- Solution: Confirm the host controller operates at 3.3V logic levels and inspect the module for physical damage.
FAQs
Q: Can the Pmod MicroSD be used with 5V logic controllers?
A: No, the Pmod MicroSD operates at 3.3V. Use a level shifter if interfacing with 5V logic controllers.
Q: What is the maximum storage capacity supported?
A: The Pmod MicroSD supports standard and SDHC cards, typically up to 32GB.
Q: Can I use the Pmod MicroSD in SPI mode?
A: Yes, the Pmod MicroSD can be used in SPI mode with appropriate configuration.
Q: How do I format the MicroSD card?
A: Use a computer or SD card formatter tool to format the card with FAT16 or FAT32.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the Pmod MicroSD (SDIO) into their embedded systems for reliable data storage and retrieval.