
How to Use GREEN LED: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with GREEN LED in Cirkit Designer
Design with GREEN LED in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A green light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits green light when an electric current flows through it. It is widely used in electronic circuits for visual indicators, status displays, and decorative lighting. Green LEDs are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and available in various sizes and brightness levels, making them a versatile component in both hobbyist and professional applications.
Explore Projects Built with GREEN LED
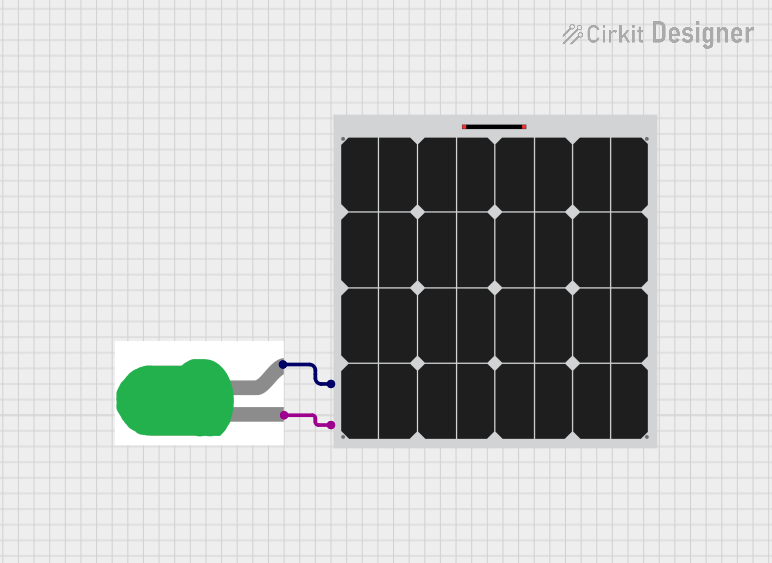
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer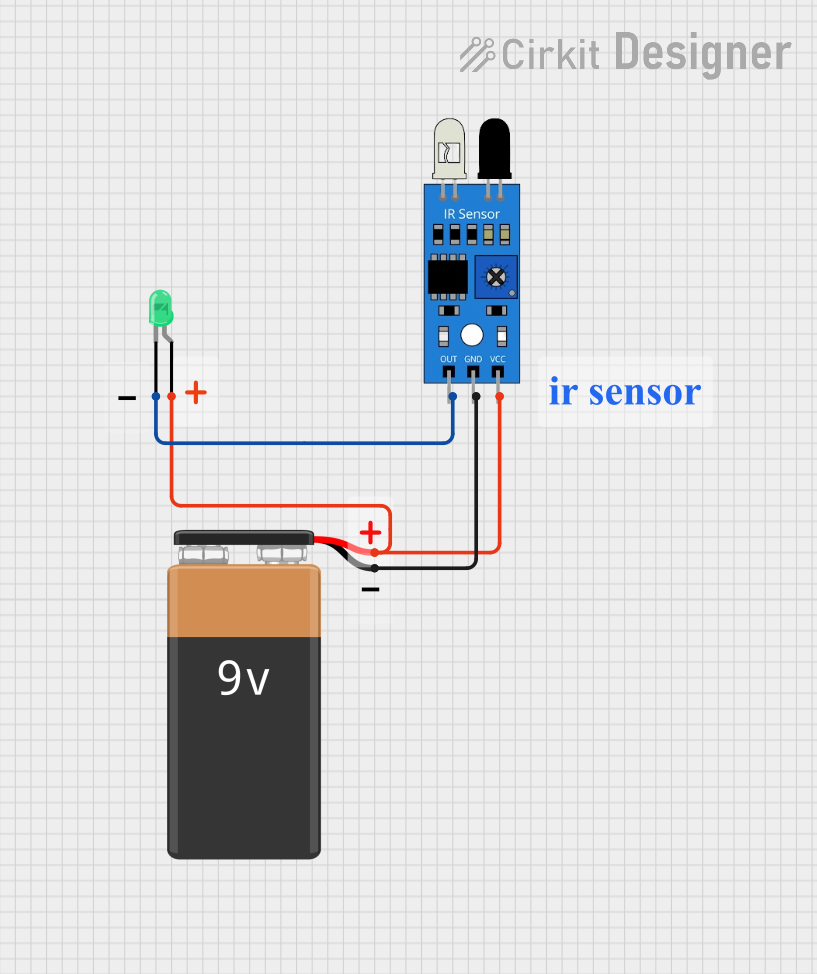
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer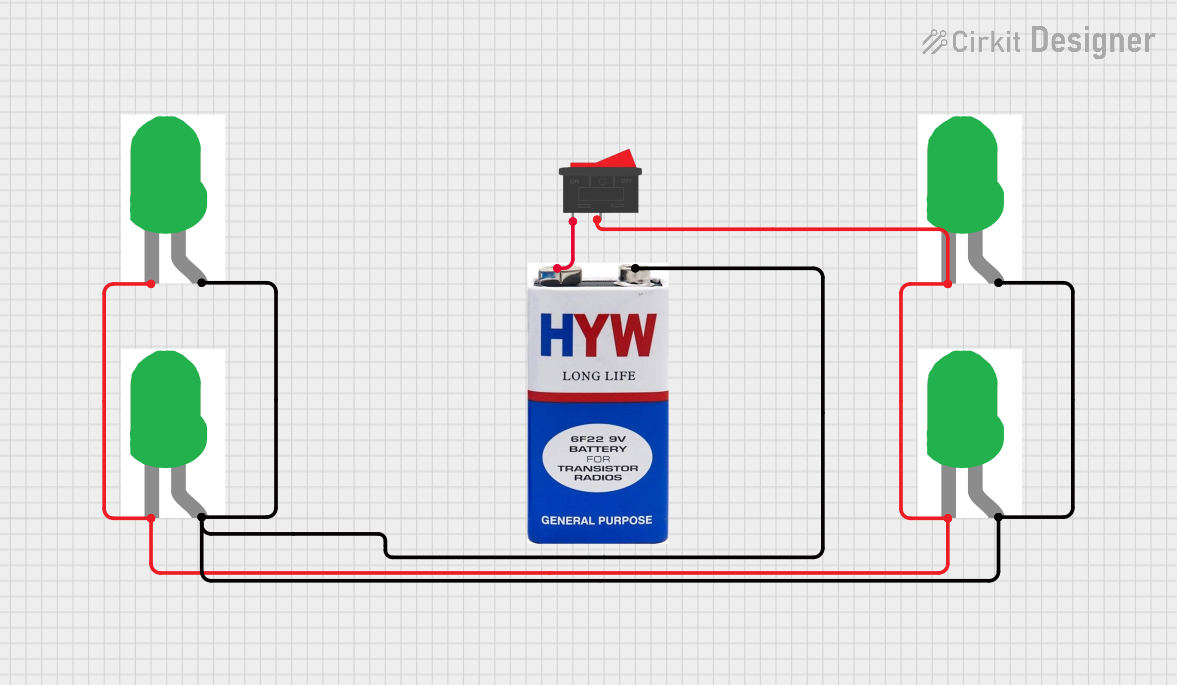
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer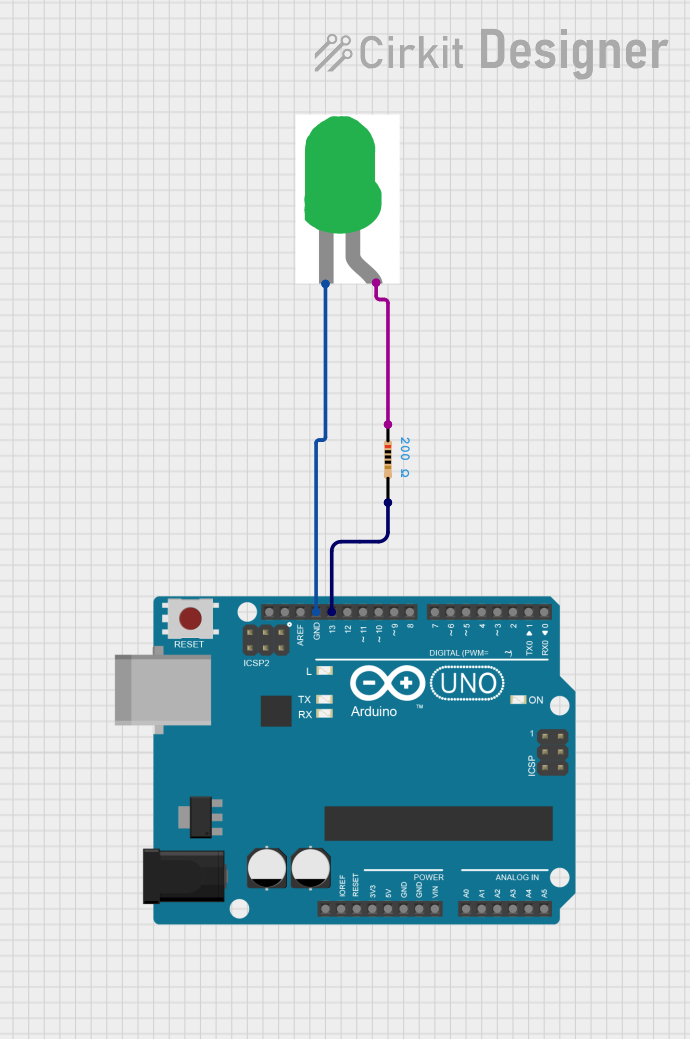
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GREEN LED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Power and status indicators in electronic devices
- Signal and warning lights
- Decorative and ambient lighting
- Displays in consumer electronics
- Prototyping and educational projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard green LED. Note that specific values may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage (Vf) | 2.0V to 3.2V |
| Forward Current (If) | 10mA to 20mA (typical) |
| Maximum Current (Imax) | 30mA |
| Wavelength | 520nm to 570nm (green light) |
| Viewing Angle | 20° to 60° |
| Power Dissipation | 60mW (typical) |
| Reverse Voltage (Vr) | 5V (maximum) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration
Green LEDs typically have two pins: the anode (positive) and the cathode (negative). The longer pin is the anode, and the shorter pin is the cathode. The cathode is also marked by a flat edge on the LED casing.
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Anode | Positive terminal (connect to +V) |
| Cathode | Negative terminal (connect to GND) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Green LED in a Circuit
Determine the Resistor Value: To prevent damage to the LED, always use a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's Law: [ R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_f}{I_f} ] Where:
- (V_{supply}) is the supply voltage
- (V_f) is the forward voltage of the LED
- (I_f) is the desired forward current (e.g., 20mA)
Connect the LED:
- Connect the anode (longer pin) to the positive voltage through the resistor.
- Connect the cathode (shorter pin) to the ground.
Power the Circuit: Apply the appropriate voltage to the circuit. The LED will emit green light when powered correctly.
Example: Connecting a Green LED to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and control a green LED using an Arduino UNO.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the anode of the LED to Arduino digital pin 9 through a 220Ω resistor.
- Connect the cathode of the LED to the GND pin of the Arduino.
Arduino Code
// Green LED Example with Arduino UNO
// This code blinks a green LED connected to pin 9 every second.
const int ledPin = 9; // Define the pin connected to the LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations
- Polarity: Ensure the LED is connected with the correct polarity. Reversing the connections may damage the LED.
- Current Limiting: Always use a resistor to limit the current through the LED. Exceeding the maximum current rating can permanently damage the LED.
- Brightness Control: Use pulse-width modulation (PWM) on a microcontroller to adjust the brightness of the LED.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
LED Does Not Light Up:
- Check the polarity of the LED. Ensure the anode is connected to the positive voltage and the cathode to ground.
- Verify the resistor value. A resistor with too high a value may prevent the LED from lighting up.
- Ensure the power supply voltage is sufficient to exceed the forward voltage of the LED.
LED is Too Dim:
- Check the resistor value. A lower resistance may increase brightness but ensure it does not exceed the maximum current rating.
- Verify the supply voltage. It should be within the operating range of the LED.
LED Burns Out Quickly:
- Ensure a current-limiting resistor is used.
- Verify that the current and voltage do not exceed the LED's maximum ratings.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect a green LED directly to a 5V power supply?
A: No, you must use a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED.
Q: How do I calculate the resistor value for a 3.3V supply?
A: Use the formula (R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_f}{I_f}). For example, with (V_{supply} = 3.3V), (V_f = 2.2V), and (I_f = 20mA):
[
R = \frac{3.3V - 2.2V}{0.02A} = 55\Omega
]
Choose the nearest standard resistor value (e.g., 56Ω).
Q: Can I use a green LED for PWM dimming?
A: Yes, green LEDs can be dimmed using pulse-width modulation (PWM) from a microcontroller or other PWM-capable devices.