
How to Use Rain Droplet: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Rain Droplet in Cirkit Designer
Design with Rain Droplet in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Rain Droplet is a small droplet of water that falls from the atmosphere. While it is a natural phenomenon, in the context of electronics, it is often simulated or detected using specialized sensors. These sensors are designed to measure precipitation levels, detect the presence of rain, or simulate weather patterns in controlled environments. Rain droplet sensors are widely used in environmental monitoring systems, agricultural automation, and weather simulation projects.
Explore Projects Built with Rain Droplet
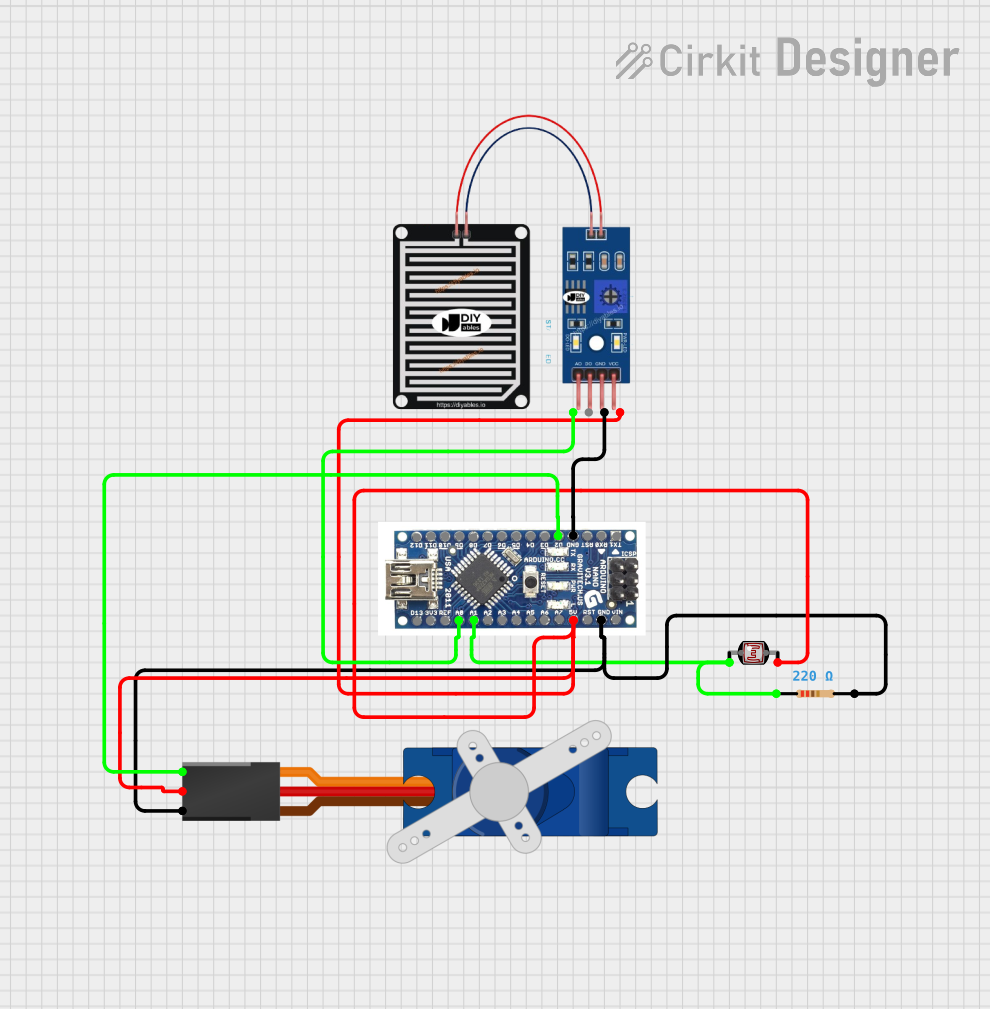
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer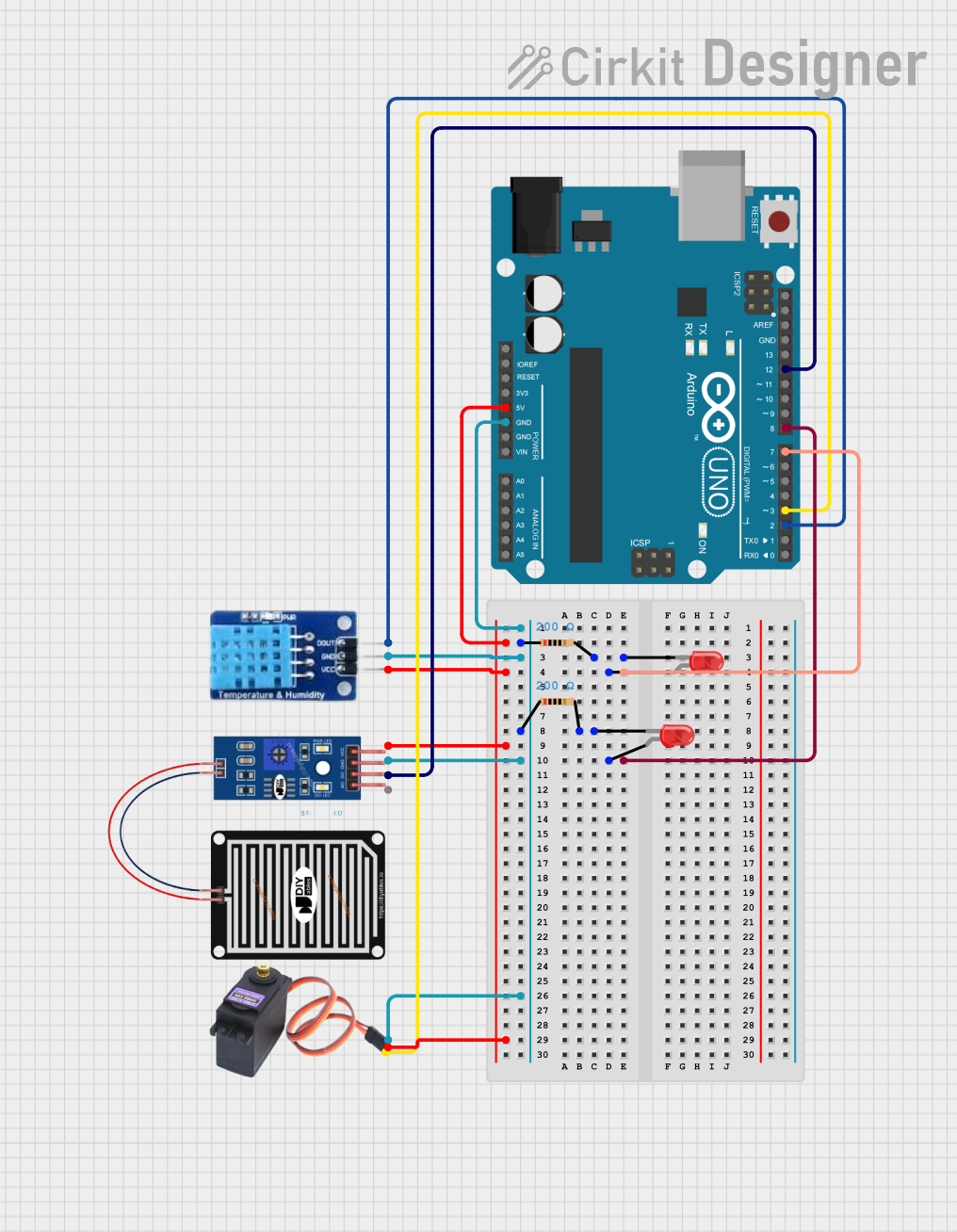
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer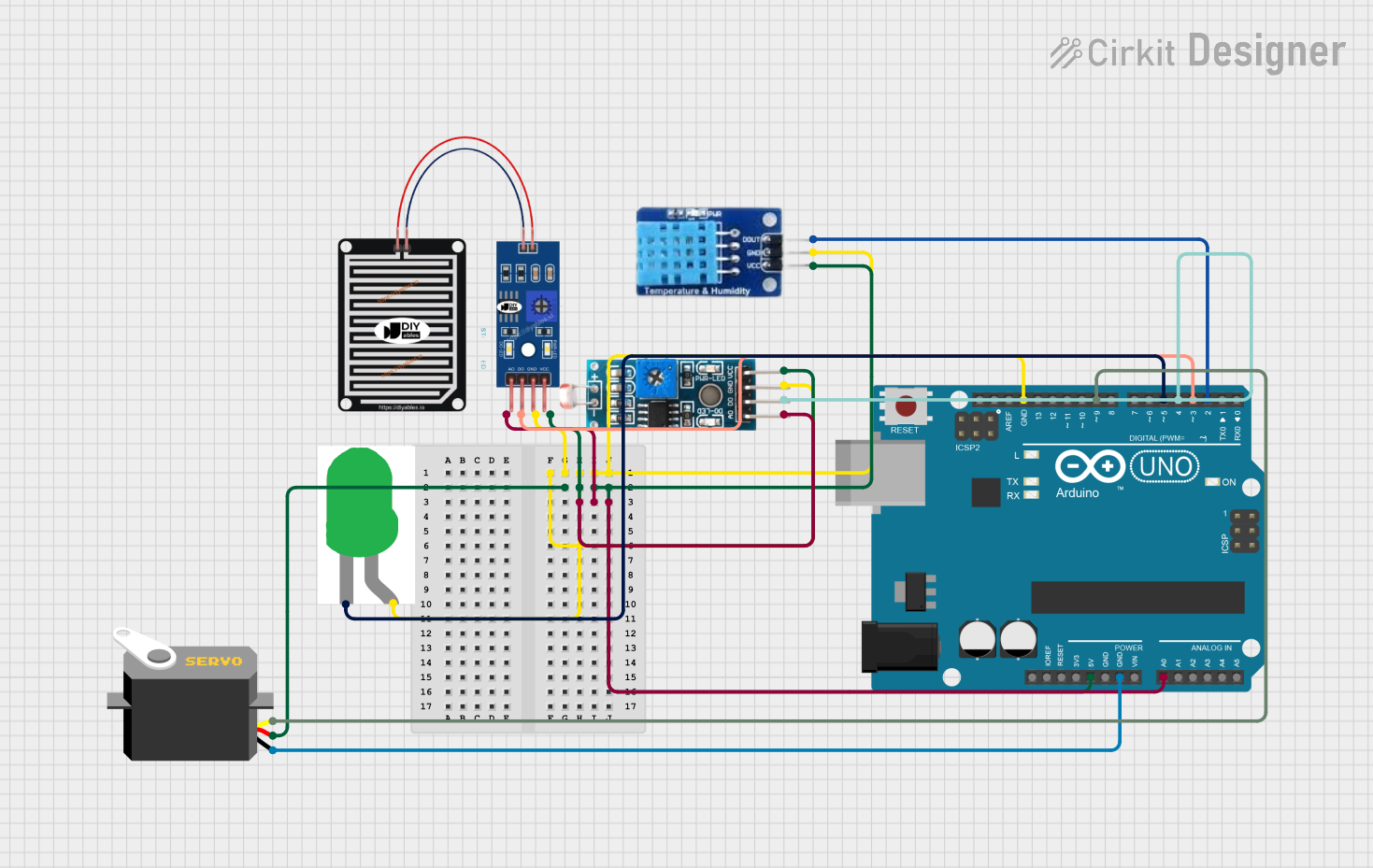
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Rain Droplet

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Weather Monitoring Systems: Detecting rainfall and measuring precipitation levels.
- Agricultural Automation: Triggering irrigation systems based on rain detection.
- Smart Home Systems: Automatically closing windows or activating rain shields.
- Educational Projects: Simulating weather patterns for learning purposes.
- IoT Devices: Integrating rain detection into smart environmental monitoring systems.
Technical Specifications
Below are the technical specifications for a typical rain droplet sensor module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Type | Analog and Digital |
| Analog Output Range | 0V - 5V (proportional to wetness) |
| Digital Output | High (no rain) / Low (rain detected) |
| Sensitivity Adjustment | Via onboard potentiometer |
| Dimensions | ~3cm x 2cm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V - 5V). Connect to the positive terminal of the power source. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| A0 | Analog output pin. Outputs a voltage proportional to the amount of water detected. |
| D0 | Digital output pin. Outputs HIGH or LOW based on the presence of rain. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Connect Outputs:
- For analog readings, connect the A0 pin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller.
- For digital readings, connect the D0 pin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller.
- Adjust Sensitivity: Use the onboard potentiometer to adjust the sensitivity of the digital output. Turn it clockwise to increase sensitivity and counterclockwise to decrease it.
- Place the Sensor: Position the sensor in an area where it can detect rain droplets. Ensure it is not submerged in water or exposed to extreme conditions beyond its operating range.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Submersion: The sensor is designed to detect rain droplets, not to be submerged in water.
- Clean Regularly: Dust or debris on the sensor surface can affect its accuracy. Clean it gently with a soft cloth.
- Protect from Corrosion: If used outdoors, consider applying a protective coating to prevent corrosion.
- Use Pull-Up Resistors: For digital output, use a pull-up resistor if the microcontroller does not have an internal one.
- Test Sensitivity: Before deployment, test the sensor's sensitivity and adjust the potentiometer as needed.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a rain droplet sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define pin connections
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog output pin connected to A0
const int digitalPin = 2; // Digital output pin connected to D2
const int ledPin = 13; // LED pin to indicate rain detection
void setup() {
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read analog value from the sensor
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
Serial.print("Analog Value: ");
Serial.println(analogValue);
// Read digital value from the sensor
int digitalValue = digitalRead(digitalPin);
Serial.print("Digital Value: ");
Serial.println(digitalValue);
// Turn on LED if rain is detected (digital output is LOW)
if (digitalValue == LOW) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
Serial.println("Rain detected!");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
Serial.println("No rain detected.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
No Output from the Sensor:
- Solution: Check the power connections to ensure the sensor is receiving the correct voltage.
- Tip: Verify that the GND pin is properly connected to the circuit ground.
Inconsistent Readings:
- Solution: Clean the sensor surface to remove dust or debris.
- Tip: Ensure the sensor is not exposed to extreme environmental conditions.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW:
- Solution: Adjust the sensitivity using the onboard potentiometer.
- Tip: Test the sensor with a small amount of water to verify its functionality.
Analog Output Not Changing:
- Solution: Check the analog pin connection and ensure it is properly configured in the code.
- Tip: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the A0 pin for troubleshooting.
FAQs
Q: Can the sensor detect humidity or only rain?
A: The sensor is designed to detect rain droplets. It is not suitable for measuring ambient humidity.
Q: Can I use this sensor indoors?
A: Yes, the sensor can be used indoors for simulations or controlled experiments, but it is primarily designed for outdoor use.
Q: How do I protect the sensor from corrosion?
A: Apply a thin layer of waterproof coating or use a protective enclosure to shield the sensor from prolonged exposure to moisture.
Q: What is the maximum distance between the sensor and the microcontroller?
A: The maximum distance depends on the quality of the wires and the environment, but it is generally recommended to keep the distance under 1 meter to avoid signal degradation.