
How to Use Power Distribution Board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
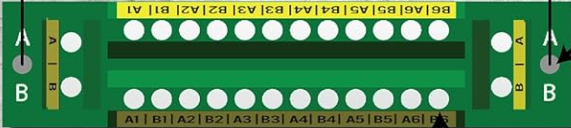
 Design with Power Distribution Board in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Distribution Board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Power Distribution Board (PDB) is an essential component in many electronic systems, particularly in complex circuits and multirotor aircraft. It serves as a hub for distributing electrical power from a single source, such as a battery, to multiple electronic devices or subsystems. PDBs are commonly used in radio-controlled (RC) models, drones, robotics, and other applications where organized power management is crucial.
Explore Projects Built with Power Distribution Board
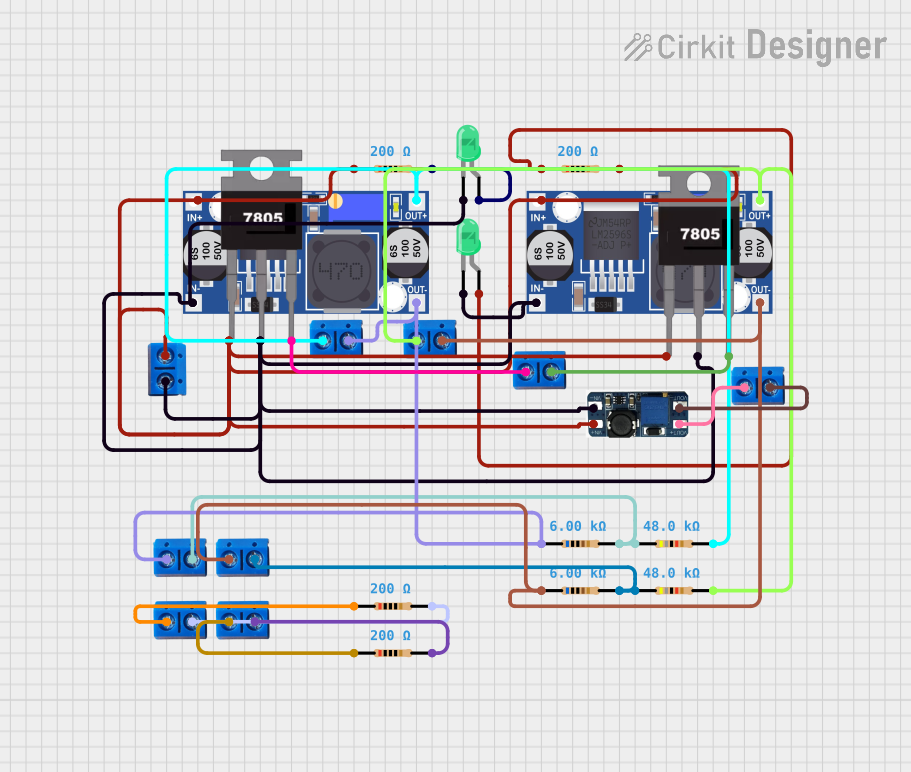
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer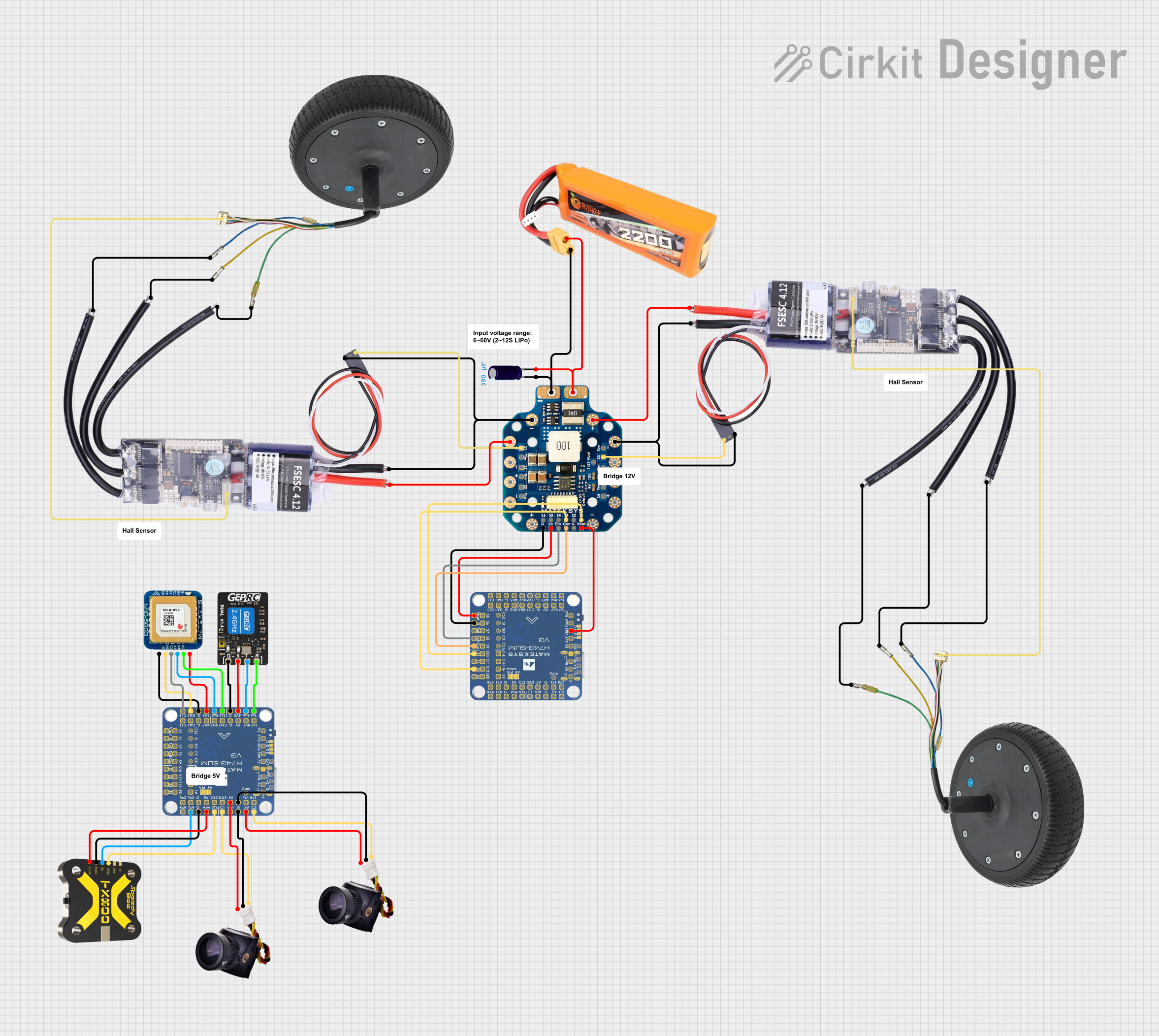
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer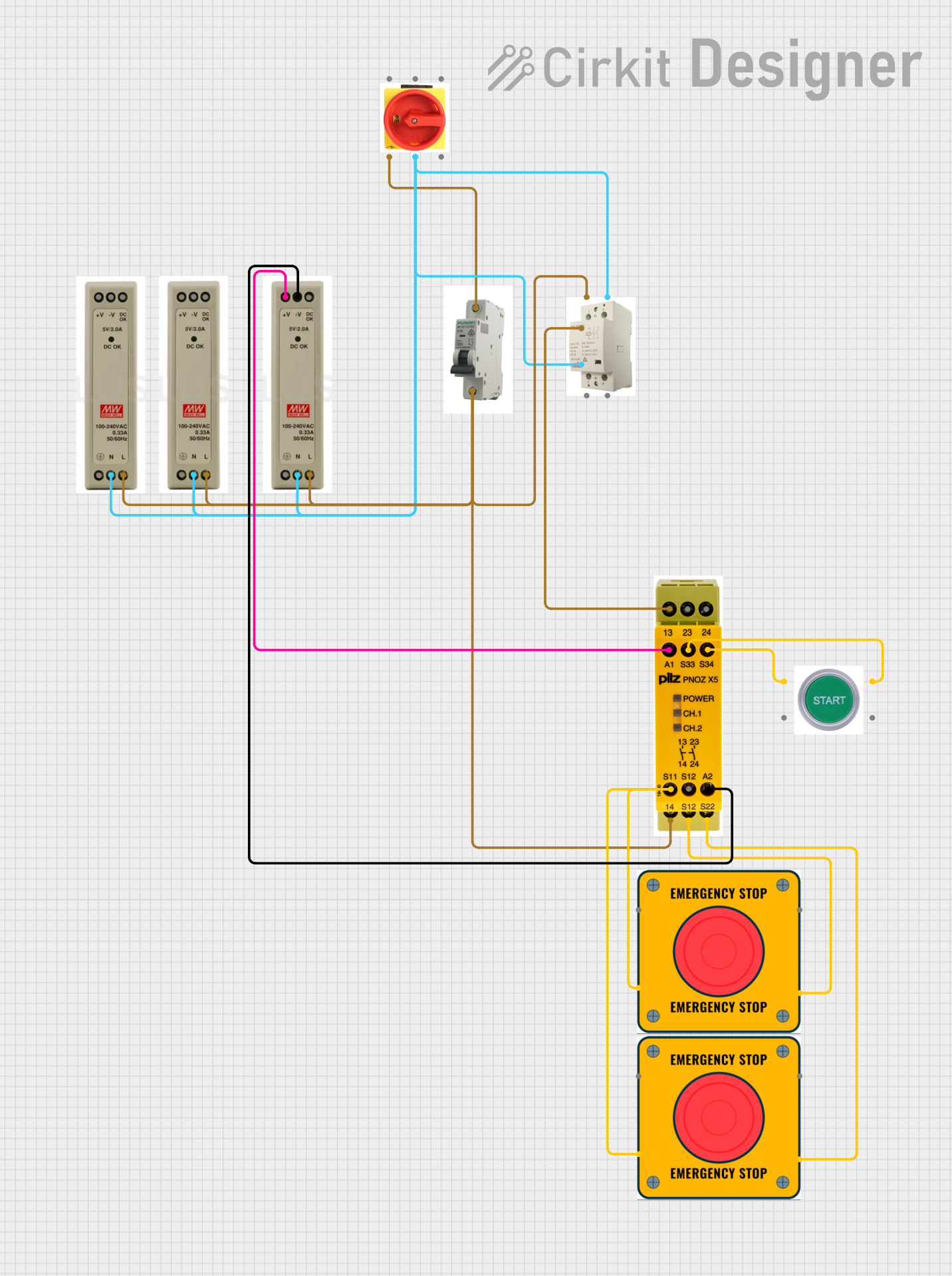
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer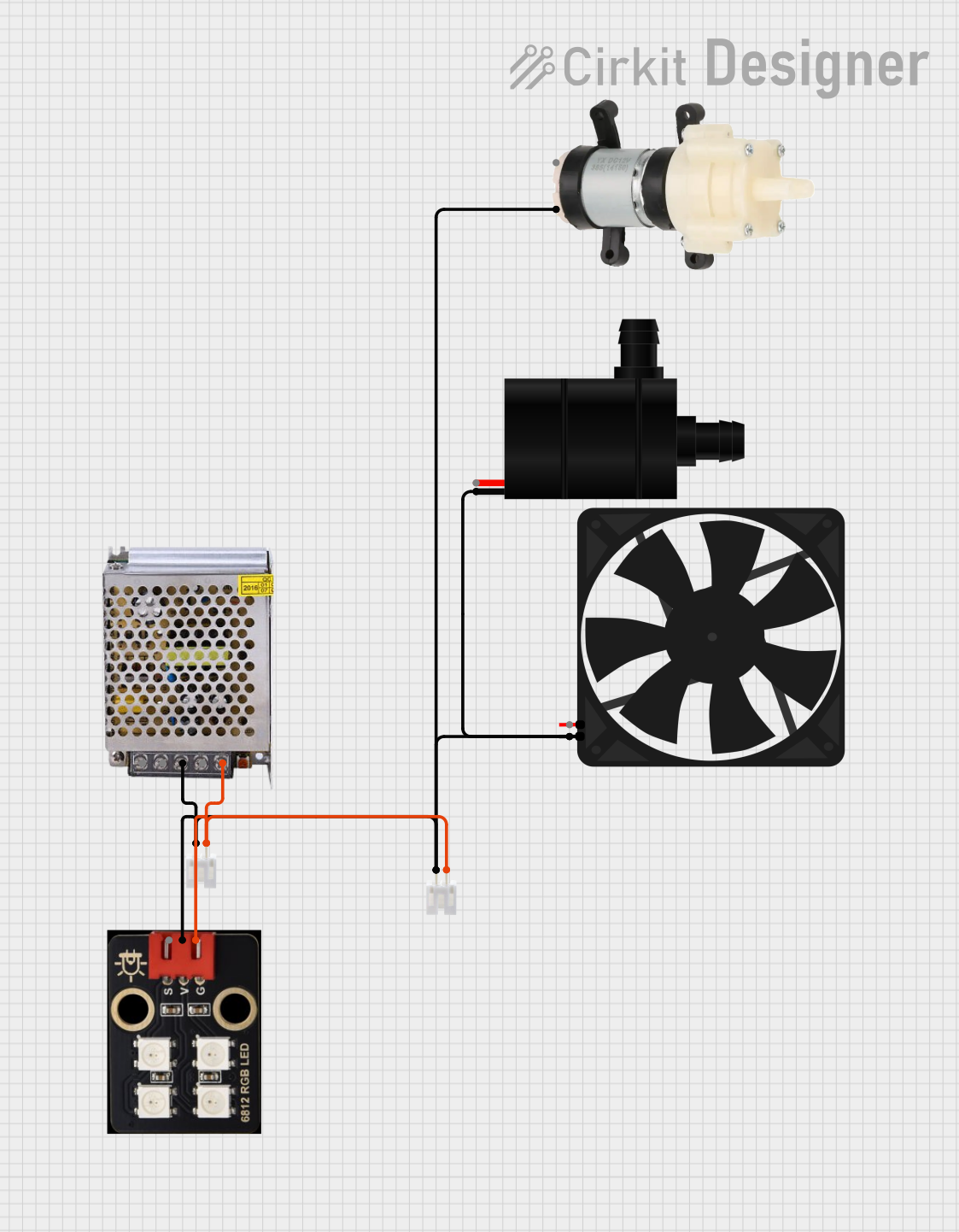
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Distribution Board

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Multirotor drones and RC aircraft for distributing power to motors and electronic speed controllers (ESCs)
- Robotics for routing power to sensors, actuators, and control units
- DIY electronics projects requiring multiple power connections
- Automotive and marine electronics for centralized power management
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: Typically ranges from 3V to 6S LiPo battery voltage (22.2V)
- Maximum Current: Varies by model, can range from 20A to 200A or more
- Power Ratings: Dependent on the specific PDB, with some capable of handling up to 1000W
- Dimensions: Varies by design, often compact to fit within tight spaces
- Weight: Lightweight, usually a few grams
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Battery Input (+) | Connect to positive battery terminal |
| 2 | Battery Input (-) | Connect to negative battery terminal |
| 3-n | ESC/Motor Outputs (+) | Number varies by PDB design |
| 3-n | ESC/Motor Outputs (-) | Number varies by PDB design |
| Aux1 | Auxiliary Power Output (+) | Optional, for accessories |
| Aux1 | Auxiliary Power Output (-) | Optional, for accessories |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Battery:
- Attach the battery's positive lead to the PDB's positive battery input (Pin 1).
- Attach the battery's negative lead to the PDB's negative battery input (Pin 2).
Connect the ESCs/Motors:
- Connect each ESC's positive lead to one of the PDB's positive ESC/Motor outputs.
- Connect each ESC's negative lead to the corresponding negative ESC/Motor output.
Connect Accessories (if applicable):
- Attach any additional accessories to the auxiliary power outputs, ensuring correct polarity.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Rating: Ensure the PDB's current rating exceeds the total expected current draw of all connected devices.
- Voltage Rating: Verify that the PDB's voltage rating is suitable for the battery and connected components.
- Insulation: Use insulating materials to prevent shorts between the PDB and conductive surfaces.
- Mounting: Secure the PDB to the frame or chassis to prevent movement and potential damage.
- Wiring: Use appropriately sized wires to handle the expected current and minimize voltage drops.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Overheating: Caused by exceeding the current rating or poor ventilation.
- Voltage Drops: Occur when wire gauge is too small or connections are loose.
- Short Circuits: Can happen due to exposed wires or incorrect connections.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correctly polarized.
- Inspect for Damage: Look for signs of physical damage or burnt components.
- Measure Voltage and Current: Use a multimeter to verify that the PDB is distributing power correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a PDB with a higher voltage rating than my system requires?
- A: Yes, it's generally safe to use a PDB with a higher voltage rating.
Q: What should I do if the PDB is getting too hot during operation?
- A: Check for overloading and improve ventilation; consider using a PDB with a higher current rating.
Q: How do I know if the PDB can handle the current from all my devices?
- A: Sum the current draw of all connected devices and compare it to the PDB's maximum current rating.
If you're using a PDB with an Arduino UNO or similar microcontroller, the PDB will typically be used to distribute power to various sensors, actuators, or shields that require more current than the Arduino can provide directly. In such cases, no specific code is needed for the PDB itself, as it is a passive component. However, ensure that the power requirements of all connected components are within the specifications of the PDB.