
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use Power Distribution Board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Power Distribution Board in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Distribution Board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Power Distribution Board (PDB) is an essential component in various electronic and electrical systems. It is designed to distribute electrical power from a single source to multiple circuits, ensuring a stable and organized supply of electricity. PDBs are commonly used in robotics, RC vehicles, drones, and other projects where multiple electronic devices must be powered simultaneously.
Explore Projects Built with Power Distribution Board
Multi-Stage Voltage Regulation and Indicator LED Circuit
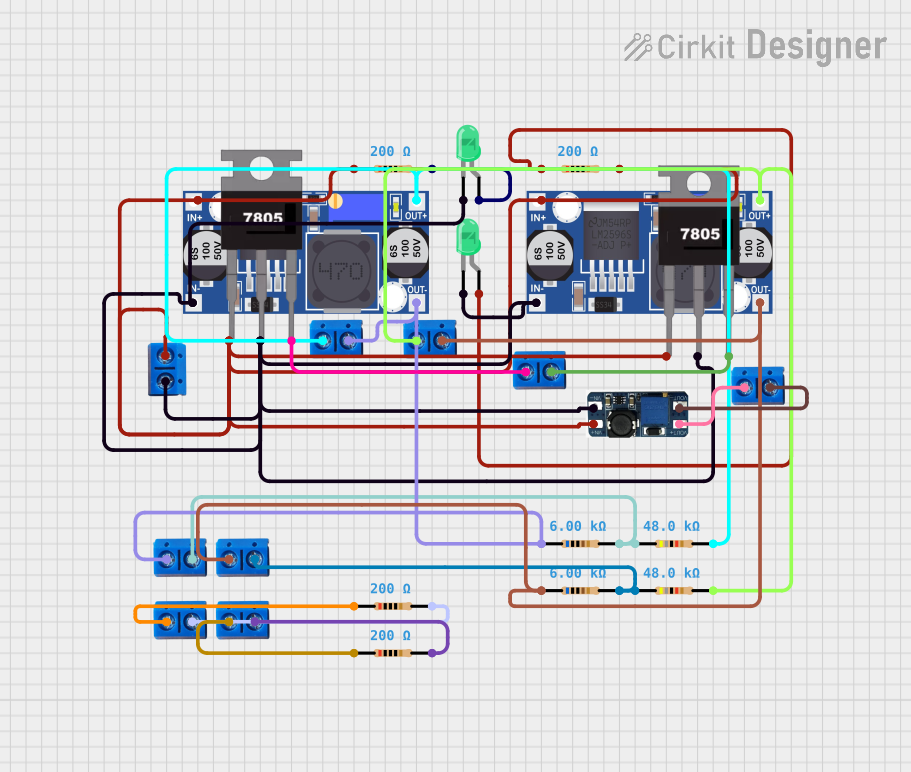
This circuit is designed for power management, featuring buck and boost converters for voltage adjustment, and linear regulators for stable voltage output. It includes LEDs for status indication, and terminal blocks for external connections.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerBattery-Powered FPV Drone with Telemetry and Dual Motor Control
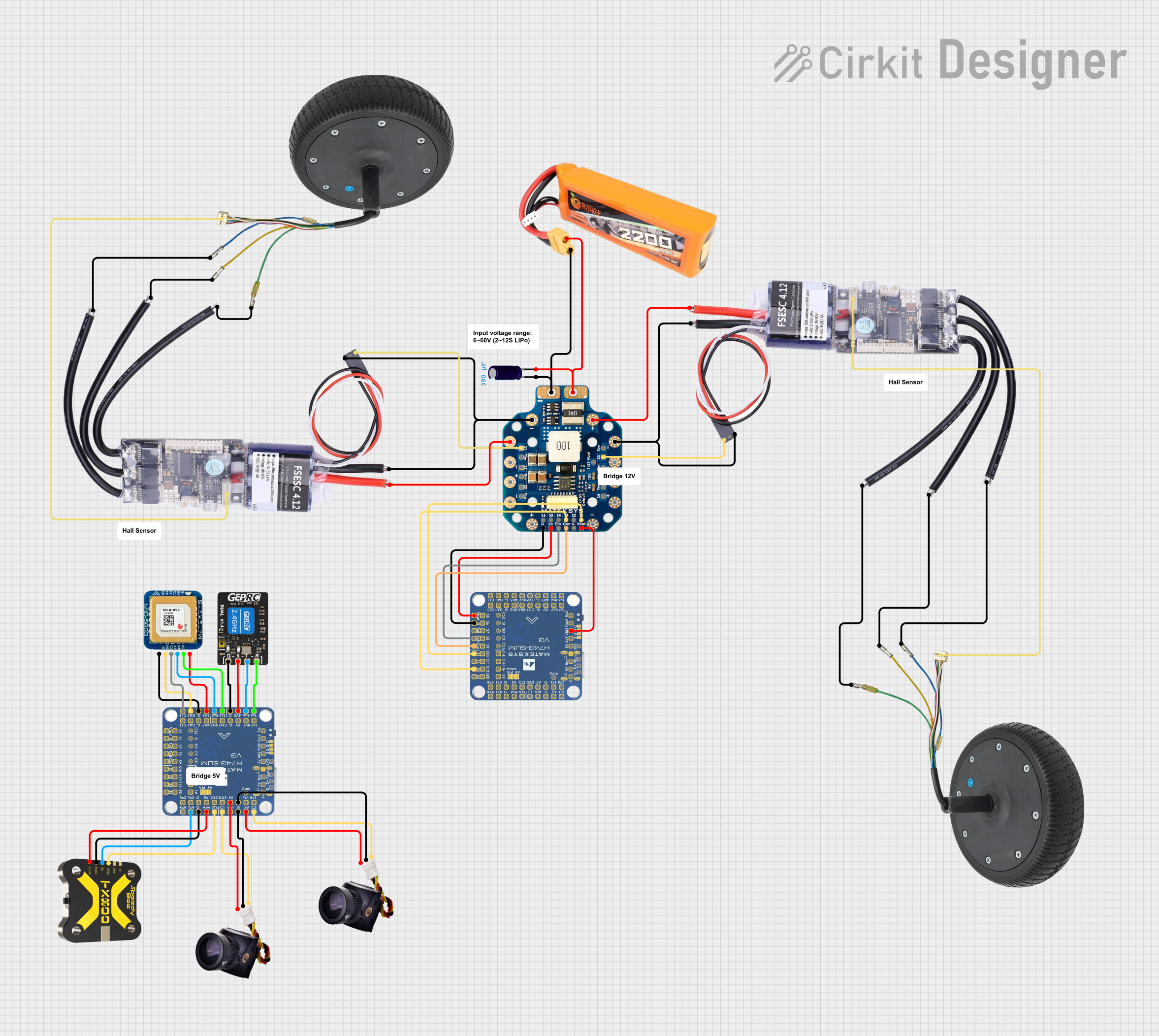
This circuit appears to be a power distribution and control system for a vehicle with two motorized wheels, possibly a drone or a robot. It includes a lipo battery connected to a Power Distribution Board (PDB) that distributes power to two Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) which in turn control the speed and direction of the motors. The system also integrates a flight controller (H743-SLIM V3) for managing various peripherals including GPS, FPV camera system, and a telemetry link (ExpressLRS).
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerIndustrial Power Distribution and Safety Control System
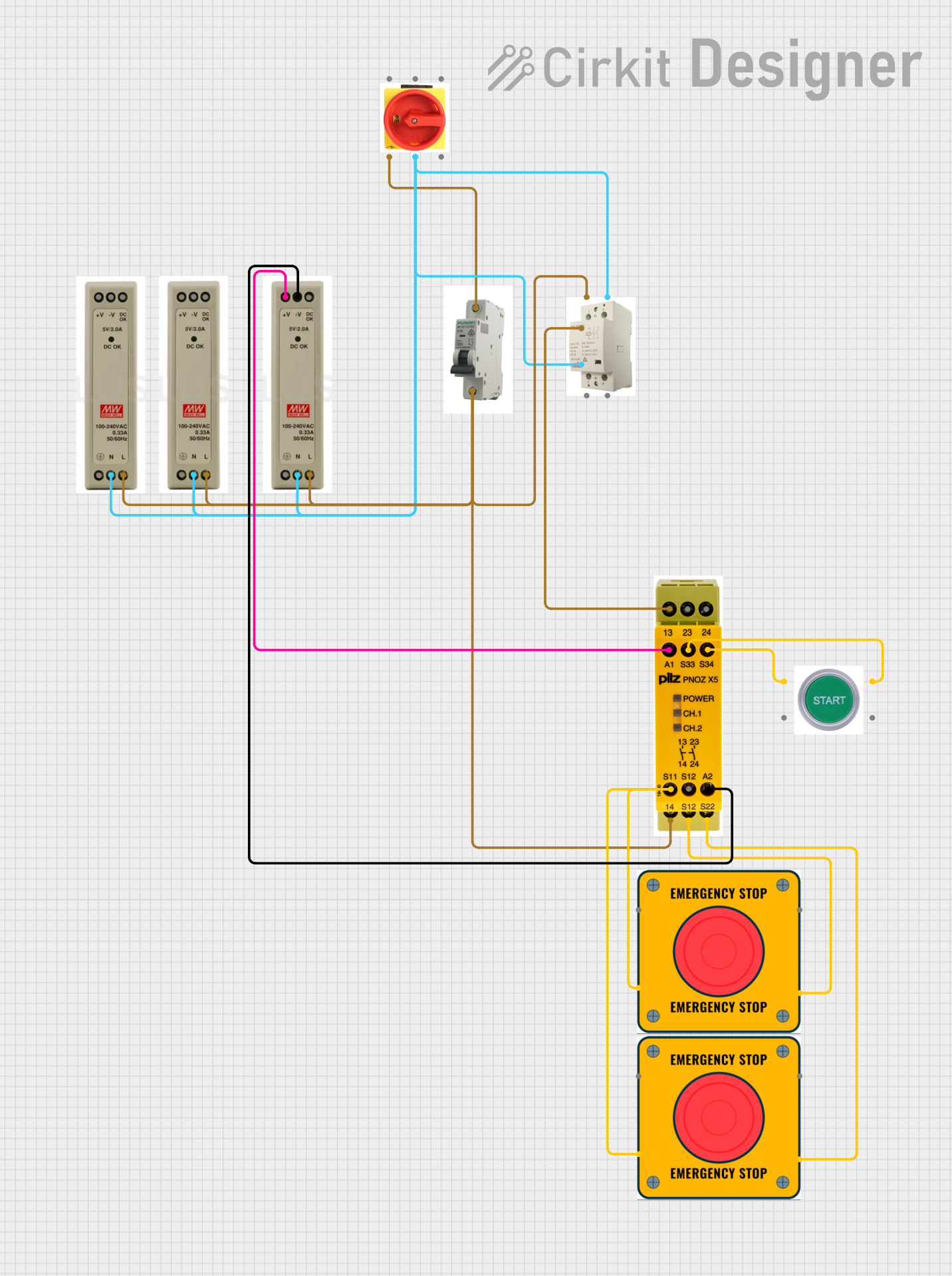
This circuit is designed for power distribution and safety control in an industrial setting. It features a main isolator and circuit breaker for power management, multiple PSUs for 5V, 12V, and 24V outputs, and a safety relay system that interfaces with E-stop buttons and a start switch to control a main contactor, ensuring safe operation and emergency power cut-off capabilities.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer12V Multi-Component Control Circuit
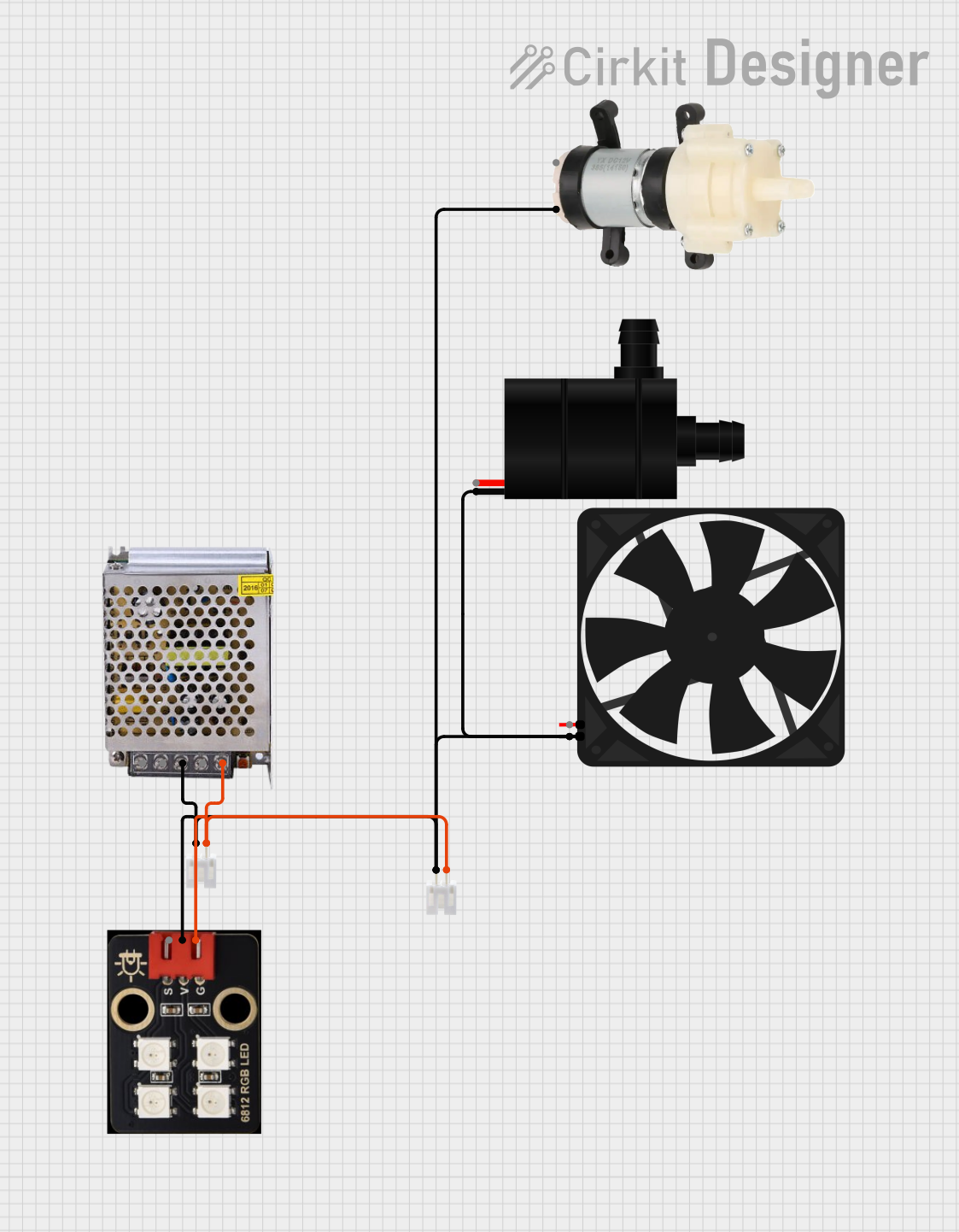
This circuit appears to be a power distribution system that supplies power to various components from a 12V 5A power supply. It connects the negative terminal of the power supply to the ground (GND) pins of a mini diaphragm water pump, an RGB LED, a fan, and a water pump, while the positive DC output is connected to the positive pins of the RGB LED and presumably to other components through JST PH 2.0 connectors. The circuit lacks a controlling element, such as a microcontroller, suggesting that the components operate continuously or are switched externally.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Distribution Board

Multi-Stage Voltage Regulation and Indicator LED Circuit
This circuit is designed for power management, featuring buck and boost converters for voltage adjustment, and linear regulators for stable voltage output. It includes LEDs for status indication, and terminal blocks for external connections.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Battery-Powered FPV Drone with Telemetry and Dual Motor Control
This circuit appears to be a power distribution and control system for a vehicle with two motorized wheels, possibly a drone or a robot. It includes a lipo battery connected to a Power Distribution Board (PDB) that distributes power to two Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) which in turn control the speed and direction of the motors. The system also integrates a flight controller (H743-SLIM V3) for managing various peripherals including GPS, FPV camera system, and a telemetry link (ExpressLRS).
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Industrial Power Distribution and Safety Control System
This circuit is designed for power distribution and safety control in an industrial setting. It features a main isolator and circuit breaker for power management, multiple PSUs for 5V, 12V, and 24V outputs, and a safety relay system that interfaces with E-stop buttons and a start switch to control a main contactor, ensuring safe operation and emergency power cut-off capabilities.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
12V Multi-Component Control Circuit
This circuit appears to be a power distribution system that supplies power to various components from a 12V 5A power supply. It connects the negative terminal of the power supply to the ground (GND) pins of a mini diaphragm water pump, an RGB LED, a fan, and a water pump, while the positive DC output is connected to the positive pins of the RGB LED and presumably to other components through JST PH 2.0 connectors. The circuit lacks a controlling element, such as a microcontroller, suggesting that the components operate continuously or are switched externally.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Multirotor drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Robotics and automation systems
- Remote-controlled (RC) cars, boats, and planes
- Custom electronics projects requiring multiple power connections
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: Typically 3.3V to 28V (varies by model)
- Maximum Current Rating: Depends on the board design (e.g., 20A continuous, 100A peak)
- Number of Output Channels: Varies by model (e.g., 4, 6, 8 outputs)
- Board Dimensions: Standard sizes or custom dimensions
- Mounting Options: Through-hole, surface mount, or standoffs
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Voltage/Signal Type | Maximum Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power Input (+) | Varies by model | - |
| 2 | Power Input (-) | Ground | - |
| 3 - N | Power Outputs (+) | Varies by model | Per channel |
| N+1 - 2N-2 | Power Outputs (-) | Ground | Per channel |
| 2N-1 | Voltage Monitoring | Analog | - |
| 2N | Current Monitoring | Analog | - |
Note: The pin configuration may vary depending on the specific model of the PDB. Please refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for exact details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Input Connection: Connect the power source to the input pins of the PDB, ensuring correct polarity.
- Output Connections: Connect the output pins to the various components that require power, such as motors, ESCs, or other electronic modules.
- Monitoring Connections (if available): Connect the voltage and current monitoring pins to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a microcontroller for real-time power monitoring.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limitations: Do not exceed the maximum current rating of the PDB or individual channels.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate ventilation around the PDB to prevent overheating.
- Short Circuit Protection: Use fuses or circuit breakers to protect against short circuits.
- Wire Gauge: Use appropriate wire gauge for the current load to prevent excessive voltage drop and overheating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Overheating: If the PDB overheats, check for overcurrent conditions or inadequate ventilation.
- Voltage Drop: Excessive voltage drop can occur if wire gauges are too small or if connections are poor.
- Intermittent Power: Loose connections can cause intermittent power issues. Ensure all connections are secure.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Regularly inspect all connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or looseness.
- Monitor Power: Use the monitoring features of the PDB to keep an eye on voltage and current levels.
- Replace Damaged Components: If a section of the PDB is damaged, it may need to be replaced.
FAQs
- Q: Can I use the PDB with a voltage higher than specified?
- A: No, exceeding the specified voltage can damage the PDB and connected devices.
- Q: How do I know if the PDB is functioning correctly?
- A: Use a multimeter to measure the output voltages and ensure they match the expected values.
Note: This documentation is based on a generic Power Distribution Board. For specific models, such as those manufactured by goBILDA, please refer to the manufacturer's datasheet and part ID for detailed information.