
How to Use Charging and Battery Boost Module Lithium 18650 - 3.7V 2A to 5V-9V TP4056 - Type C Port: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
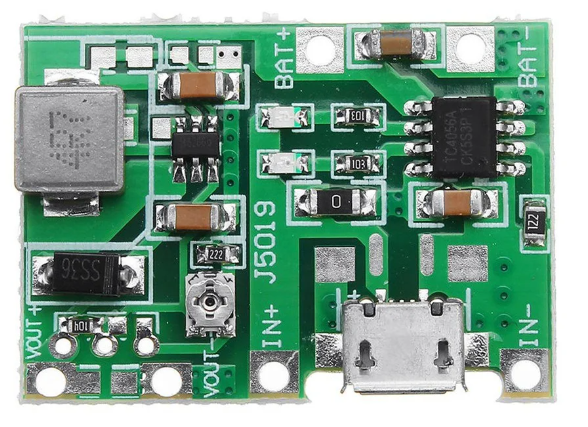
 Design with Charging and Battery Boost Module Lithium 18650 - 3.7V 2A to 5V-9V TP4056 - Type C Port in Cirkit Designer
Design with Charging and Battery Boost Module Lithium 18650 - 3.7V 2A to 5V-9V TP4056 - Type C Port in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Charging and Battery Boost Module is a versatile electronic component designed to charge and boost the voltage of a single-cell lithium-ion 18650 battery. It efficiently converts the battery's nominal voltage of 3.7V to a higher output voltage range of 5V to 9V, making it suitable for powering a variety of devices. The module is equipped with the TP4056 chip for reliable and efficient charging and features a Type C port for modern connectivity.
Explore Projects Built with Charging and Battery Boost Module Lithium 18650 - 3.7V 2A to 5V-9V TP4056 - Type C Port

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer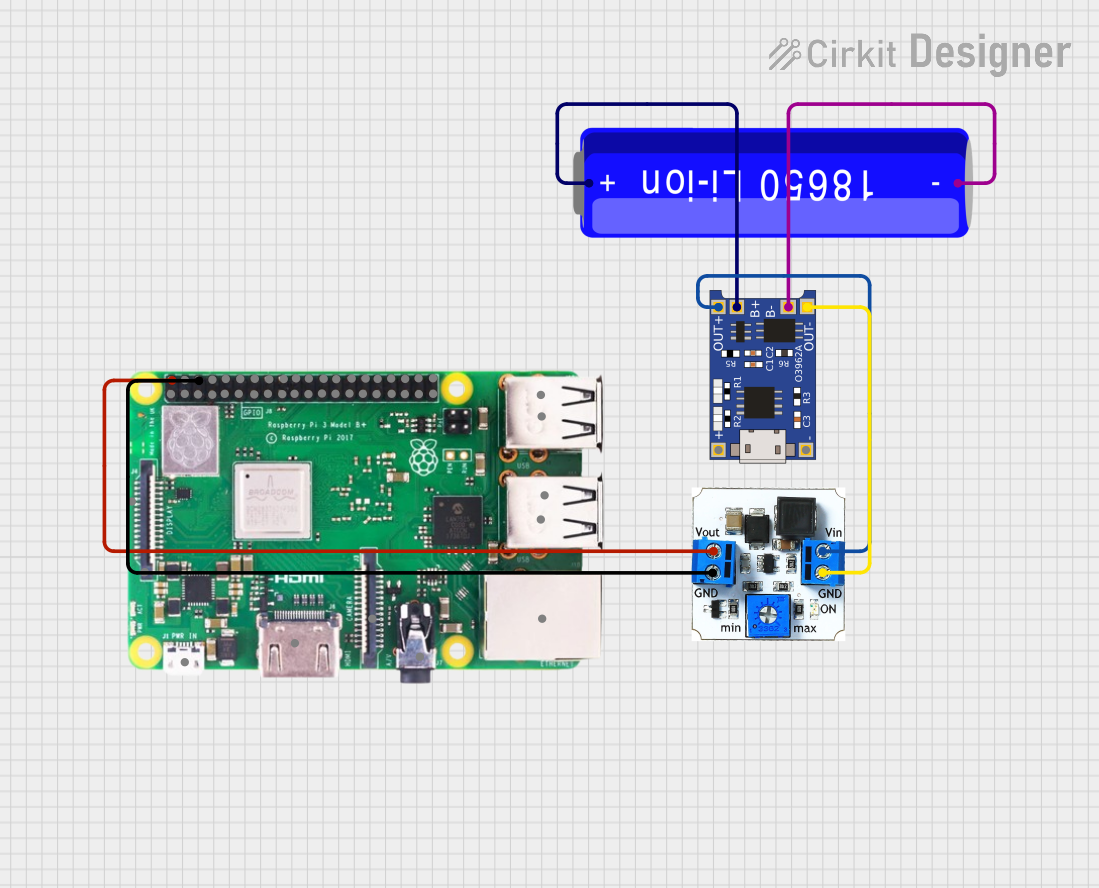
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer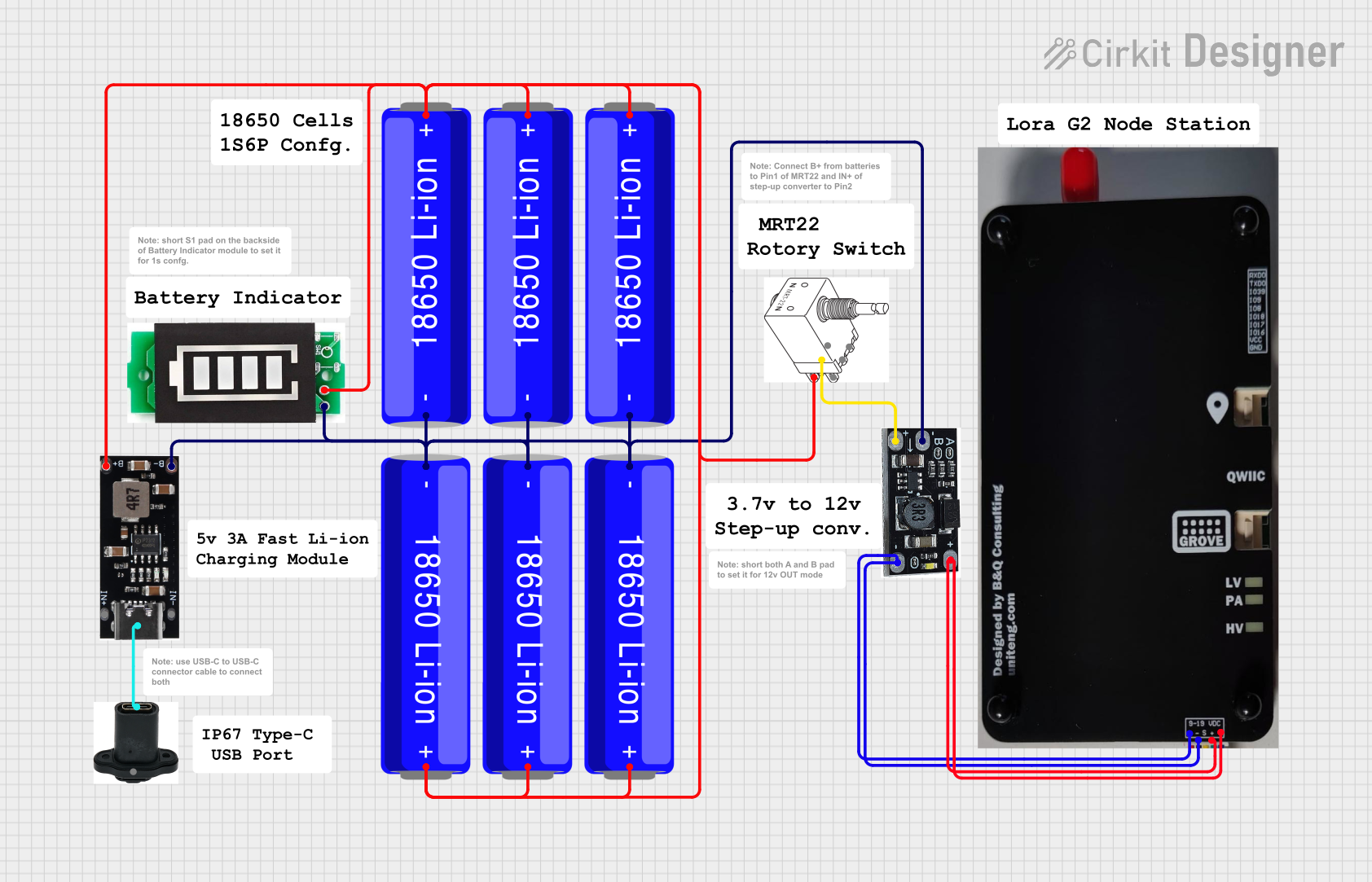
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer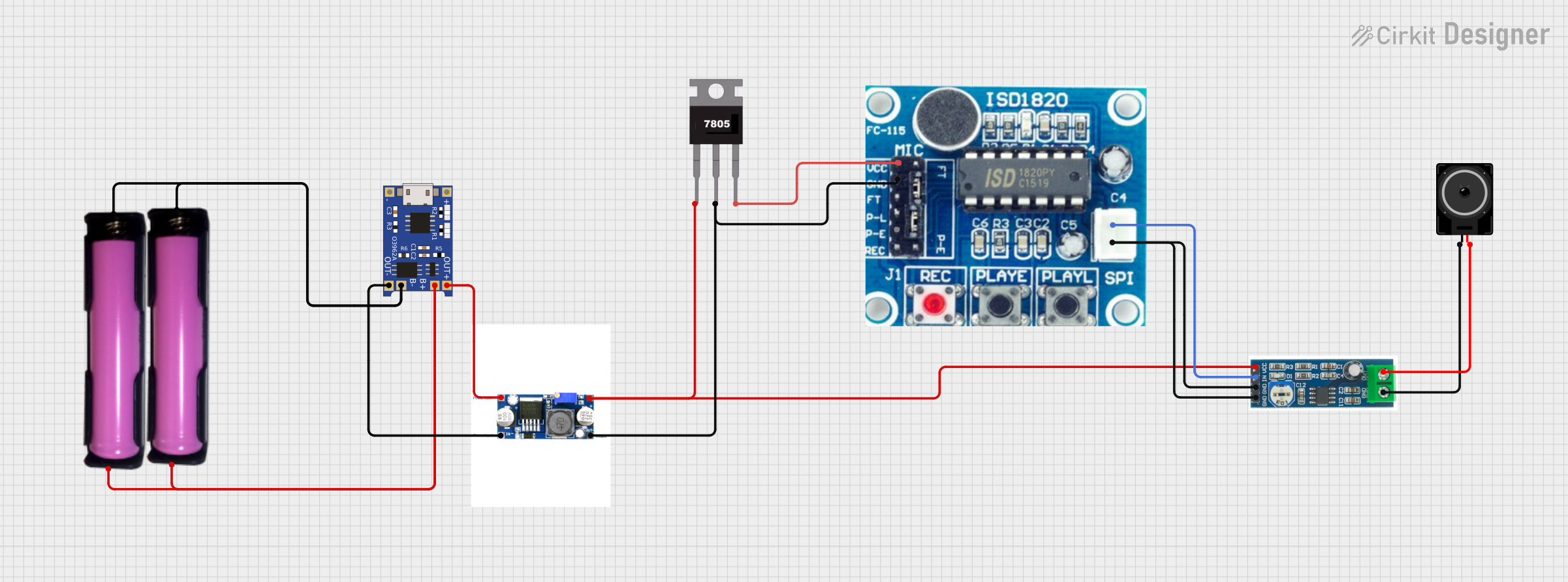
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Charging and Battery Boost Module Lithium 18650 - 3.7V 2A to 5V-9V TP4056 - Type C Port

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering portable devices such as smartphones, small gadgets, and IoT devices.
- DIY power banks and battery-powered projects.
- Emergency backup power supplies.
- Prototyping and testing circuits requiring 5V or 9V power.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 4.5V to 5.5V (via Type C port) |
| Battery Type Supported | Single-cell 18650 Lithium-Ion |
| Battery Nominal Voltage | 3.7V |
| Charging Current | 1A (default, adjustable) |
| Output Voltage | 5V, 9V (selectable) |
| Output Current | Up to 2A |
| Efficiency | Up to 92% |
| Charging Chip | TP4056 |
| Connectivity Port | Type C |
| Protection Features | Overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| B+ | Positive terminal for the 18650 battery. |
| B- | Negative terminal for the 18650 battery. |
| OUT+ | Positive output terminal for the boosted voltage (5V or 9V). |
| OUT- | Negative output terminal for the boosted voltage. |
| Type C Port | Input port for charging the 18650 battery (connects to a 5V power source). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Battery:
- Attach the positive terminal of the 18650 battery to the
B+pin. - Attach the negative terminal of the battery to the
B-pin.
- Attach the positive terminal of the 18650 battery to the
- Connect the Load:
- Connect the device or circuit requiring power to the
OUT+andOUT-pins. - Ensure the load does not exceed the module's maximum output current of 2A.
- Connect the device or circuit requiring power to the
- Select Output Voltage:
- Use the onboard switch or jumper (if available) to select the desired output voltage (5V or 9V).
- Charge the Battery:
- Connect a 5V power source (e.g., USB adapter) to the Type C port to charge the battery.
- The onboard LED indicators will show the charging status (e.g., red for charging, blue for fully charged).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use only a single 18650 lithium-ion battery with this module. Do not connect multiple batteries in series or parallel.
- Ensure the battery is in good condition and has a built-in protection circuit if possible.
- Avoid exceeding the module's input voltage range (4.5V to 5.5V) to prevent damage.
- Do not short-circuit the output terminals (
OUT+andOUT-). - For Arduino projects, ensure the module's output voltage matches the Arduino's input voltage requirements (e.g., 5V for Arduino UNO).
Example: Using the Module with an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO using this module, follow these steps:
- Connect the
OUT+pin to the Arduino's5Vpin. - Connect the
OUT-pin to the Arduino'sGNDpin. - Ensure the module is set to output 5V.
Here is a simple Arduino code example to blink an LED while powered by the module:
// Blink an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The module is not charging the battery:
- Ensure the input voltage to the Type C port is within the range of 4.5V to 5.5V.
- Check the battery connections to
B+andB-for proper polarity. - Verify that the battery is not damaged or over-discharged.
The output voltage is incorrect:
- Confirm that the output voltage selection switch or jumper is set correctly.
- Check the load's power requirements to ensure compatibility with the module.
The module overheats during operation:
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum output current of 2A.
- Verify that the input voltage is within the specified range.
The LED indicators are not working:
- Check the power source and ensure the module is receiving input voltage.
- Inspect the module for physical damage or loose connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module with other types of batteries?
A: No, this module is specifically designed for single-cell 18650 lithium-ion batteries. Using other types of batteries may damage the module or the battery.
Q: Can I charge the battery and power a load simultaneously?
A: Yes, the module supports simultaneous charging and discharging. However, ensure the input power source can handle the combined current requirements of the load and charging process.
Q: How do I know when the battery is fully charged?
A: The onboard LED indicator will change from red (charging) to blue (fully charged) when the battery is fully charged.
Q: Can I use this module to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, but only if the output voltage is set to 5V and the current requirements of the Raspberry Pi (including peripherals) do not exceed 2A.