
How to Use 5V to 12V Step-up Converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
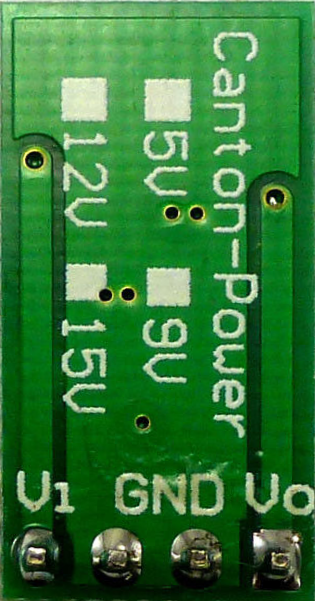
 Design with 5V to 12V Step-up Converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with 5V to 12V Step-up Converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 5V to 12V Step-up Converter is an electronic device that efficiently increases a low input voltage level of 5 volts to a higher output voltage level of 12 volts. This type of DC-DC converter is essential in applications where the available power supply voltage is lower than what is required by the electronic circuit or device. Common applications include battery-powered devices, portable electronics, and systems that require a stable 12V supply from a USB or other 5V sources.
Explore Projects Built with 5V to 12V Step-up Converter
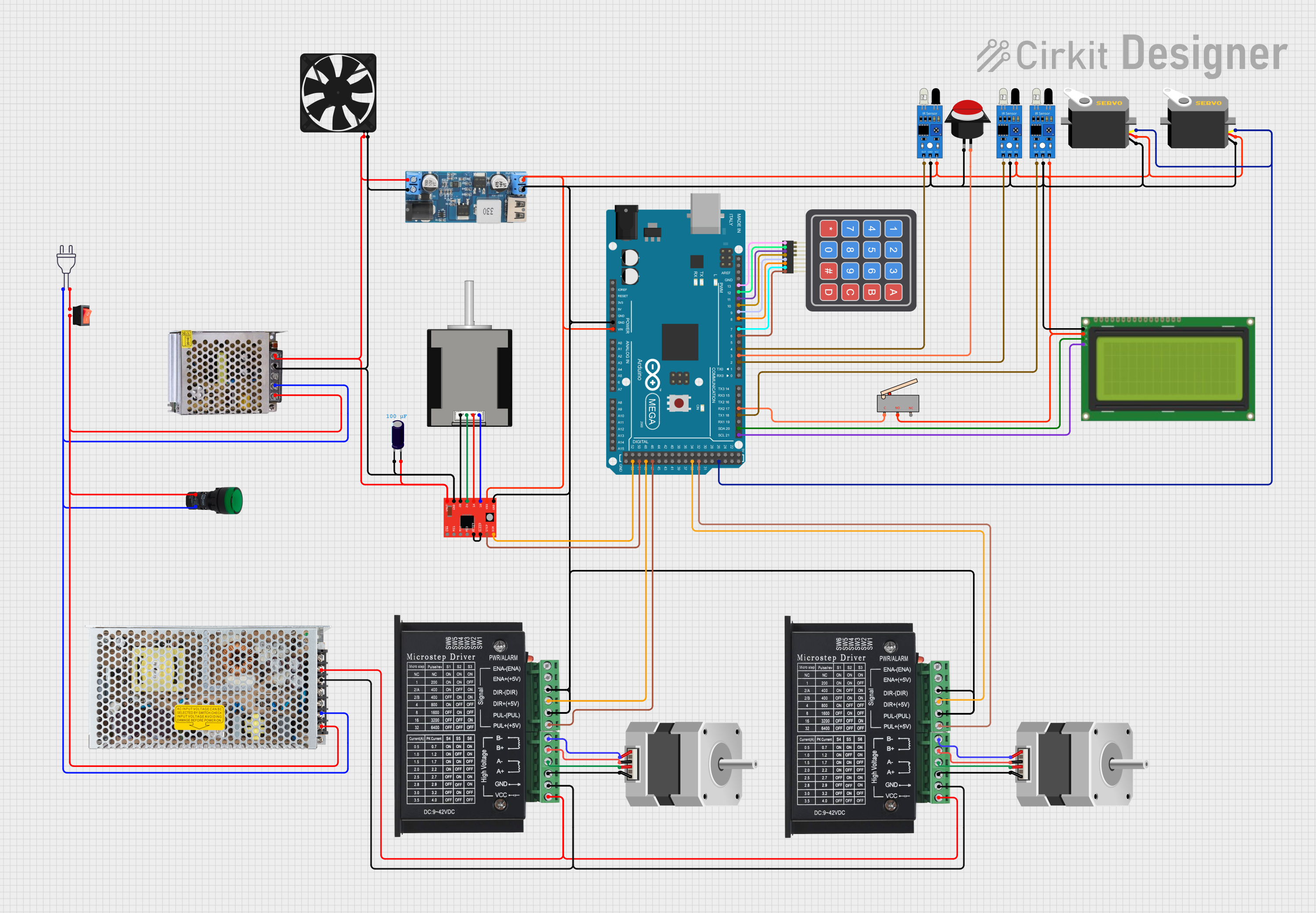
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer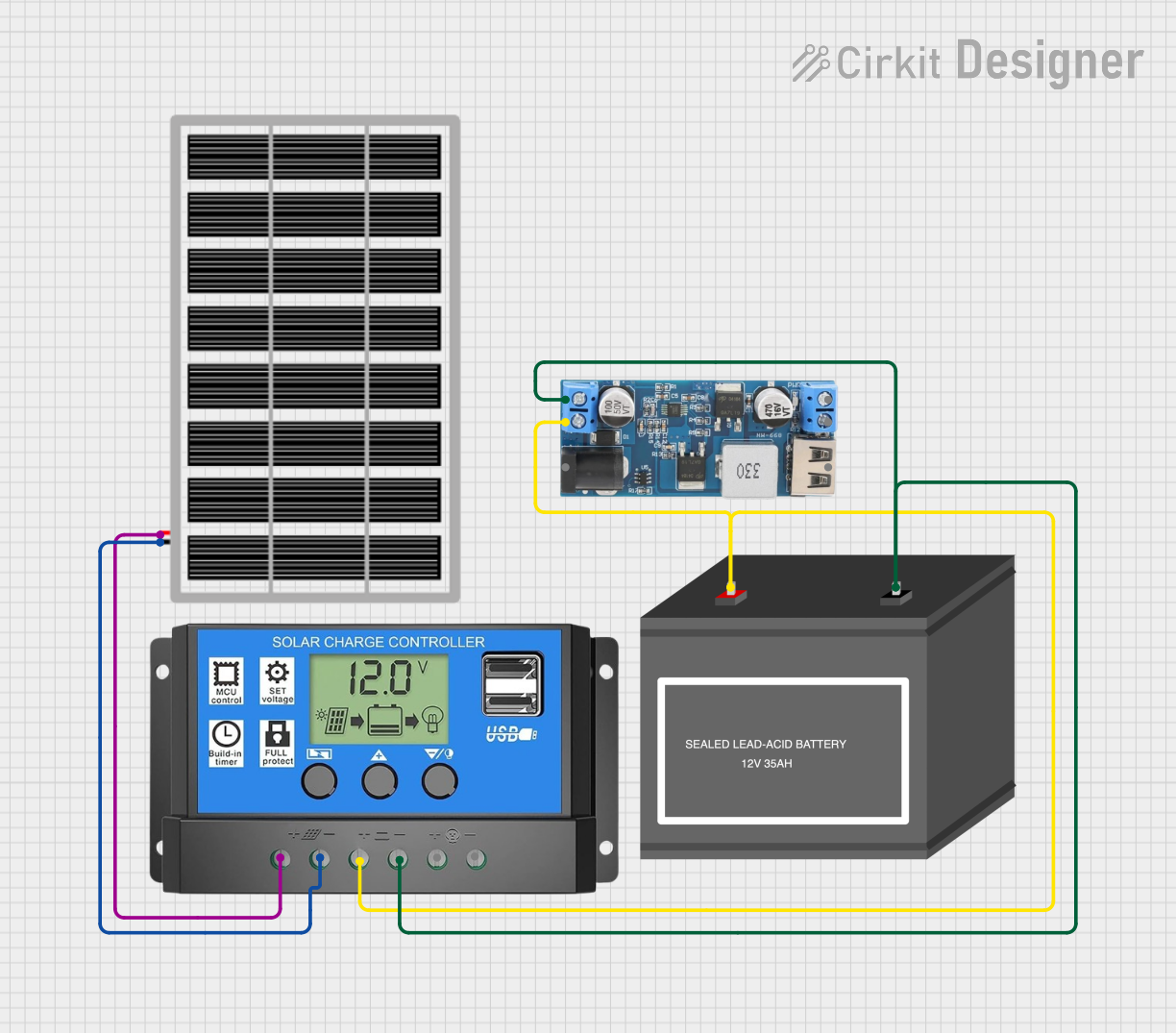
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 5V to 12V Step-up Converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage (Vin): 5V DC
- Output Voltage (Vout): 12V DC
- Maximum Output Current: Specified by the model (e.g., 1A)
- Efficiency: Typically >90% under full load
- Switching Frequency: Specified by the model (e.g., 1.5MHz)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground reference for the input voltage |
| 2 | Vin | Input voltage (5V) |
| 3 | Vout | Output voltage (12V) |
| 4 | GND | Ground reference for the output voltage |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting Input Power: Connect the 5V power supply to the Vin and GND pins. Ensure that the power supply can provide sufficient current for the expected load.
Connecting the Load: Attach the device or circuit requiring 12V to the Vout and GND pins. Ensure that the load does not exceed the maximum output current rating of the converter.
Powering On: Once the connections are secure, power on the 5V supply. The step-up converter will begin converting the voltage to 12V.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Capacitive Loading: Some converters may require a minimum load capacitance on the output for stable operation. Refer to the datasheet for specifics.
- Thermal Management: Ensure adequate ventilation or heat sinking if the converter is expected to operate near its maximum power rating.
- Input Voltage: Do not exceed the recommended input voltage as it may damage the converter.
- Output Voltage Ripple: For sensitive applications, additional filtering may be required to reduce voltage ripple.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Insufficient Output Voltage: Check if the input voltage is stable and within the specified range. Also, verify that the load does not exceed the maximum current rating.
- Overheating: Ensure that the converter is not operating above its rated current and that there is sufficient heat dissipation.
- Noise Issues: Switching converters can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Proper layout, grounding, and filtering can mitigate this.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Output Voltage Measurement: Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage under load and ensure it is close to 12V.
- Input Power Quality: Ensure the input power source is stable and clean. A low-quality power source can affect the converter's performance.
- Check Connections: Loose or poor connections can cause voltage drops and erratic behavior.
FAQs
Q: Can I adjust the output voltage of the step-up converter? A: Some models may offer an adjustable output via a feedback pin or potentiometer. Check the specific model's datasheet.
Q: Is it possible to parallel two converters for more current? A: Paralleling converters is generally not recommended unless they are specifically designed for that purpose.
Q: How do I choose the right converter for my application? A: Consider the maximum output current, efficiency, physical size, and thermal requirements for your application.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
If you're using the step-up converter with an Arduino UNO to power a 12V component, here's an example of how you might control it via a digital pin:
// Define the control pin
const int controlPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the control pin as an output
pinMode(controlPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the step-up converter
digitalWrite(controlPin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the converter on for 5 seconds
// Turn off the step-up converter
digitalWrite(controlPin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the converter off for 5 seconds
}
Note: This code assumes that the step-up converter can be controlled by a digital signal, which may not be the case for all converters. Always refer to the specific converter's datasheet for accurate control methods.