
How to Use 12v RGB LED Strip: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
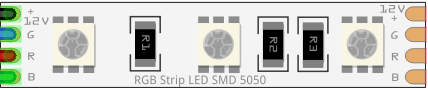
 Design with 12v RGB LED Strip in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12v RGB LED Strip in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 12V RGB LED strip is a flexible lighting solution that consists of multiple RGB (Red, Green, Blue) LEDs mounted on a flexible PCB. Each LED can produce a wide range of colors by mixing the three primary colors. The strip is powered by a 12V DC supply and is commonly used for decorative lighting, ambient lighting, signage, and displays. Its flexibility and ease of installation make it a popular choice for both DIY projects and professional applications.
Explore Projects Built with 12v RGB LED Strip
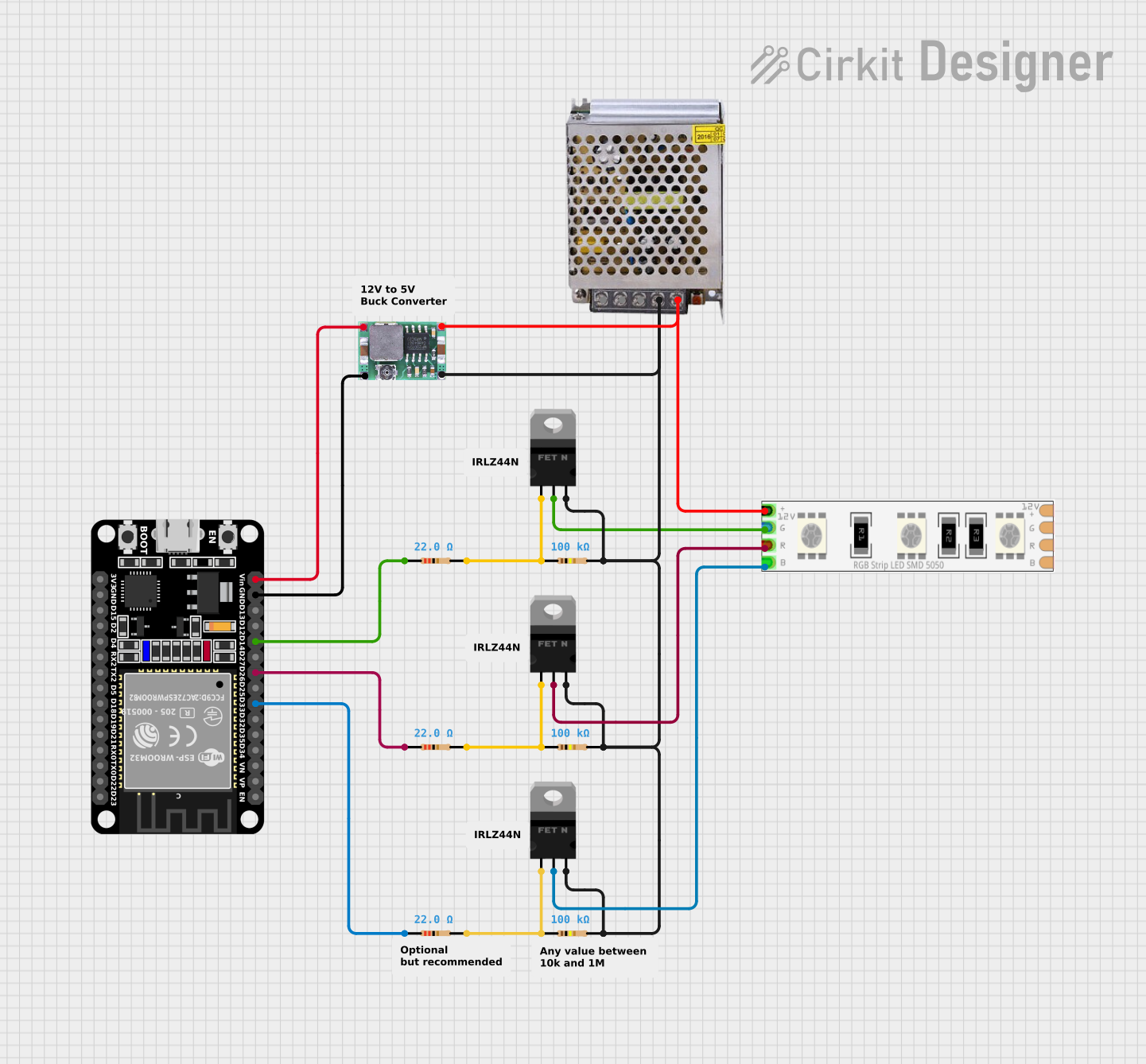
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer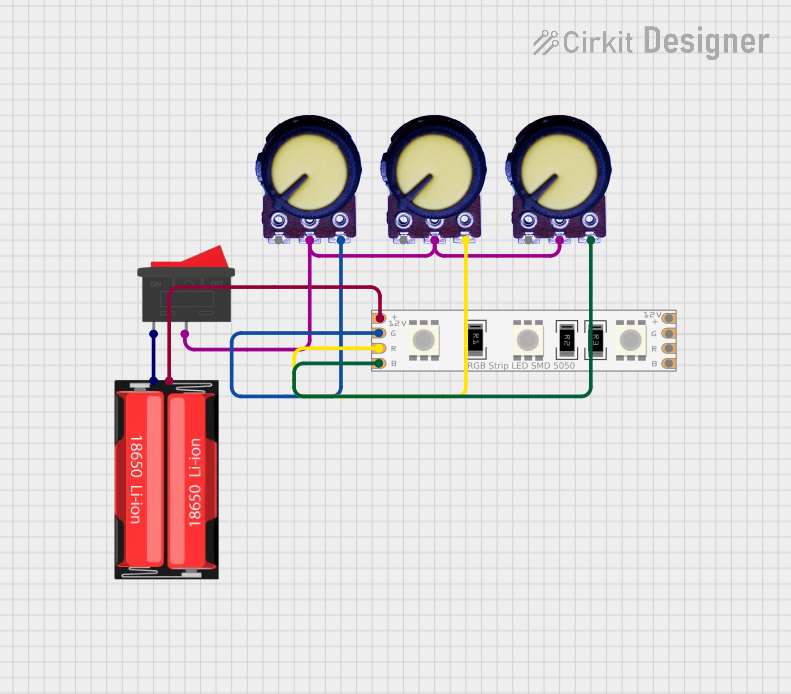
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer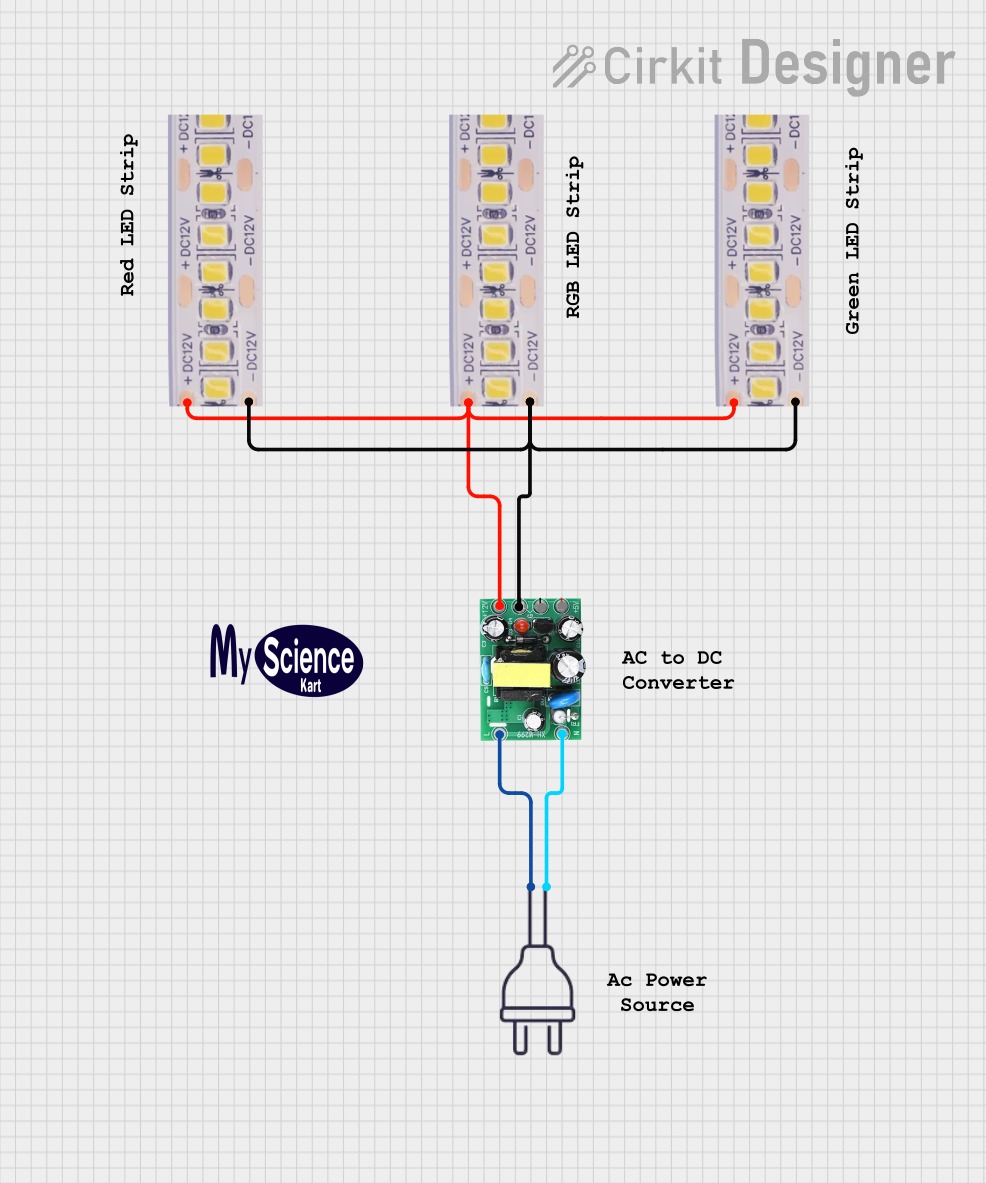
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer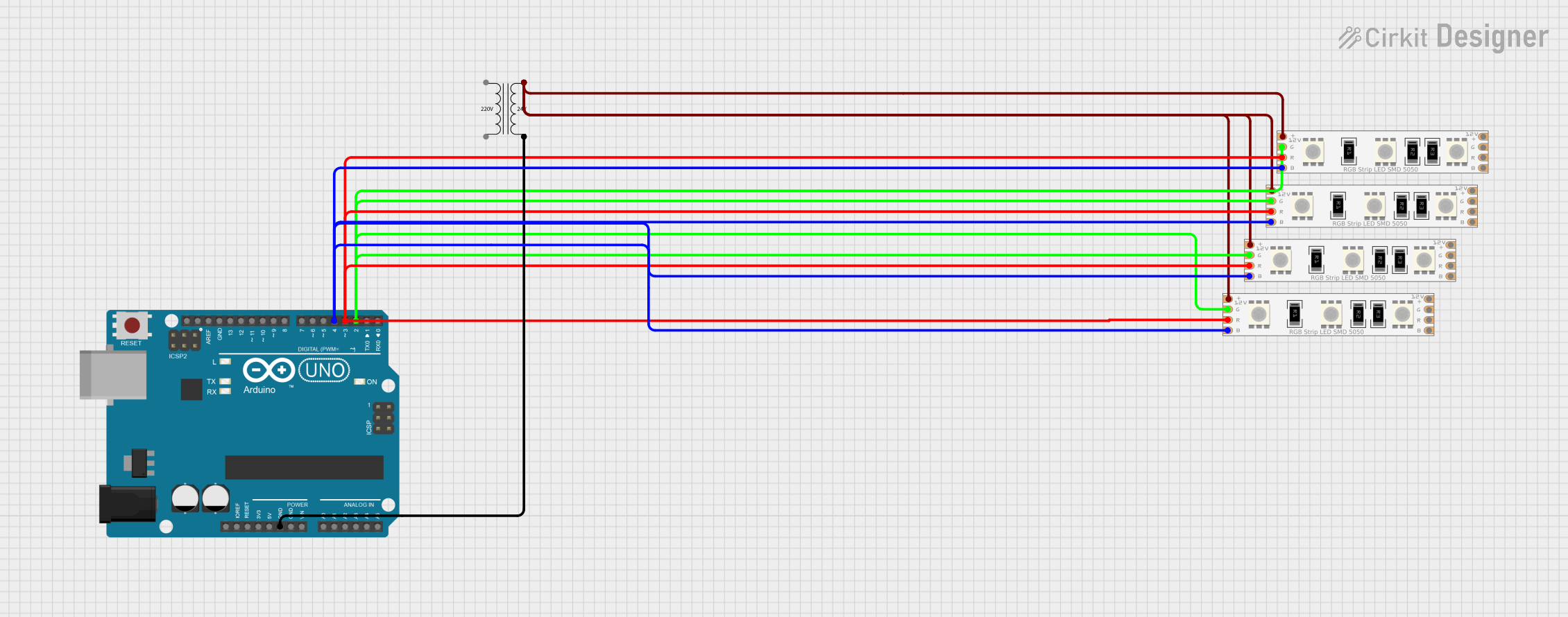
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12v RGB LED Strip

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Home and office decorative lighting
- Accent lighting for furniture, shelves, and cabinets
- Event and stage lighting
- Signage and advertising displays
- Automotive interior and exterior lighting
- DIY electronics and Arduino projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 12V RGB LED strip:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 12V DC |
| Power Consumption | ~14.4W per meter (varies by model) |
| LED Type | SMD 5050 (commonly used) |
| Number of LEDs | 30, 60, or 120 LEDs per meter (varies) |
| Color Output | Full RGB spectrum (16.7 million colors) |
| Control Method | Common Anode (shared positive) |
| Strip Width | ~10mm |
| Cuttable Sections | Every 3 LEDs (typically 5cm intervals) |
| Waterproofing | IP20 (non-waterproof) or IP65 (waterproof) |
| Lifespan | ~50,000 hours |
Pin Configuration
The 12V RGB LED strip typically has four pins or wires for connection. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin/Wire | Description |
|---|---|
| 12V | Positive voltage input (common anode) |
| R | Red channel (negative terminal for red LEDs) |
| G | Green channel (negative terminal for green LEDs) |
| B | Blue channel (negative terminal for blue LEDs) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the 12V RGB LED Strip
- Power Supply: Use a 12V DC power supply with sufficient current capacity. For example, a 5-meter strip with 60 LEDs per meter will require approximately 6A (14.4W/m × 5m ÷ 12V = 6A).
- Controller: Connect the LED strip to an RGB controller or microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) to control the colors and brightness. Ensure the controller supports common-anode RGB strips.
- Wiring:
- Connect the 12V pin of the strip to the positive terminal of the power supply.
- Connect the R, G, and B pins to the corresponding outputs of the controller or to MOSFETs for PWM control.
- Cutting the Strip: If needed, cut the strip at the marked cut points (usually every 3 LEDs). Ensure the cut section is properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
Example: Controlling with Arduino UNO
To control the 12V RGB LED strip with an Arduino UNO, you will need three N-channel MOSFETs (e.g., IRF540N) to handle the current. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the 12V pin of the LED strip to the positive terminal of a 12V power supply.
- Connect the R, G, and B pins of the strip to the drain terminals of three MOSFETs.
- Connect the source terminals of the MOSFETs to the ground of the power supply.
- Connect the gate terminals of the MOSFETs to Arduino PWM pins (e.g., pins 9, 10, and 11) through 220-ohm resistors.
- Connect the ground of the Arduino to the ground of the power supply.
Arduino Code
// Define PWM pins for RGB channels
const int redPin = 9; // Red channel connected to pin 9
const int greenPin = 10; // Green channel connected to pin 10
const int bluePin = 11; // Blue channel connected to pin 11
void setup() {
// Set RGB pins as output
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Fade through red, green, and blue colors
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) {
analogWrite(redPin, i); // Increase red intensity
analogWrite(greenPin, 255 - i); // Decrease green intensity
analogWrite(bluePin, 0); // Keep blue off
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth fading
}
}
Best Practices
- Use a power supply with at least 20% more current capacity than the calculated requirement to ensure reliable operation.
- Avoid bending the strip at sharp angles to prevent damage to the PCB and LEDs.
- If using a waterproof strip, ensure the ends are properly sealed after cutting to maintain waterproofing.
- Use appropriate heat sinks or ventilation if the strip is used at full brightness for extended periods.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
LEDs not lighting up:
- Check the power supply voltage and current rating.
- Ensure all connections are secure and polarity is correct.
- Verify that the controller or Arduino is functioning properly.
Incorrect colors or dim output:
- Check for loose or damaged connections on the R, G, or B pins.
- Ensure the MOSFETs or controller outputs are functioning correctly.
- Verify that the power supply is not overloaded.
Flickering LEDs:
- Check for insufficient power supply capacity or voltage drops.
- Use thicker wires for long strips to reduce resistance.
- Add a capacitor (e.g., 1000µF) across the power supply terminals to stabilize voltage.
Overheating:
- Ensure the strip is not enclosed in a poorly ventilated space.
- Reduce brightness or use a heat sink if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect multiple strips together?
A: Yes, but ensure the power supply can handle the total current draw. For long runs, use power injection at intervals to prevent voltage drops.
Q: How do I control individual LEDs on the strip?
A: The 12V RGB LED strip does not support individual LED control. For this functionality, use addressable LED strips like WS2812B or APA102.
Q: Can I use a 5V power supply?
A: No, the strip is designed for 12V operation. Using a lower voltage will result in dim or non-functional LEDs.
Q: Is the strip safe to use outdoors?
A: Only waterproof versions (IP65 or higher) are suitable for outdoor use. Ensure all connections are weatherproofed.