
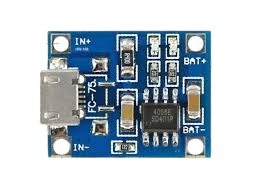
How to Use FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging module in Cirkit Designer
Design with FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging Module is a compact and efficient solution for charging lithium-ion batteries. It is designed to provide safe and reliable charging with features such as overcharge protection, adjustable output voltage, and high charging efficiency. This module is ideal for applications requiring rechargeable power sources, such as portable electronics, IoT devices, and DIY projects.
Explore Projects Built with FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer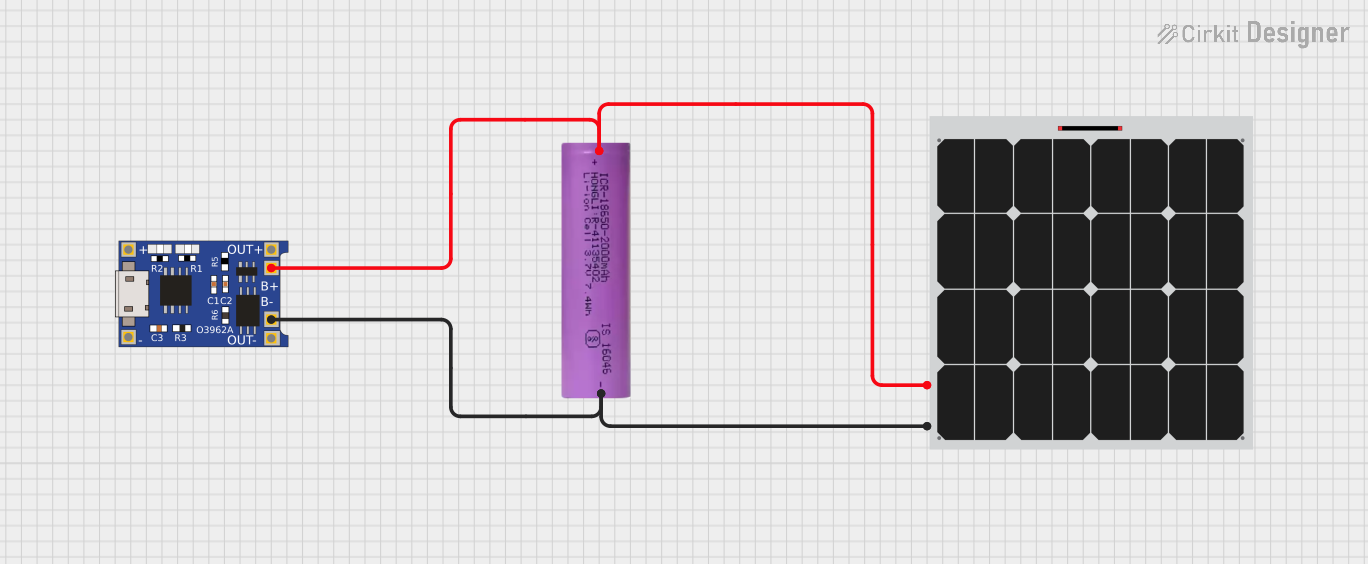
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with FC-75 Li-Ion Battery Charging module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries
- Powering portable electronic devices
- DIY electronics and robotics projects
- IoT devices requiring rechargeable power solutions
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the FC-75 module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.5V to 6V |
| Output Voltage Range | Adjustable (default: 4.2V) |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A |
| Battery Type Supported | Single-cell Li-Ion/Li-Po (3.7V) |
| Protection Features | Overcharge, overcurrent, short-circuit |
| Efficiency | Up to 92% |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 19mm x 5mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The FC-75 module has a simple pinout for easy integration into circuits:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| IN+ | Positive input voltage terminal (connect to power source, e.g., USB or adapter) |
| IN- | Negative input voltage terminal (connect to ground of power source) |
| BAT+ | Positive terminal for the lithium-ion battery |
| BAT- | Negative terminal for the lithium-ion battery |
| OUT+ | Positive output terminal (for powering external circuits, optional) |
| OUT- | Negative output terminal (for powering external circuits, optional) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the FC-75 Module in a Circuit
Connect the Power Source:
- Attach the positive terminal of your power source (e.g., USB 5V or DC adapter) to the
IN+pin. - Connect the ground of the power source to the
IN-pin.
- Attach the positive terminal of your power source (e.g., USB 5V or DC adapter) to the
Connect the Battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery to the
BAT+pin. - Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the
BAT-pin.
- Connect the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery to the
Optional Output Connection:
- If you want to power an external circuit while charging the battery, connect the load to the
OUT+andOUT-pins.
- If you want to power an external circuit while charging the battery, connect the load to the
Adjust the Output Voltage (if needed):
- Use the onboard potentiometer to adjust the output voltage. The default is set to 4.2V, which is suitable for most single-cell lithium-ion batteries.
Monitor Charging Status:
- The module typically includes an LED indicator to show the charging status:
- Red LED: Charging in progress
- Green LED: Charging complete
- The module typically includes an LED indicator to show the charging status:
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the specified range (4.5V to 6V) to avoid damaging the module.
- Use a heat sink or ensure proper ventilation if charging at the maximum current (1A) for extended periods.
- Verify the battery's specifications to ensure compatibility with the module's default output voltage (4.2V).
- Avoid short-circuiting the
BAT+andBAT-terminals, as this can damage the module and the battery.
Example: Using the FC-75 with an Arduino UNO
The FC-75 module can be used to power an Arduino UNO via its OUT+ and OUT- pins. Below is an example of how to monitor the battery voltage using the Arduino's analog input:
// Define the analog pin connected to the battery output
const int batteryPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog voltage
float batteryVoltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0) * 2;
// Convert the analog reading to voltage. Multiply by 2 if using a voltage divider.
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: If the battery voltage exceeds 5V, use a voltage divider to scale it down before connecting to the Arduino's analog pin.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Overheating:
- Cause: Charging at maximum current (1A) for extended periods without proper ventilation.
- Solution: Use a heat sink or ensure adequate airflow around the module.
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the input voltage is within the 4.5V to 6V range.
Output Voltage Not Adjustable:
- Cause: Faulty potentiometer or incorrect adjustment.
- Solution: Gently turn the potentiometer with a small screwdriver and verify the output voltage with a multimeter.
LED Indicators Not Working:
- Cause: Damaged LEDs or incorrect input voltage.
- Solution: Verify the input voltage and check the module for physical damage.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the FC-75 module to charge multiple batteries in series?
A1: No, the FC-75 is designed for single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries only. Charging multiple batteries in series requires a specialized balancing charger.
Q2: What happens if I connect a battery with a different nominal voltage?
A2: Using a battery with a nominal voltage other than 3.7V may result in improper charging or damage to the battery. Always ensure compatibility with the module's default output voltage (4.2V).
Q3: Can I use the module without a battery connected?
A3: Yes, the module can function as a voltage regulator to power external circuits, but it is primarily designed for charging batteries.
Q4: Is the module protected against reverse polarity?
A4: No, the FC-75 does not include reverse polarity protection. Ensure correct wiring to avoid damage.