
How to Use Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer in Cirkit Designer
Design with Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer by DFRobot is a versatile module designed to expand the capabilities of a single I2C bus. It allows up to eight I2C devices to be connected simultaneously, even if they share the same I2C address. By dynamically switching between different channels, this multiplexer eliminates address conflicts and simplifies the integration of multiple I2C devices in a single project.
Explore Projects Built with Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer
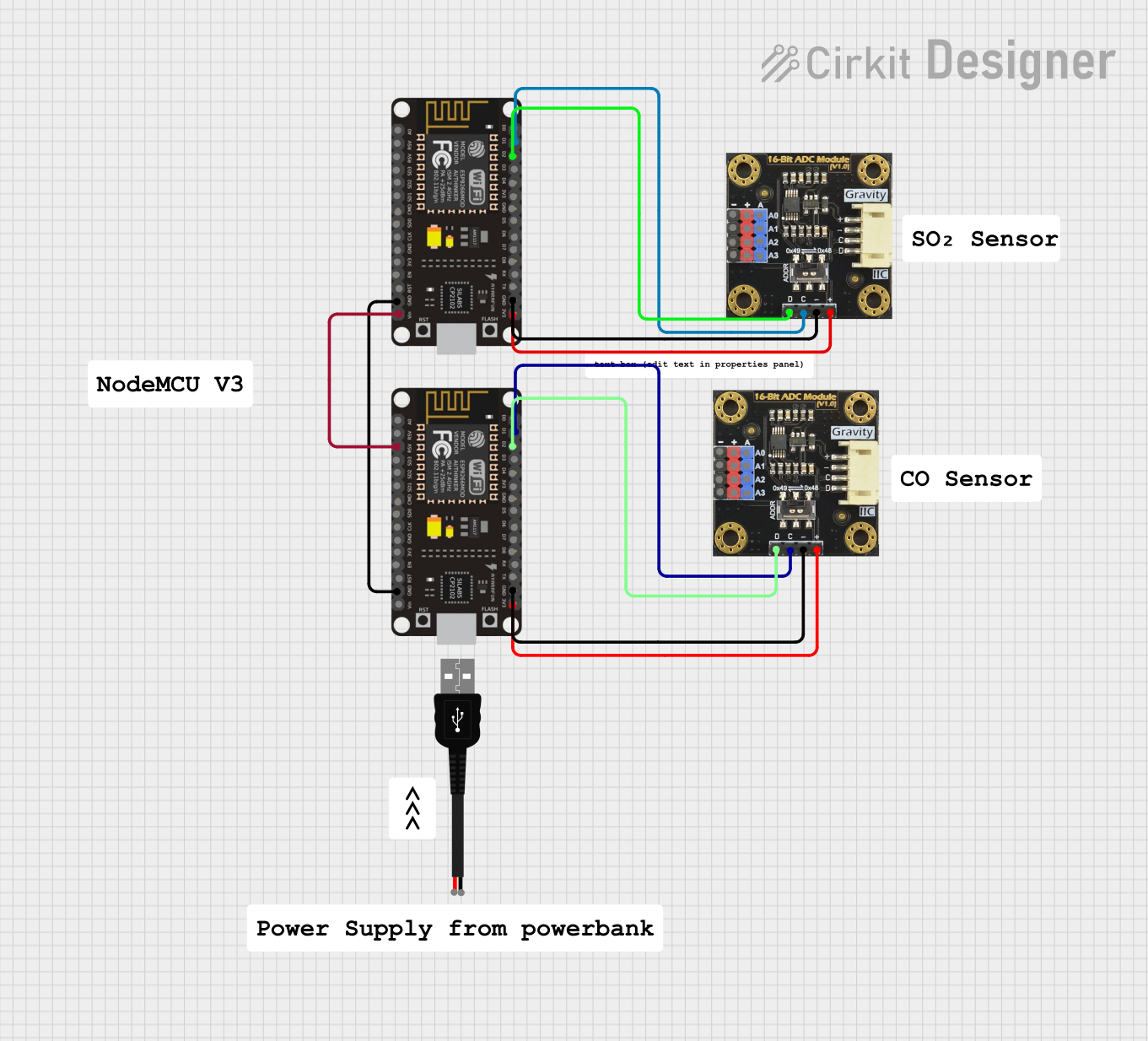
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer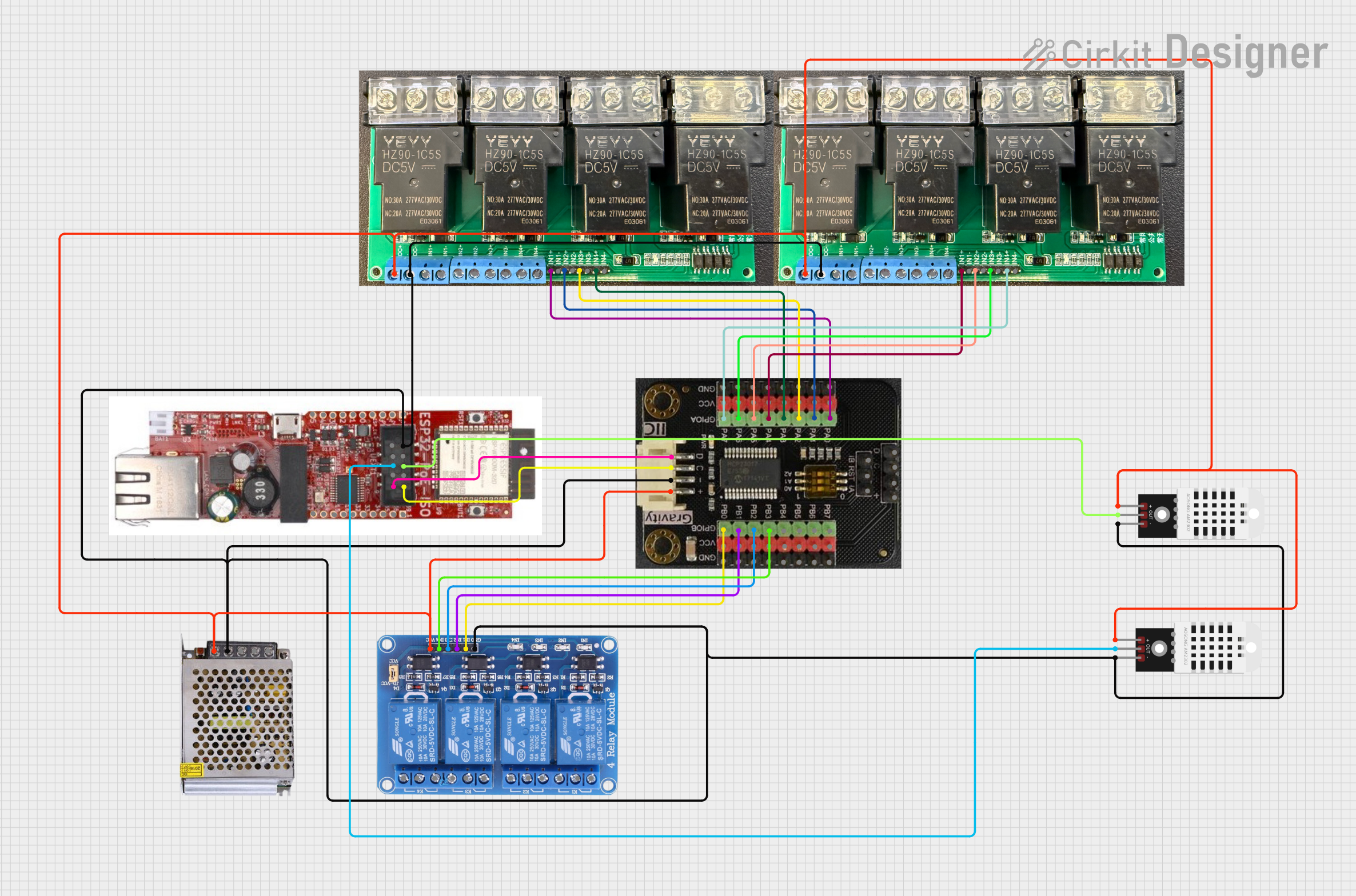
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer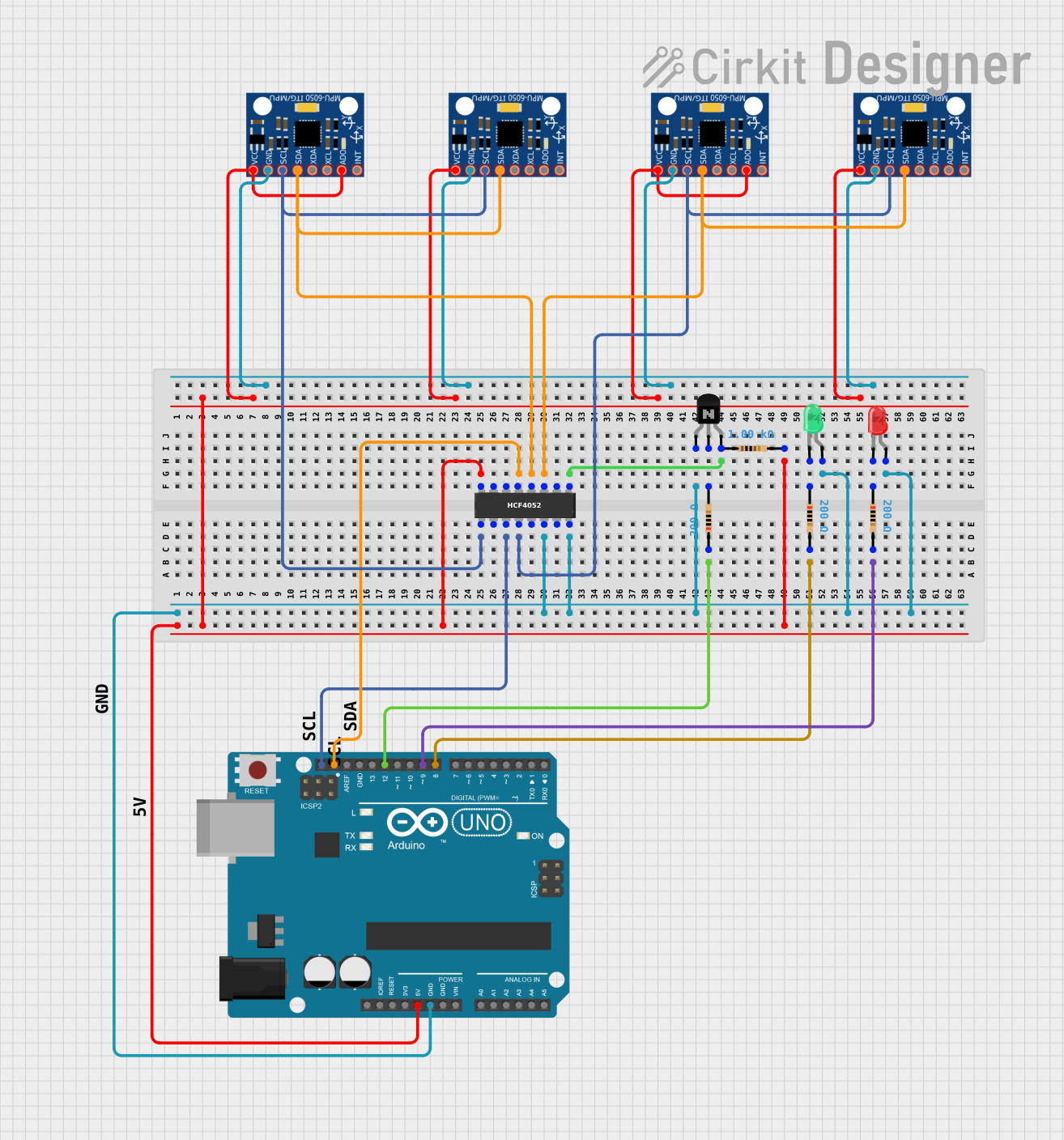
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer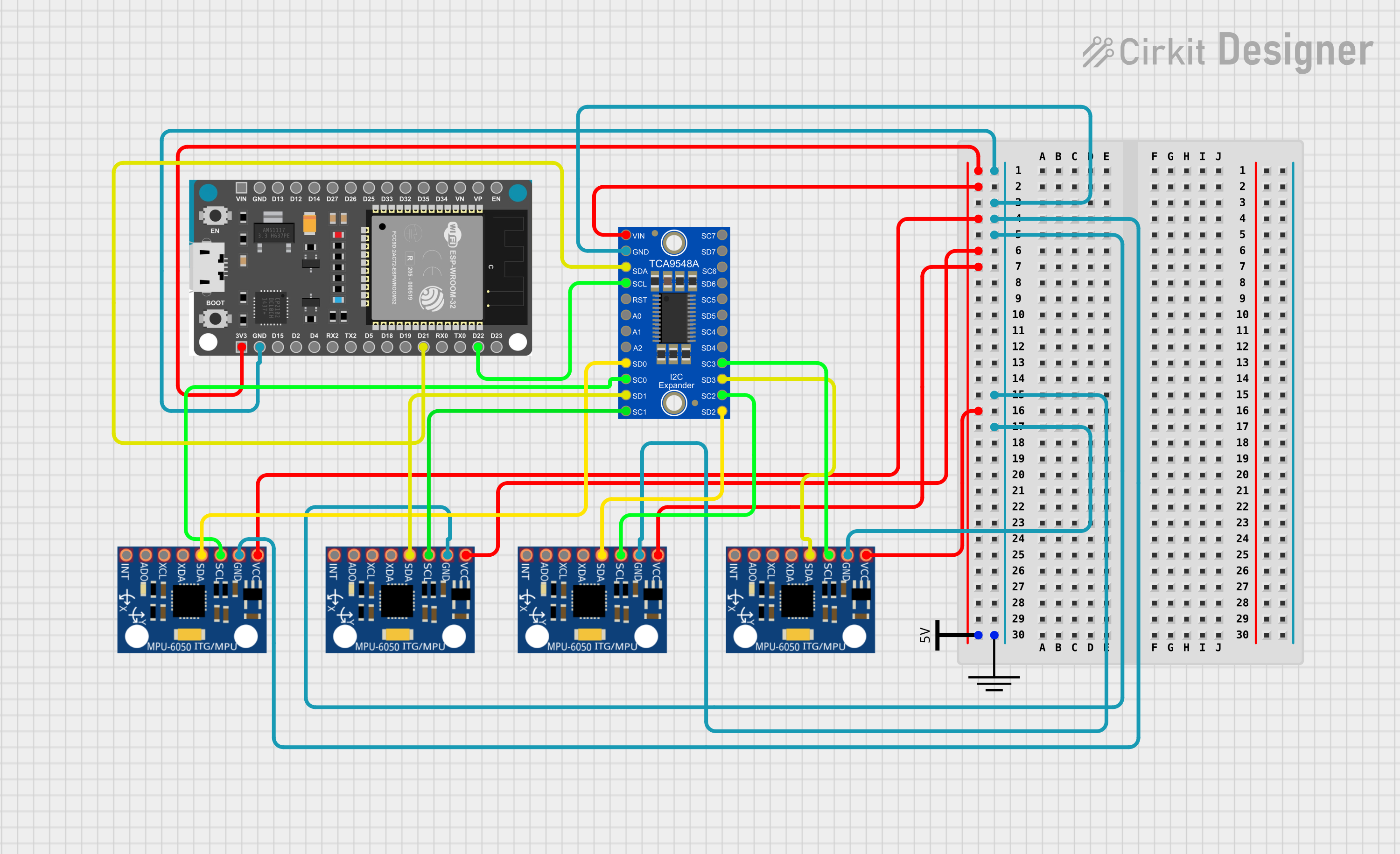
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Connecting multiple sensors or modules with identical I2C addresses.
- Expanding the I2C bus for complex projects with numerous peripherals.
- Prototyping and testing multiple I2C devices in parallel.
- Robotics, IoT, and automation systems requiring multiple I2C devices.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Communication Protocol | I2C |
| Default I2C Address | 0x70 (modifiable via solder pads) |
| Number of Channels | 8 |
| Maximum I2C Speed | 400 kHz |
| Dimensions | 42mm x 32mm |
| Mounting Holes | 3mm diameter |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer features the following pin layout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power input (3.3V to 5V). |
| GND | Ground connection. |
| SDA | I2C data line (connect to the master device's SDA). |
| SCL | I2C clock line (connect to the master device's SCL). |
| CH0-CH7 | Eight I2C channels for connecting devices. Each channel has its own SDA and SCL. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Multiplexer: Connect the VIN pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Connect the I2C Bus: Attach the SDA and SCL pins of the multiplexer to the corresponding SDA and SCL pins of your microcontroller or master device.
- Connect I2C Devices: Attach up to eight I2C devices to the CH0-CH7 channels. Each channel has its own SDA and SCL pins.
- Select a Channel: Use I2C commands to select the desired channel for communication. Only one channel can be active at a time.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Address Conflicts: The multiplexer is specifically designed to handle devices with identical I2C addresses. Ensure that devices connected to different channels do not share the same address on the same channel.
- I2C Address Configuration: The default I2C address of the multiplexer is 0x70. If multiple multiplexers are used, modify their addresses by adjusting the solder pads on the board.
- Pull-Up Resistors: The module includes onboard pull-up resistors for the I2C bus. If additional pull-up resistors are present in your circuit, ensure the total resistance is within acceptable limits to avoid signal integrity issues.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Gravity 1-8 I2C Multiplexer with an Arduino UNO:
#include <Wire.h>
// Define the I2C address of the multiplexer
#define TCA9548A_ADDR 0x70
// Function to select a specific channel on the multiplexer
void selectChannel(uint8_t channel) {
if (channel > 7) return; // Ensure the channel is within range (0-7)
Wire.beginTransmission(TCA9548A_ADDR);
Wire.write(1 << channel); // Activate the desired channel
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
Serial.println("Initializing I2C Multiplexer...");
selectChannel(0); // Select channel 0 as an example
}
void loop() {
// Example: Communicate with a device on channel 0
selectChannel(0); // Ensure channel 0 is active
Wire.beginTransmission(0x40); // Replace 0x40 with the I2C address of your device
Wire.write(0x00); // Example command to the device
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
I2C Devices Not Responding:
- Ensure the correct channel is selected using the
selectChannel()function. - Verify that the I2C address of the device is correct.
- Check the wiring and ensure proper connections to the SDA and SCL pins.
- Ensure the correct channel is selected using the
Address Conflicts Persist:
- Confirm that devices with identical addresses are connected to different channels.
- If using multiple multiplexers, ensure each has a unique I2C address.
Communication Errors at High Speeds:
- Reduce the I2C clock speed if communication errors occur at 400 kHz.
- Check for excessive capacitance on the I2C lines, which can degrade signal quality.
FAQs
Q: Can I use more than one multiplexer in a single project?
A: Yes, you can use multiple multiplexers by assigning each a unique I2C address. Modify the solder pads on the board to change the address.
Q: Do I need to deactivate a channel after use?
A: No, the multiplexer automatically deactivates other channels when a new channel is selected.
Q: Can I connect devices with different voltage levels?
A: No, all devices connected to the multiplexer must operate at the same voltage level as the multiplexer (3.3V or 5V). Use level shifters if necessary.
Q: How do I check if the multiplexer is working?
A: Use an I2C scanner sketch to detect the multiplexer at its default address (0x70). If detected, the multiplexer is functioning correctly.