
How to Use Zener Diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Zener Diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with Zener Diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Zener diode is a special type of semiconductor diode that permits current to flow in the forward direction like a typical diode, but also in the reverse direction if the voltage is larger than the Zener breakdown voltage. It is named after Clarence Zener, who discovered this electrical property. Zener diodes are widely used in electronic circuits for voltage regulation and as a voltage reference.
Explore Projects Built with Zener Diode
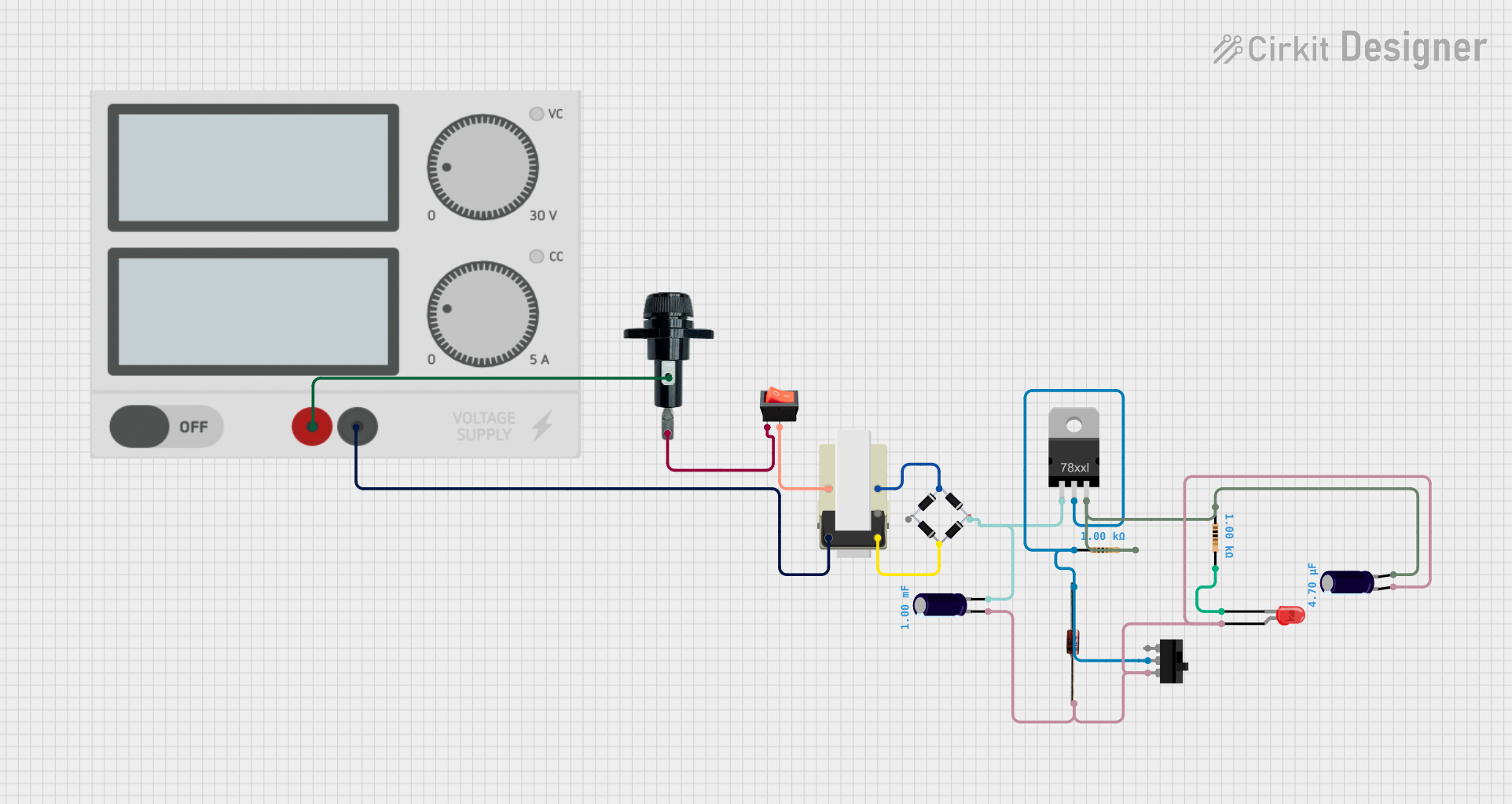
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer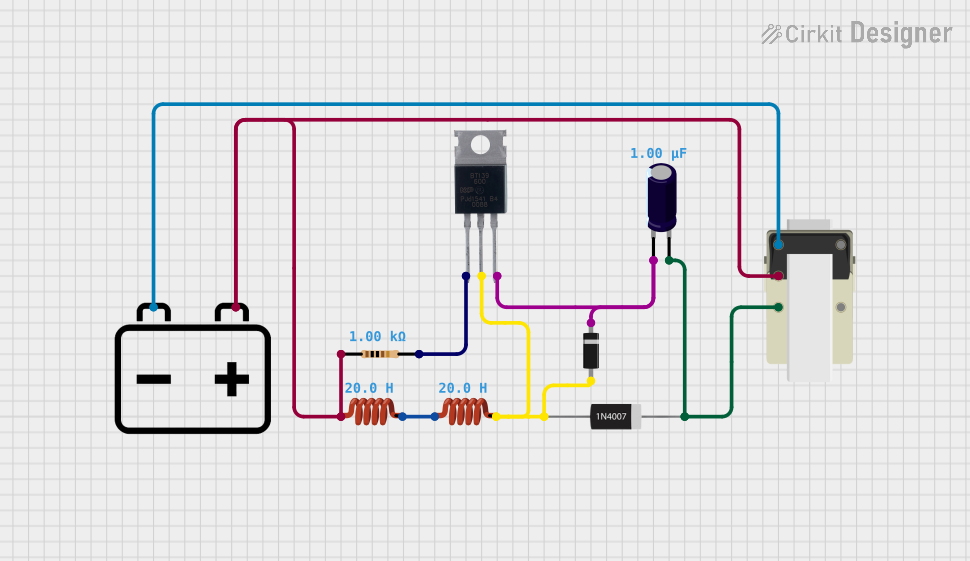
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer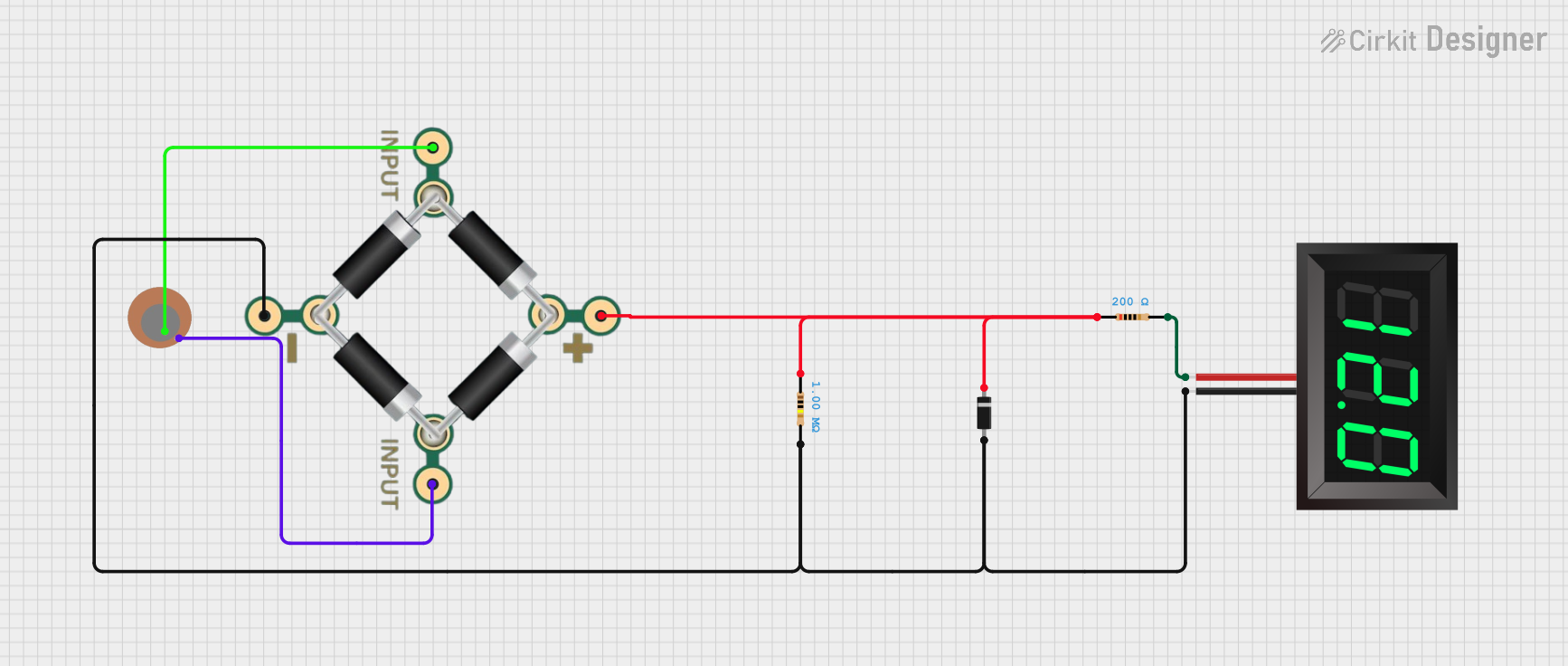
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer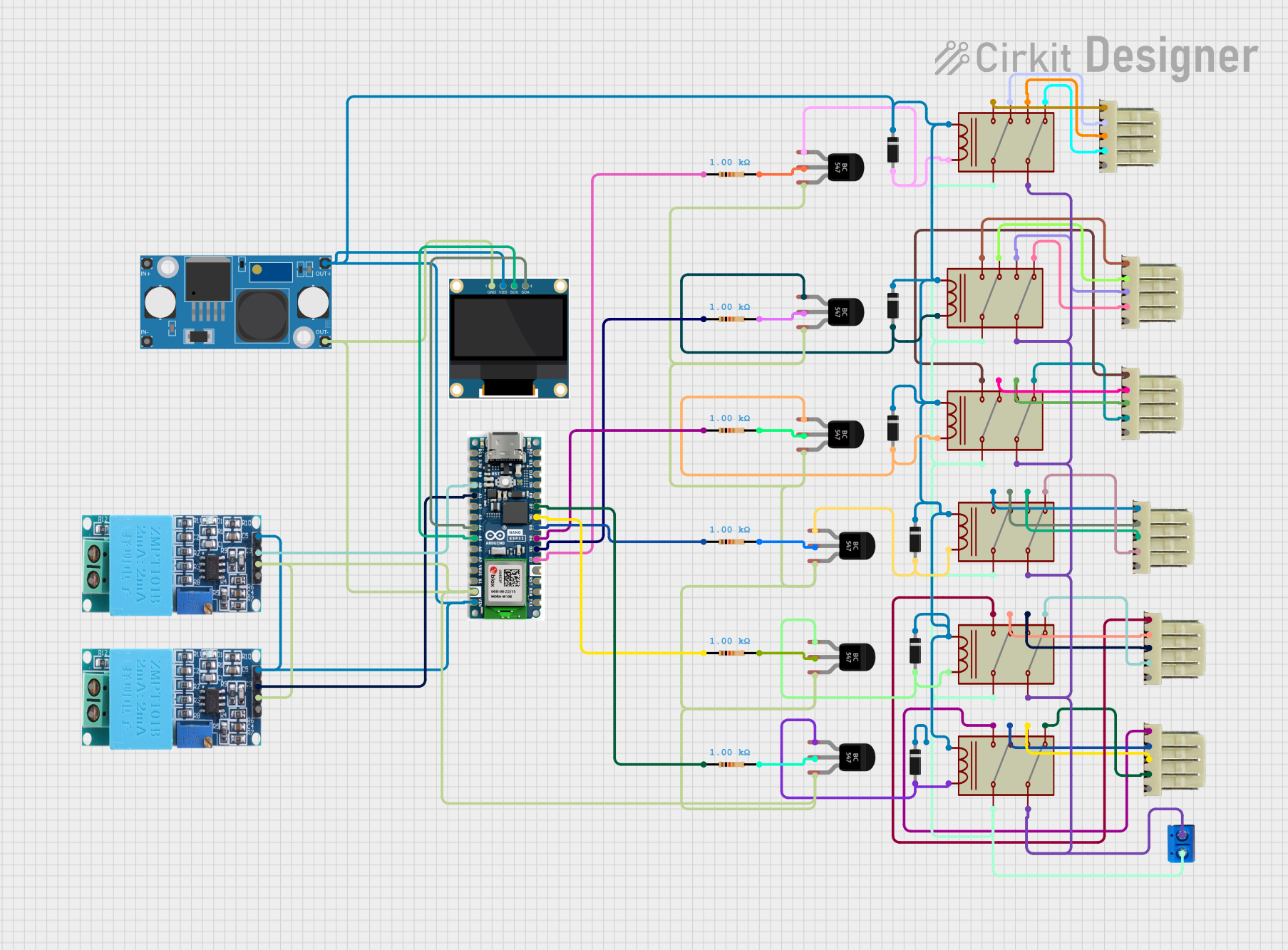
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Zener Diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voltage regulation in power supplies
- Protection circuits against overvoltage conditions
- Voltage reference in precision circuits
- Waveform clipping and shaping circuits
- Surge suppressors in data transmission lines
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Nominal Zener Voltage (Vz): The specified reverse breakdown voltage.
- Test Current (Iz): The current at which Vz is measured.
- Maximum Zener Impedance (Zz): The dynamic resistance of the Zener diode in the breakdown region.
- Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd): The maximum power the Zener diode can dissipate without damage.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode | The terminal to connect to the lower potential in forward bias |
| 2 | Cathode | The terminal to connect to the higher potential for Zener action |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Zener Diode in a Circuit
Voltage Regulation:
- Connect the cathode to the positive side of the power supply for reverse bias operation.
- Place a resistor in series with the anode to limit the current through the diode.
- The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law:
R = (Vin - Vz) / Iz, whereVinis the input voltage,Vzis the Zener voltage, andIzis the desired current through the Zener diode.
Voltage Reference:
- Use the Zener diode in conjunction with an operational amplifier to create a stable voltage reference.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the power dissipation does not exceed the maximum rating by calculating the power using
P = Vz * Iz. - Use a current-limiting resistor to prevent the Zener diode from drawing excessive current.
- For temperature-sensitive applications, consider the temperature coefficient of the Zener voltage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Excessive Heat: If the Zener diode is too hot, it may be dissipating too much power. Check the series resistor value and the power rating of the diode.
- No Voltage Regulation: If the Zener diode is not regulating voltage, ensure it is correctly biased and the input voltage is above the Zener voltage.
Solutions and Tips
- Use a heat sink if the power dissipation is close to the diode's maximum rating.
- Verify the input voltage and the Zener voltage to ensure proper operation.
- Check the series resistor for correct value and power rating.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Zener diode to drop voltage? A: Yes, Zener diodes can be used to drop voltage to a stable value, but they are not as efficient as linear voltage regulators for this purpose.
Q: What happens if the reverse current exceeds the maximum rating? A: Exceeding the maximum reverse current can lead to overheating and potential failure of the Zener diode.
Q: How do I choose the right Zener diode for my circuit? A: Select a Zener diode based on the required Zener voltage, the maximum current it needs to handle, and the power dissipation capability.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a Zener diode with an Arduino UNO to create a simple voltage reference:
// Define the analog pin connected to the Zener diode
const int zenerPin = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the voltage across the Zener diode
int sensorValue = analogRead(zenerPin);
// Convert the analog reading to voltage (for 5V Arduino boards)
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print out the voltage
Serial.println(voltage);
// Wait for a second
delay(1000);
}
This code reads the voltage across the Zener diode and prints it to the serial monitor. Ensure that the Zener diode is connected in reverse bias with a suitable series resistor to the analog pin A0.