
How to Use Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA in Cirkit Designer
Design with Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA is a compact and efficient photovoltaic module designed to convert sunlight into electrical energy. With a maximum output of 1 watt, 5 volts, and 200 milliamps, this solar panel is ideal for small-scale solar applications. It is lightweight, durable, and easy to integrate into various projects, making it a popular choice for hobbyists, students, and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA
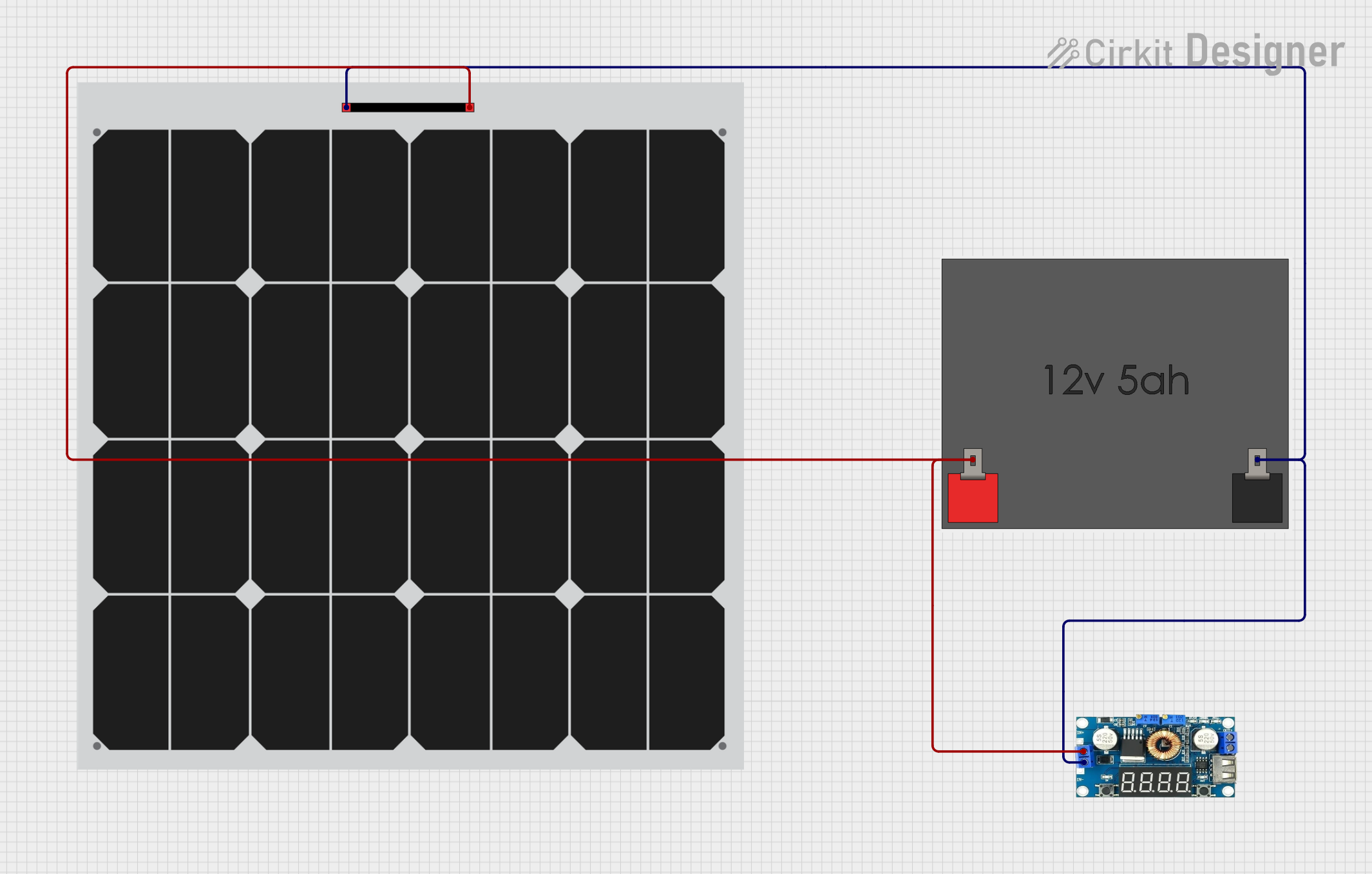
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer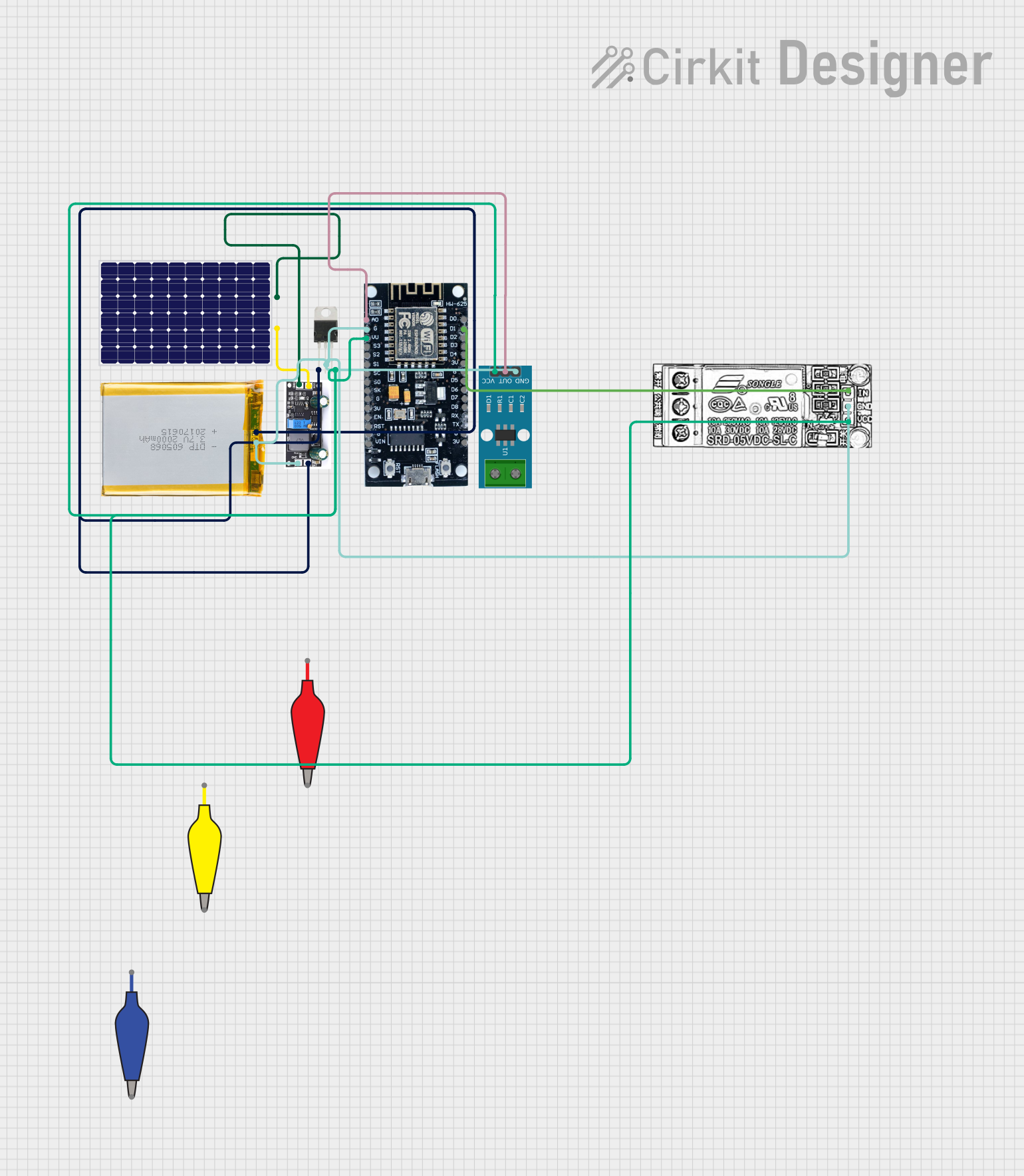
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer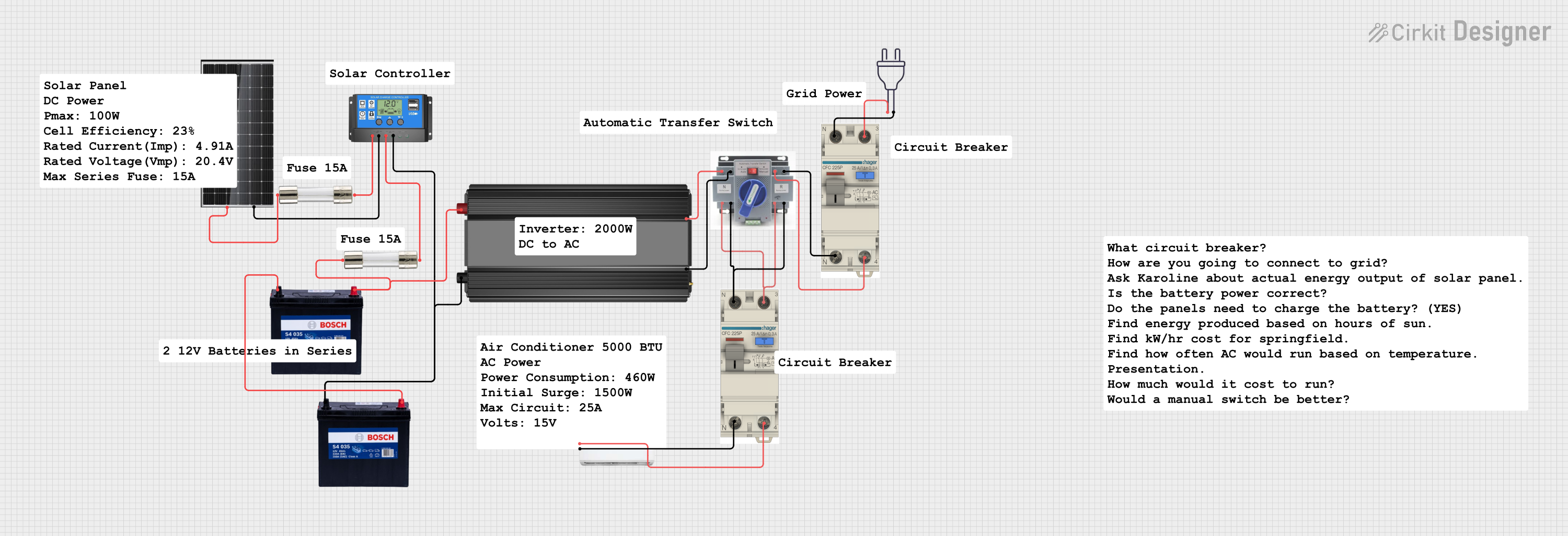
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer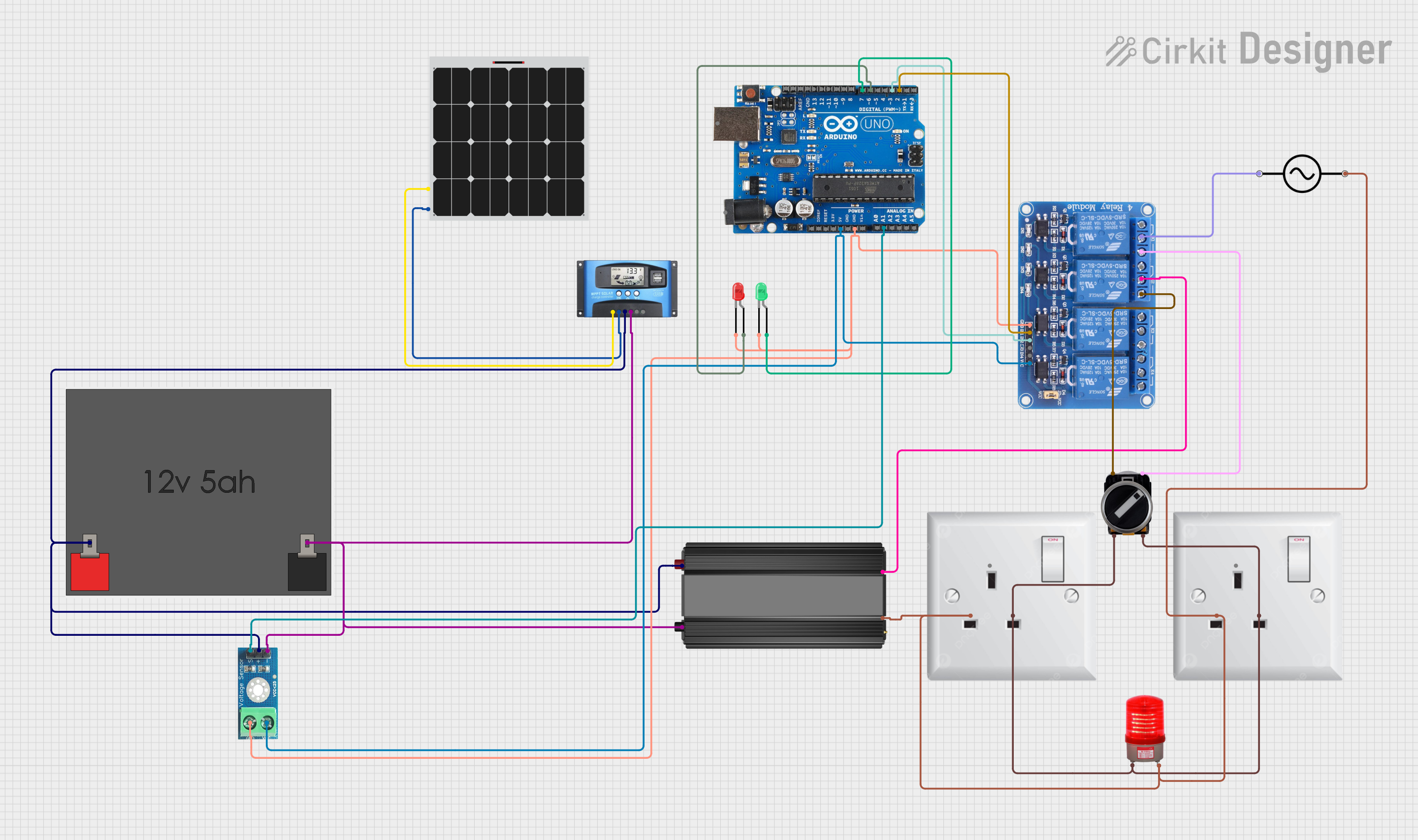
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging small batteries (e.g., Li-ion, NiMH)
- Powering low-power devices such as sensors, microcontrollers, or LED lights
- Portable solar-powered gadgets
- Educational projects and renewable energy demonstrations
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices in remote locations
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power (Pmax) | 1 Watt |
| Voltage at Pmax (Vmp) | 5 Volts |
| Current at Pmax (Imp) | 200 mA |
| Open Circuit Voltage | ~5.5 Volts |
| Short Circuit Current | ~220 mA |
| Dimensions | ~110 mm x 69 mm x 3 mm |
| Weight | ~50 grams |
| Material | Monocrystalline Silicon |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The solar panel has two output terminals, typically labeled as follows:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive (+) | Positive terminal for power output |
| 2 | Negative (-) | Negative terminal (ground) for output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Solar Panel in a Circuit
- Positioning the Panel: Place the solar panel in direct sunlight for optimal performance. Ensure there are no obstructions (e.g., shadows, dirt) on the panel's surface.
- Connecting the Terminals:
- Connect the positive terminal of the solar panel to the positive input of your circuit or battery.
- Connect the negative terminal to the ground or negative input of your circuit.
- Using a Voltage Regulator (Optional): If your circuit requires a stable voltage, use a 5V voltage regulator (e.g., LM7805) to ensure consistent output.
- Charging a Battery: When charging a battery, use a charge controller to prevent overcharging and to regulate the current flow.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Sunlight Intensity: The output of the solar panel depends on the intensity of sunlight. Ensure the panel is exposed to direct sunlight for maximum efficiency.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not connect devices that draw more than 200 mA, as this may damage the panel or reduce its lifespan.
- Use a Diode: To prevent reverse current flow (e.g., at night), connect a Schottky diode (e.g., 1N5819) in series with the positive terminal.
- Weatherproofing: If used outdoors, ensure the panel is adequately protected from water and extreme weather conditions.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Solar Panel 1W 5V 200mA can be used to power an Arduino UNO with a rechargeable battery. Below is an example setup:
- Connect the solar panel to a 3.7V Li-ion battery through a charge controller module (e.g., TP4056).
- Use a DC-DC boost converter to step up the battery voltage to 5V for the Arduino UNO.
Sample Arduino Code
// Example: Reading a sensor powered by a solar panel and displaying data
// Ensure the solar panel is connected to a battery and the Arduino is powered
// through the battery's output.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Low or No Output Voltage
- Cause: Insufficient sunlight or shading on the panel.
- Solution: Ensure the panel is in direct sunlight and clean the surface if dirty.
Device Not Powering On
- Cause: The connected device may require more current than the panel can provide.
- Solution: Check the device's power requirements and ensure they do not exceed 200 mA.
Reverse Current Flow
- Cause: At night or in low light, current may flow back into the panel.
- Solution: Use a Schottky diode in series with the positive terminal to block reverse current.
Overheating
- Cause: Prolonged exposure to extreme heat or overloading.
- Solution: Ensure proper ventilation and avoid exceeding the panel's current rating.
FAQs
Q1: Can I connect multiple solar panels together?
A1: Yes, you can connect multiple panels in series to increase voltage or in parallel to increase current. Ensure the combined output matches your circuit's requirements.
Q2: Can this panel charge a smartphone directly?
A2: No, the panel's output is not sufficient to charge a smartphone directly. Use a power bank or a charge controller with a battery for this purpose.
Q3: How do I store the solar panel when not in use?
A3: Store the panel in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation over time.