
How to Use 16x2 I2C LCD: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with 16x2 I2C LCD in Cirkit Designer
Design with 16x2 I2C LCD in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 16x2 I2C LCD is a liquid crystal display capable of showing 16 characters per line across 2 lines. It is equipped with an I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) interface, which significantly reduces the number of pins required for connection compared to traditional parallel LCDs. This makes it an ideal choice for projects where pin availability is limited or simplicity is desired.
Explore Projects Built with 16x2 I2C LCD
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer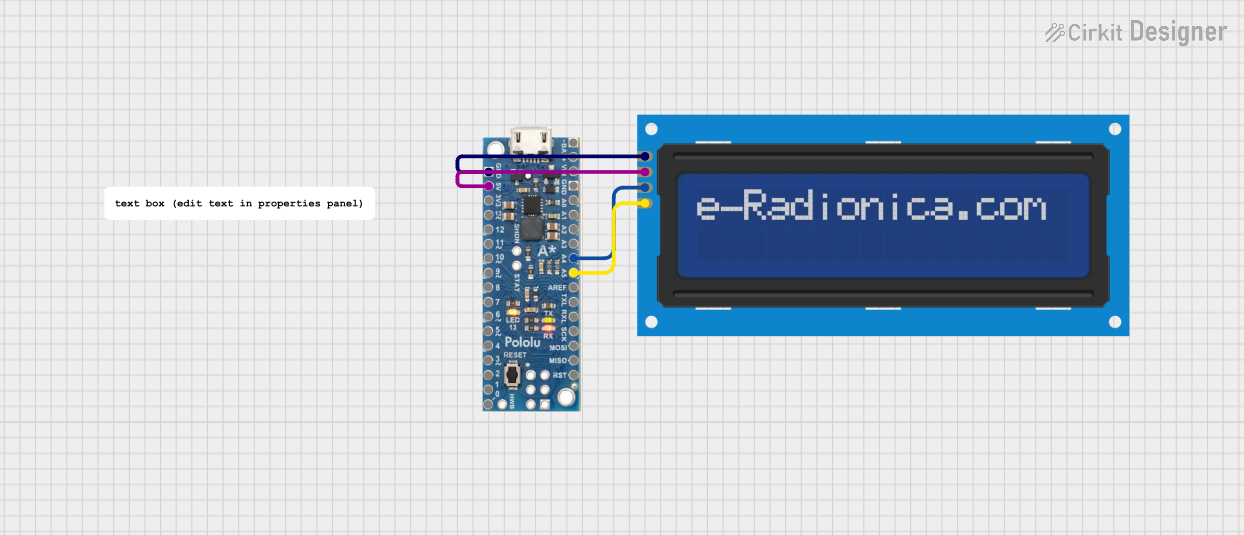
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 16x2 I2C LCD

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Displaying sensor readings in real-time
- User interfaces for embedded systems
- Menu systems for microcontroller-based projects
- Debugging and status monitoring in prototypes
- Educational projects and DIY electronics
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Display Type: 16x2 character LCD
- Interface: I2C (4 pins: VCC, GND, SDA, SCL)
- Operating Voltage: 5V DC (some modules support 3.3V)
- Backlight: LED with adjustable brightness
- I2C Address: Typically 0x27 or 0x3F (configurable on some modules)
- Character Size: 5x8 dot matrix
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
- Dimensions: Approximately 80mm x 36mm x 12mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 16x2 I2C LCD has a 4-pin interface for easy connection. Below is the pinout:
| Pin Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply (5V or 3.3V) | Connect to the microcontroller's power pin. |
| GND | Ground | Connect to the microcontroller's ground. |
| SDA | Serial Data Line | Connect to the microcontroller's SDA pin. |
| SCL | Serial Clock Line | Connect to the microcontroller's SCL pin. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Wiring the LCD:
- Connect the
VCCpin of the LCD to the 5V (or 3.3V) pin of the microcontroller. - Connect the
GNDpin of the LCD to the ground (GND) of the microcontroller. - Connect the
SDApin of the LCD to the SDA pin of the microcontroller (e.g., A4 on Arduino UNO). - Connect the
SCLpin of the LCD to the SCL pin of the microcontroller (e.g., A5 on Arduino UNO).
- Connect the
Install Required Libraries:
- Use the Arduino IDE and install the
LiquidCrystal_I2Clibrary. To do this:- Go to
Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries. - Search for
LiquidCrystal_I2Cand install the library by Frank de Brabander.
- Go to
- Use the Arduino IDE and install the
Write and Upload Code:
- Use the example code below to test the LCD.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // Include the LiquidCrystal_I2C library
// Initialize the LCD with I2C address 0x27 and 16x2 dimensions
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
void setup() {
lcd.begin(); // Initialize the LCD
lcd.backlight(); // Turn on the backlight
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); // Set the cursor to the first column, first row
lcd.print("Hello, World!"); // Print a message on the first row
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); // Set the cursor to the first column, second row
lcd.print("I2C LCD Test"); // Print a message on the second row
}
void loop() {
// No actions in the loop for this example
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- I2C Address: Ensure the correct I2C address is used in the code. If the LCD does not respond, use an I2C scanner sketch to determine the address.
- Power Supply: Verify that the LCD is powered with the correct voltage (5V or 3.3V, depending on the module).
- Contrast Adjustment: Some modules have a potentiometer to adjust the contrast. Turn it to ensure characters are visible.
- Pull-Up Resistors: If the I2C bus is not functioning correctly, check if pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) are present on the SDA and SCL lines. Most I2C LCD modules include these resistors.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Display or Backlight:
- Ensure the
VCCandGNDconnections are correct. - Verify the power supply voltage matches the module's requirements.
- Check if the backlight is enabled in the code (
lcd.backlight()).
- Ensure the
Incorrect or No Text Displayed:
- Confirm the I2C address in the code matches the module's address.
- Use an I2C scanner sketch to detect the correct address.
- Adjust the contrast potentiometer on the module.
Flickering or Unstable Display:
- Check for loose connections or poor solder joints.
- Ensure proper pull-up resistors are present on the I2C lines.
Compilation Errors in Arduino IDE:
- Ensure the
LiquidCrystal_I2Clibrary is installed correctly. - Use the latest version of the Arduino IDE and libraries.
- Ensure the
FAQs
Q1: How do I find the I2C address of my LCD?
A1: Use an I2C scanner sketch available online. It will scan the I2C bus and display the address of connected devices.
Q2: Can I use the 16x2 I2C LCD with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A2: Yes, but ensure the module supports 3.3V operation. If not, use a level shifter to convert 3.3V signals to 5V.
Q3: Can I connect multiple I2C devices to the same bus?
A3: Yes, as long as each device has a unique I2C address. Use an I2C multiplexer if address conflicts occur.
Q4: Why is my text not aligned properly on the display?
A4: Ensure the lcd.setCursor() function is used correctly to position the text. The first column is 0, and the first row is 0.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot the 16x2 I2C LCD in your projects.