
How to Use NAU7802 ADC Converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
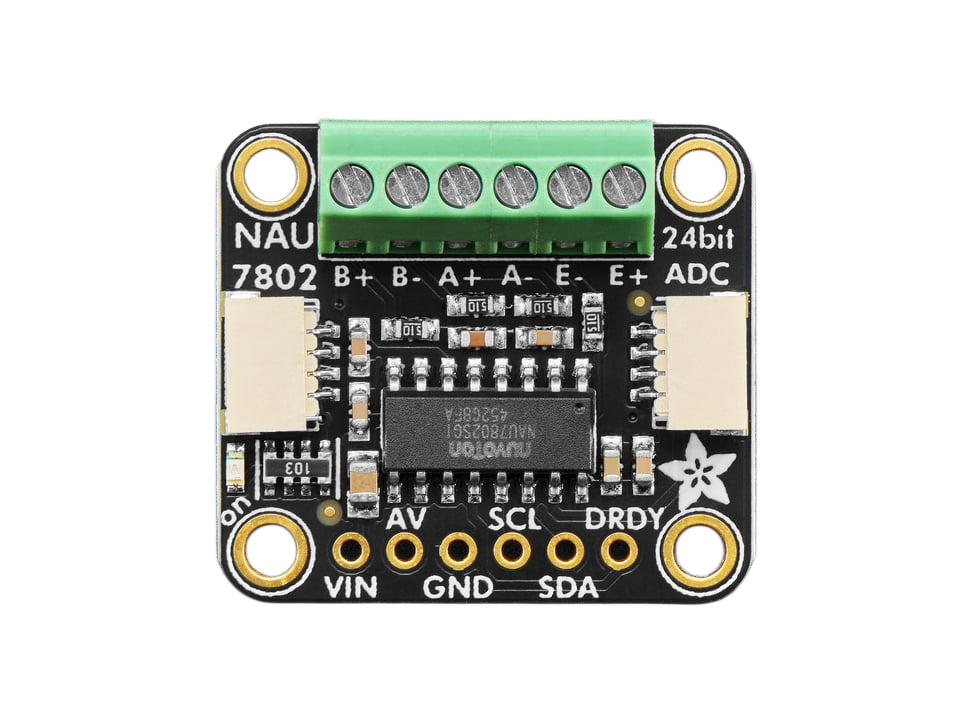
 Design with NAU7802 ADC Converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with NAU7802 ADC Converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The NAU7802 24-Bit ADC by Adafruit is a high-precision, low-power analog-to-digital converter (ADC) designed for applications requiring accurate measurement of analog signals. It is particularly well-suited for weighing scales, load cells, and other precision measurement systems. The NAU7802 features a 24-bit resolution, an integrated programmable gain amplifier (PGA), and supports I2C communication, making it easy to interface with microcontrollers such as the Arduino UNO or Raspberry Pi.
Explore Projects Built with NAU7802 ADC Converter
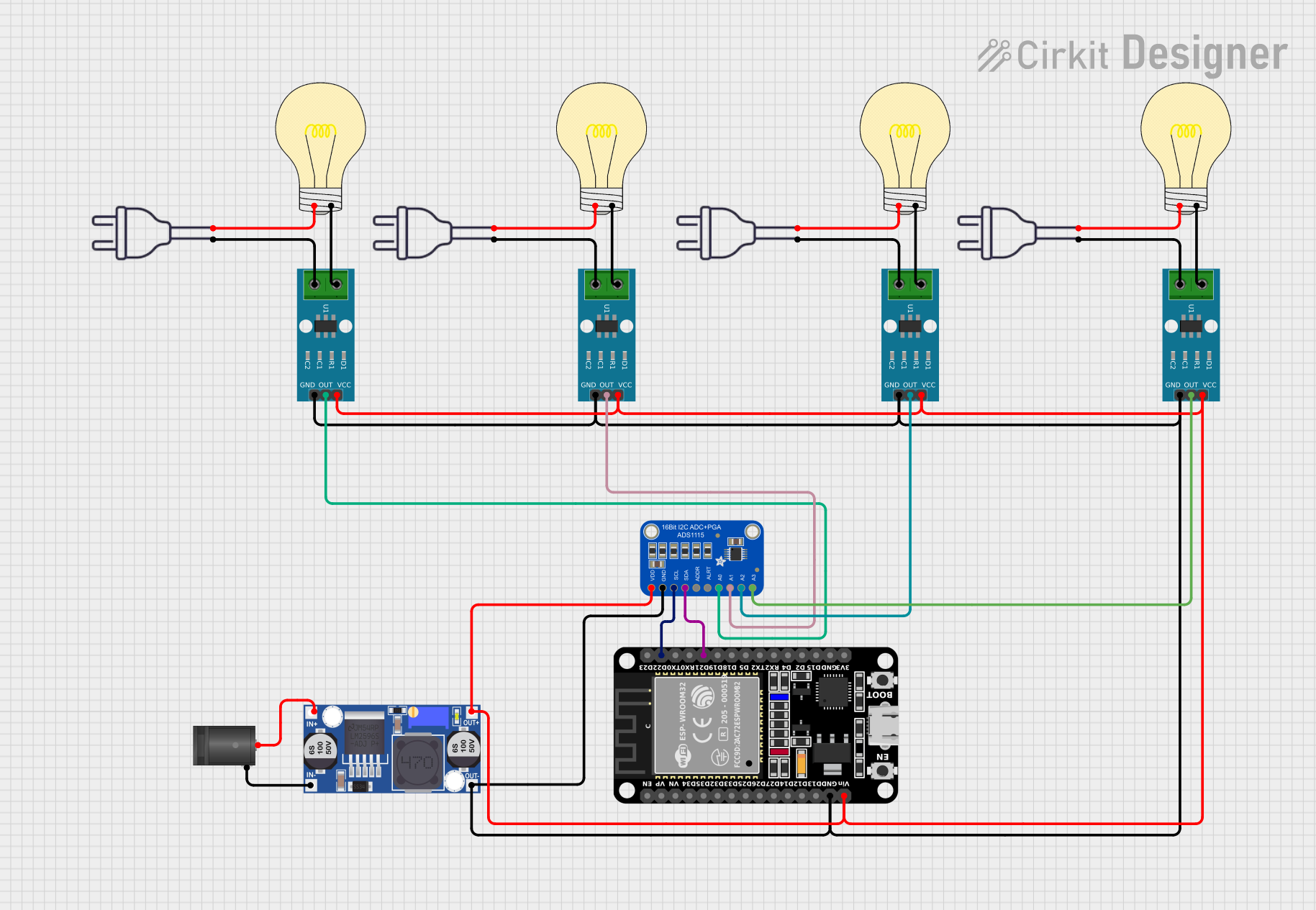
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer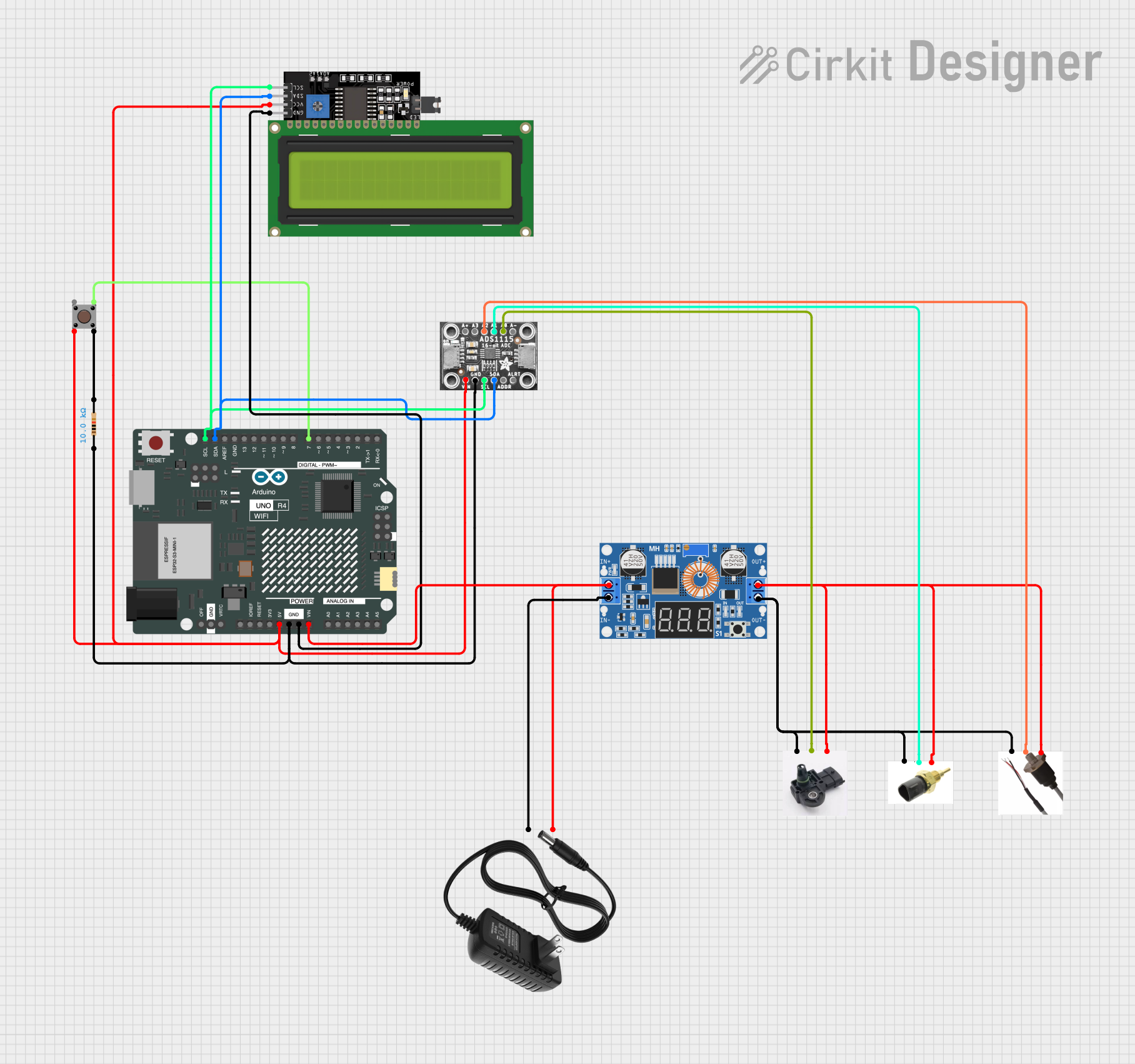
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer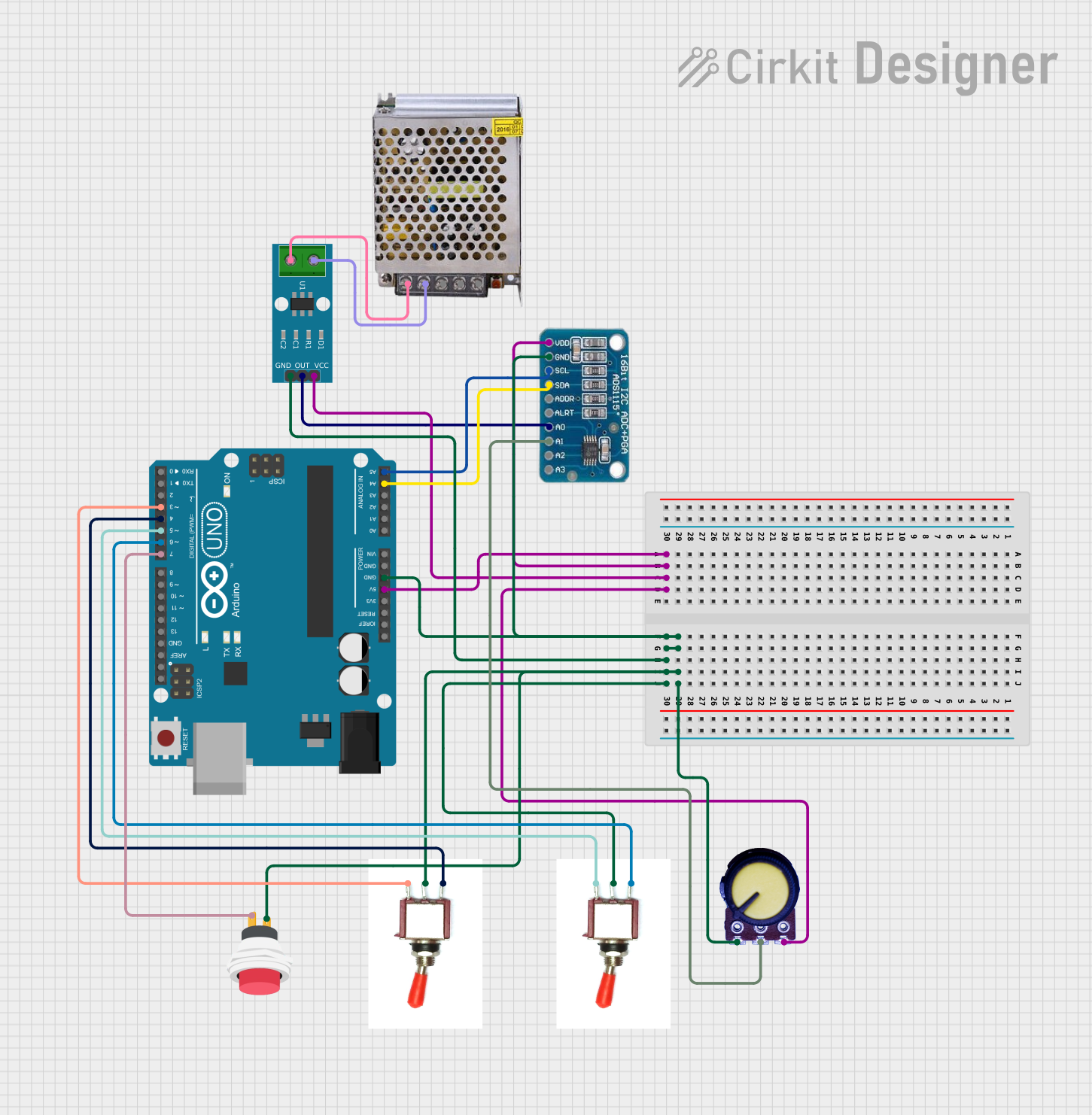
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer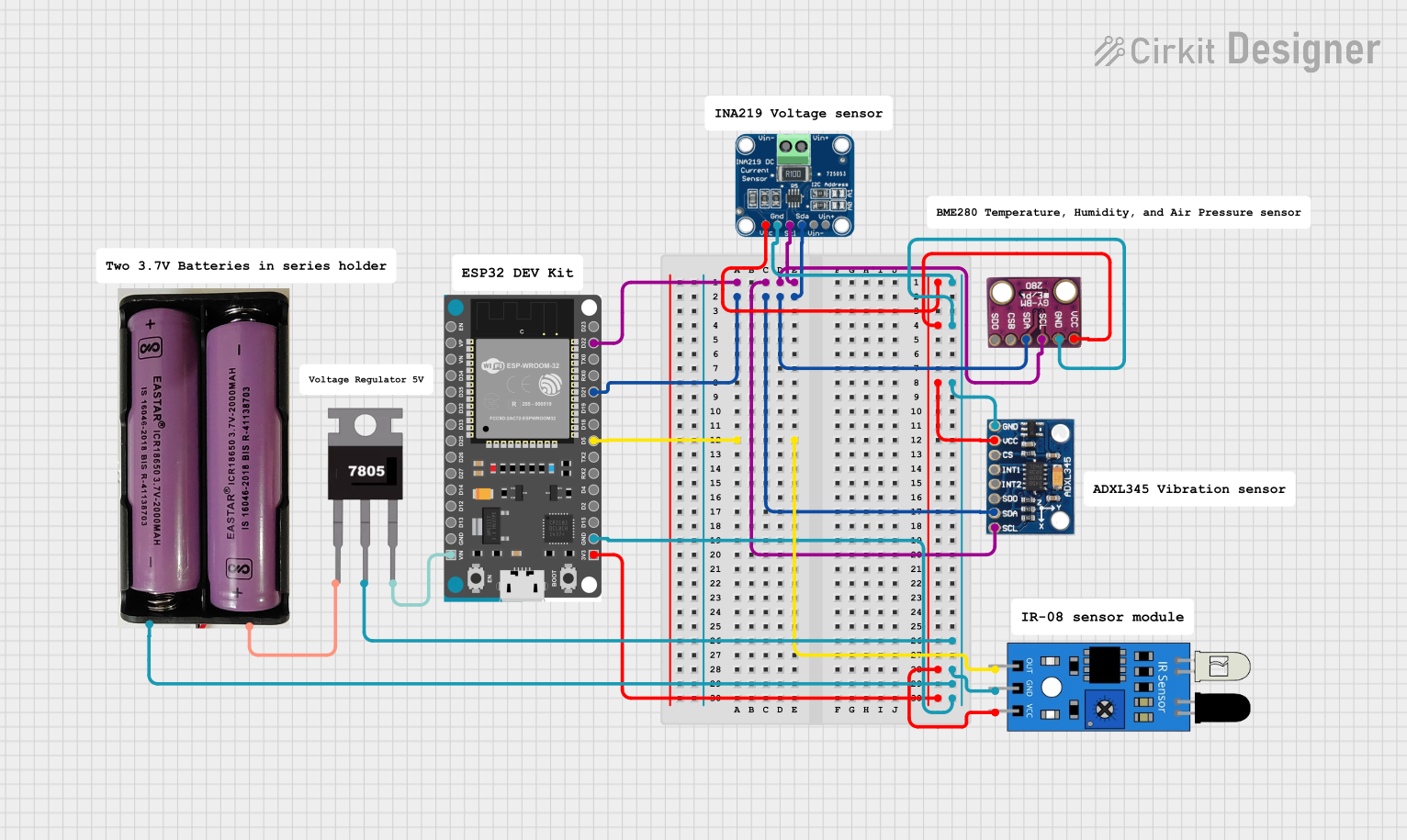
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with NAU7802 ADC Converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Weighing scales and load cell systems
- Industrial measurement systems
- Portable instrumentation
- IoT devices requiring precise analog signal measurement
- Sensor data acquisition
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the NAU7802 ADC:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Resolution | 24-bit |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to AVDD (Analog Supply Voltage) |
| Analog Supply Voltage (AVDD) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Digital Supply Voltage (DVDD) | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Programmable Gain | 1x, 2x, 4x, 8x, 16x, 32x, 64x |
| Communication Interface | I2C |
| I2C Address (Default) | 0x2A |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | Low-power mode: ~1.2mA |
Pin Configuration
The NAU7802 ADC is available on a breakout board with the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power input (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| SCL | I2C clock line |
| SDA | I2C data line |
| DRDY | Data ready output (optional, for interrupt use) |
| F1, F2 | Filter pins (not typically used in basic setups) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the NAU7802 to an Arduino UNO
To use the NAU7802 ADC with an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
Wiring:
- Connect the
VINpin of the NAU7802 to the 5V pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
GNDpin of the NAU7802 to the GND pin on the Arduino. - Connect the
SCLpin of the NAU7802 to the A5 pin on the Arduino (I2C clock line). - Connect the
SDApin of the NAU7802 to the A4 pin on the Arduino (I2C data line).
- Connect the
Install Required Libraries:
- Install the Adafruit NAU7802 library from the Arduino Library Manager.
Example Code: Use the following example code to read data from the NAU7802:
#include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_NAU7802.h> // Create an instance of the NAU7802 ADC Adafruit_NAU7802 nau7802; void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication while (!Serial); // Wait for the serial monitor to open // Initialize the NAU7802 if (!nau7802.begin()) { Serial.println("Failed to find NAU7802 chip!"); while (1); // Halt execution if the chip is not found } Serial.println("NAU7802 found!"); // Calibrate the internal offset if (!nau7802.calibrateAFE()) { Serial.println("Failed to calibrate AFE!"); while (1); // Halt execution if calibration fails } Serial.println("Calibration complete."); } void loop() { // Check if data is ready if (nau7802.available()) { // Read the raw ADC value int32_t adcValue = nau7802.read(); Serial.print("ADC Value: "); Serial.println(adcValue); } delay(100); // Small delay for readability }
Important Considerations
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the operating range of the NAU7802 (2.7V to 5.5V for AVDD).
- I2C Pull-Up Resistors: The breakout board includes pull-up resistors for the I2C lines. If multiple I2C devices are connected, ensure the total pull-up resistance is appropriate.
- Calibration: Always perform an internal offset calibration (
calibrateAFE()) before taking measurements to ensure accuracy. - Load Cell Connection: When using the NAU7802 with a load cell, connect the load cell's excitation and signal lines to the appropriate pins on the breakout board.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
The NAU7802 is not detected on the I2C bus:
- Ensure the wiring is correct and matches the pin configuration.
- Verify that the I2C address (default: 0x2A) is not conflicting with other devices on the bus.
- Check the pull-up resistors on the I2C lines.
ADC readings are unstable or noisy:
- Ensure proper grounding and shielding of the analog input signals.
- Use a stable power supply to minimize noise.
- Verify that the load cell or sensor is properly connected and calibrated.
Calibration fails:
- Ensure the load cell or sensor is not under stress during calibration.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is stable and within the specified range.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the NAU7802 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the NAU7802 supports a wide range of supply voltages (2.7V to 5.5V for AVDD). Ensure the I2C logic levels are compatible with your microcontroller.
Q: What is the maximum sampling rate of the NAU7802?
A: The NAU7802 supports a maximum sampling rate of 320 samples per second (SPS), depending on the selected gain and filter settings.
Q: How do I change the I2C address of the NAU7802?
A: The I2C address of the NAU7802 is fixed at 0x2A and cannot be changed. If multiple NAU7802 devices are needed, consider using an I2C multiplexer.
Q: Can I use the NAU7802 for non-weighing applications?
A: Yes, the NAU7802 can be used for any application requiring high-precision analog-to-digital conversion, such as sensor data acquisition or instrumentation.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the NAU7802 ADC into your projects and achieve accurate, high-resolution measurements.