
How to Use Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
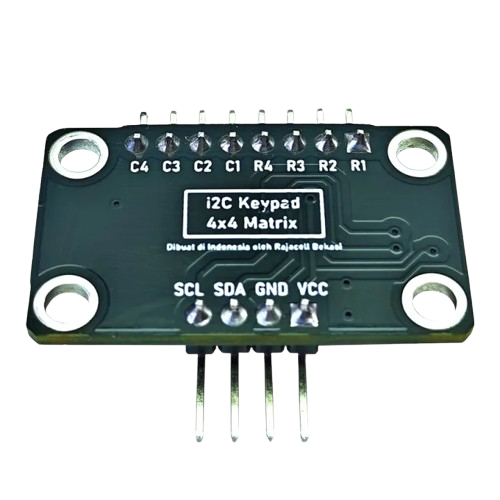
 Design with Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C in Cirkit Designer
Design with Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C is a versatile electronic component designed to simplify the process of interfacing a 4x4 matrix keypad with microcontrollers. By converting the keypad's row-column signals into I2C communication, this module reduces the number of GPIO pins required and streamlines the process of reading key presses. It is particularly useful in applications where GPIO pin availability is limited or where I2C communication is preferred.
Explore Projects Built with Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C
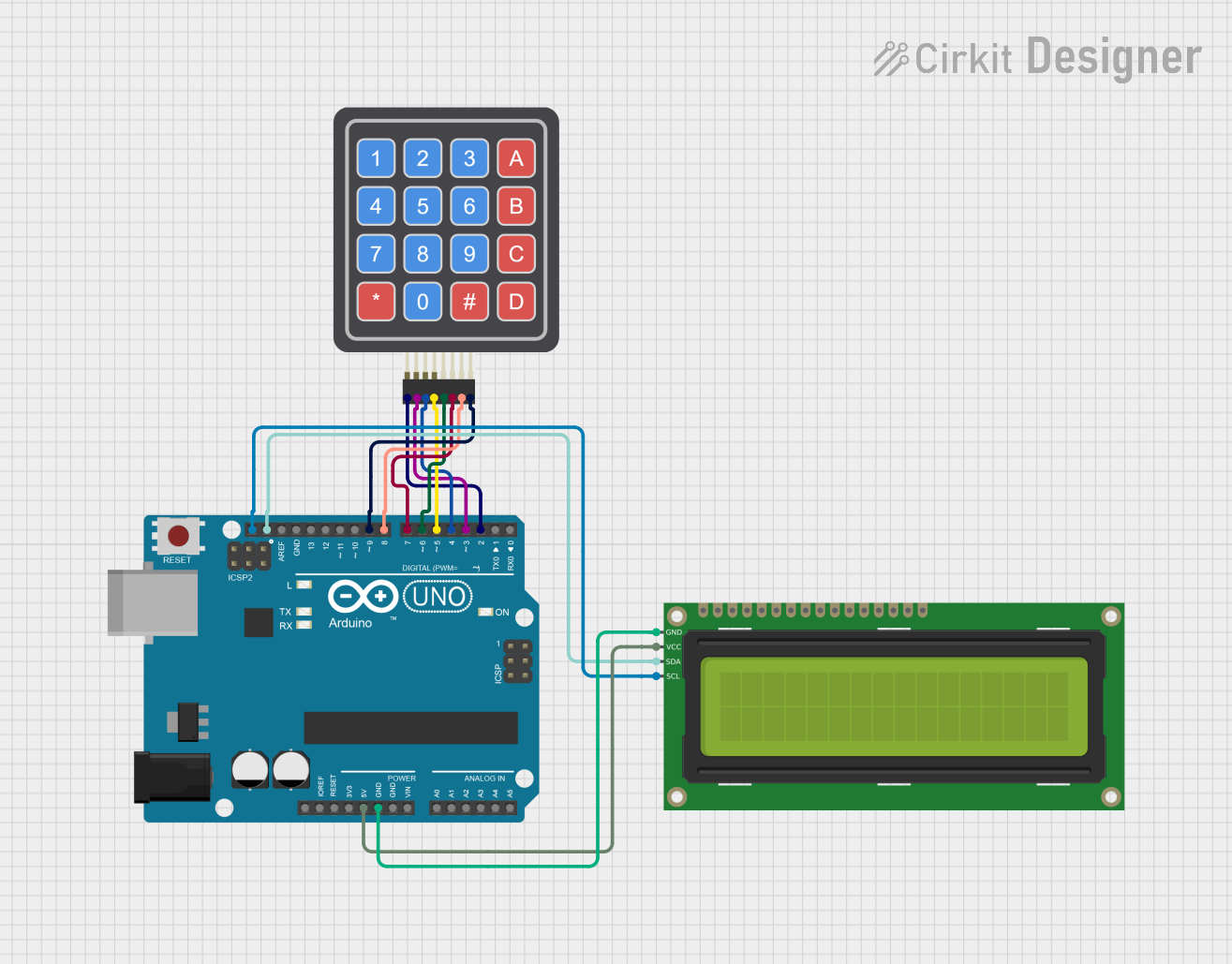
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer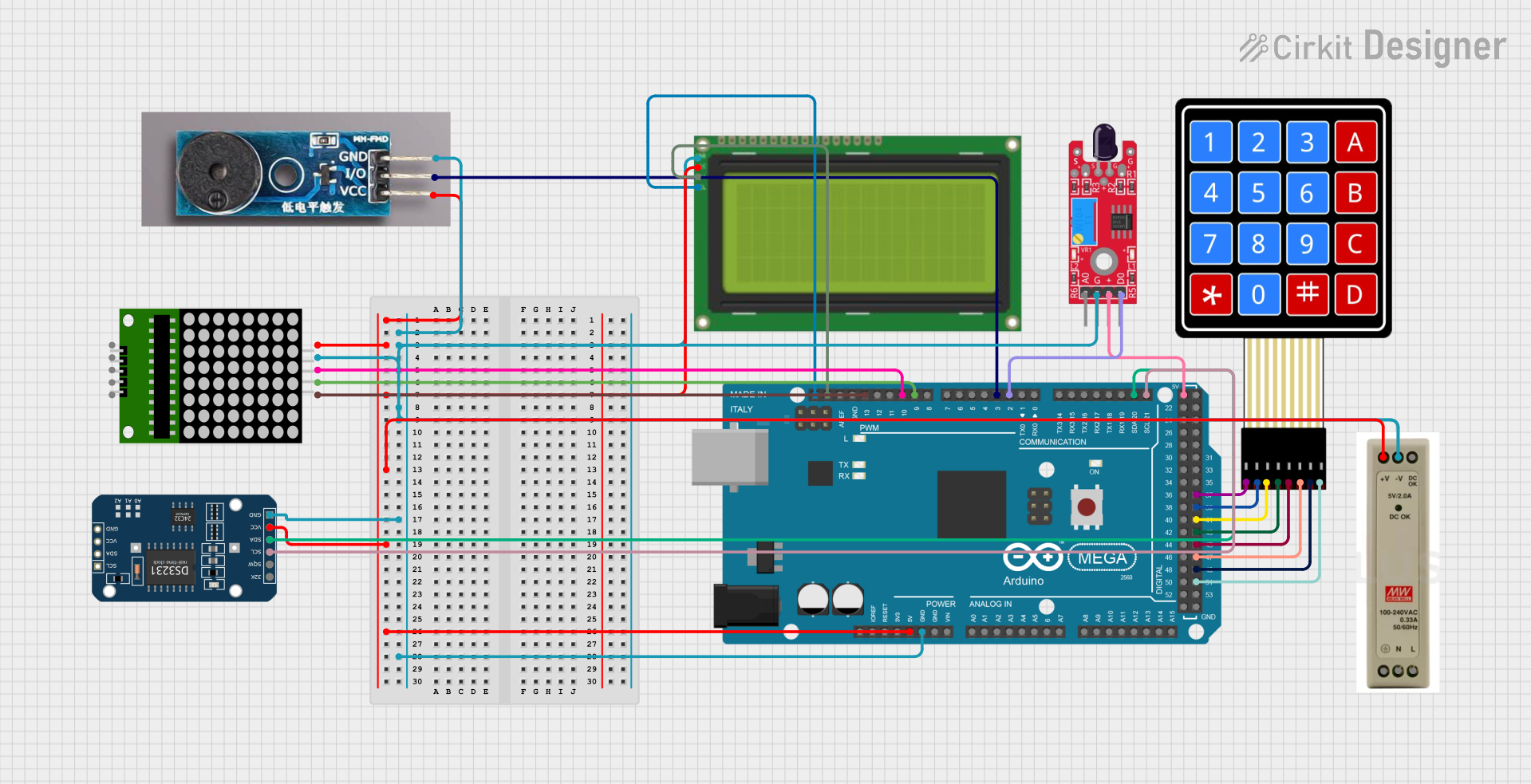
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer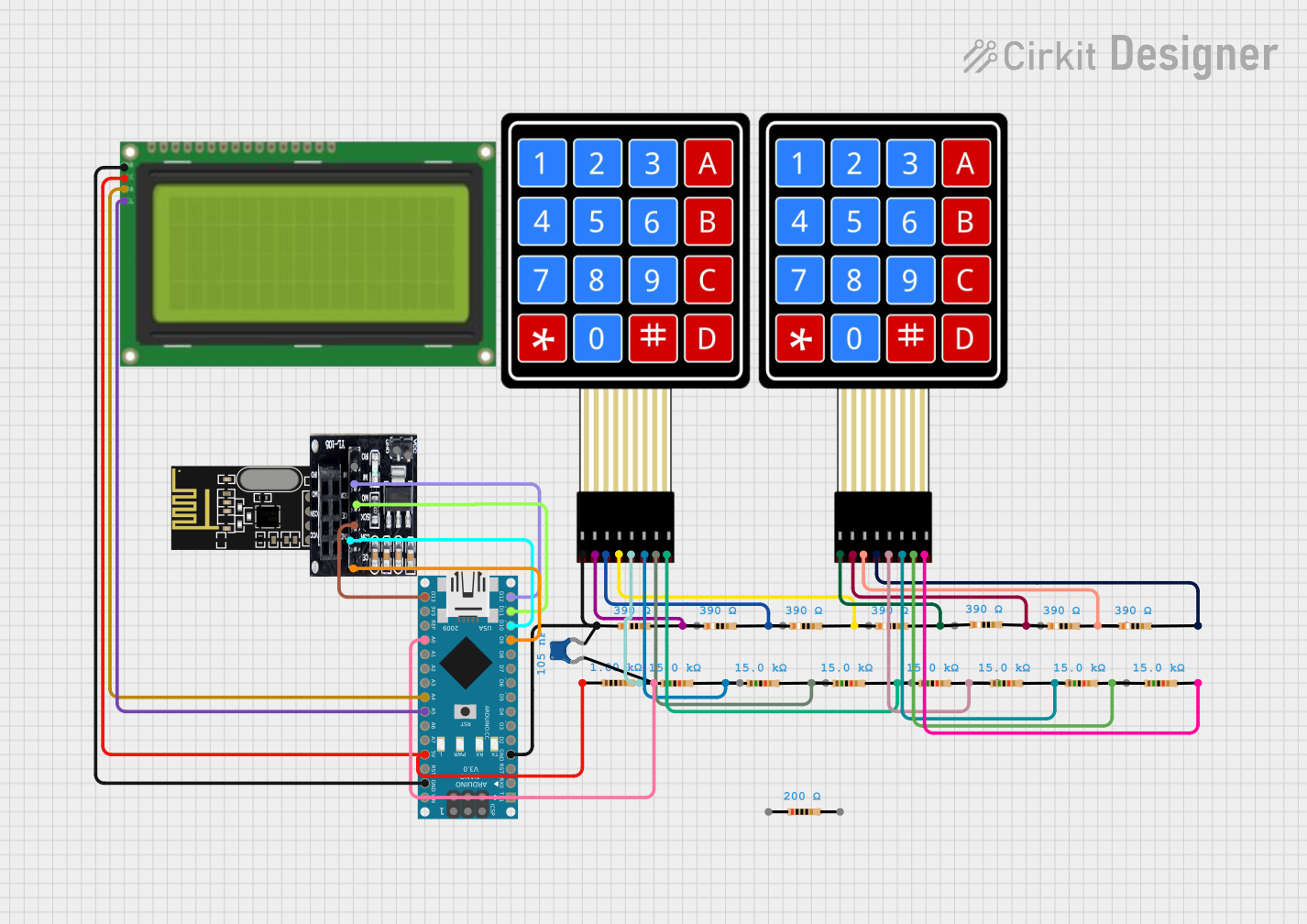
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer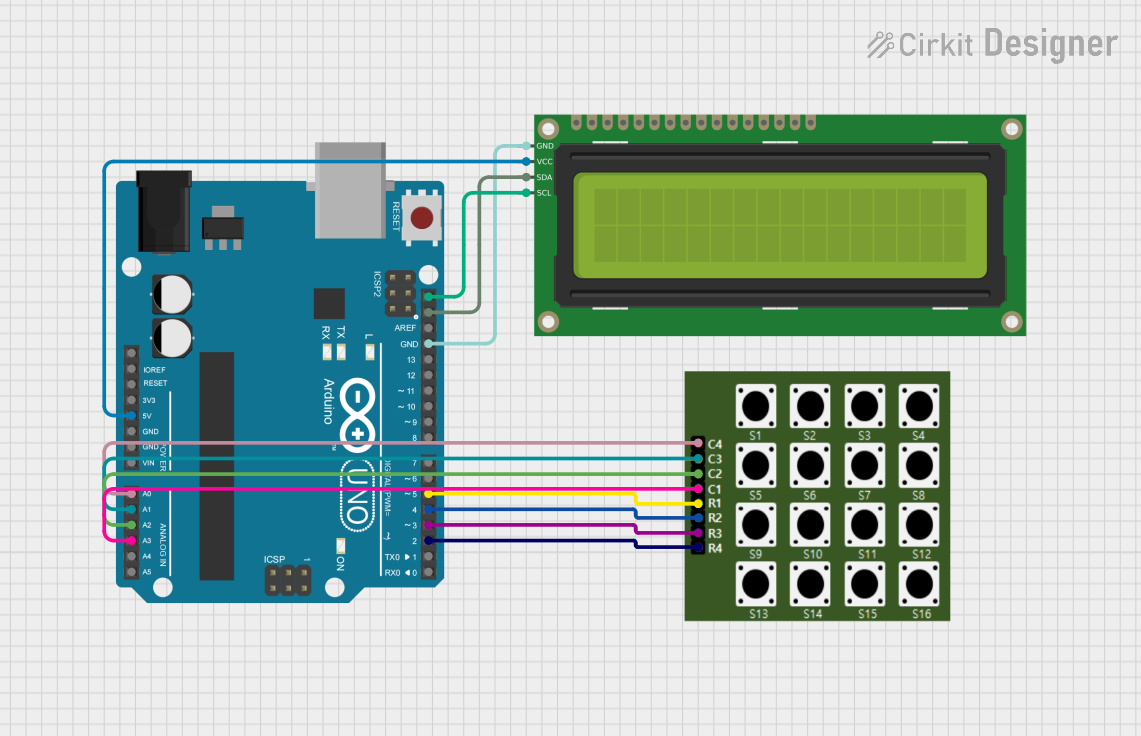
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Module Converter Keypad Matrix 4x4 to I2C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Embedded systems requiring keypad input (e.g., password entry, menu navigation)
- Home automation systems
- Security systems and access control
- Industrial control panels
- Prototyping and development with microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Communication Protocol: I2C
- Default I2C Address: 0x20 (configurable via solder jumpers)
- Keypad Compatibility: 4x4 matrix keypads
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C
- Dimensions: 30mm x 25mm x 10mm (approx.)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The module has two main interfaces: the keypad input pins and the I2C communication pins.
Keypad Input Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| R1 | Row 1 input from the keypad |
| R2 | Row 2 input from the keypad |
| R3 | Row 3 input from the keypad |
| R4 | Row 4 input from the keypad |
| C1 | Column 1 input from the keypad |
| C2 | Column 2 input from the keypad |
| C3 | Column 3 input from the keypad |
| C4 | Column 4 input from the keypad |
I2C Communication Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| SDA | I2C data line |
| SCL | I2C clock line |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Keypad: Attach the rows (R1-R4) and columns (C1-C4) of your 4x4 matrix keypad to the corresponding pins on the module.
- Connect Power: Provide a 3.3V or 5V power supply to the VCC pin and connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect I2C Lines: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller.
- Configure the I2C Address (if needed): If multiple I2C devices are used, adjust the module's I2C address by modifying the solder jumpers on the PCB.
- Write Code: Use your microcontroller's I2C library to communicate with the module and read key presses.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the I2C pull-up resistors are present in your circuit. Many microcontroller boards (e.g., Arduino) include built-in pull-up resistors, but verify this in your setup.
- Avoid long I2C wires to minimize signal degradation and communication errors.
- If using multiple I2C devices, ensure each device has a unique address to prevent conflicts.
- Debounce the keypad input in software to avoid false key presses.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the module with an Arduino UNO to read key presses:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x20 // Default I2C address of the module
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
Serial.println("4x4 Keypad I2C Module Test");
}
void loop() {
Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 1); // Request 1 byte from the module
if (Wire.available()) {
byte key = Wire.read(); // Read the key press data
if (key != 0) { // Check if a key is pressed
Serial.print("Key Pressed: ");
Serial.println(key, HEX); // Print the key value in hexadecimal
}
}
delay(100); // Small delay to avoid flooding the serial monitor
}
Notes on the Code
- The module sends a unique hexadecimal value for each key press. Refer to the module's datasheet for the key-to-value mapping.
- Modify the
I2C_ADDRESSif you change the module's default address.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Key Press Detected
- Ensure the keypad is properly connected to the module.
- Verify the I2C connections (SDA, SCL) and check for loose wires.
- Confirm the module's I2C address matches the one in your code.
Incorrect Key Values
- Check the keypad wiring to ensure rows and columns are correctly connected.
- Verify the module's datasheet for the correct key-to-value mapping.
I2C Communication Errors
- Ensure pull-up resistors are present on the SDA and SCL lines.
- Check for address conflicts if multiple I2C devices are connected.
Module Overheating
- Verify the input voltage is within the specified range (3.3V to 5V).
- Check for short circuits in the wiring.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module with a 3x4 keypad?
A: Yes, but you will need to leave one row or column unconnected. The module will still function, but some key positions will be unused.
Q: How do I change the I2C address?
A: The module's I2C address can be changed by modifying the solder jumpers on the PCB. Refer to the module's datasheet for detailed instructions.
Q: Is this module compatible with Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the module is compatible with Raspberry Pi. Use the smbus library in Python to communicate with the module over I2C.
Q: Do I need to debounce the keypad in software?
A: Yes, it is recommended to implement software debouncing to avoid false key presses caused by mechanical bounce.