
How to Use brushless esc: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with brushless esc in Cirkit Designer
Design with brushless esc in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Brushless Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) is a critical component used to regulate the speed, direction, and braking of brushless motors. It achieves this by converting direct current (DC) from a power source into a three-phase alternating current (AC) to drive the motor. Brushless ESCs are widely used in applications requiring precise motor control, such as drones, remote-controlled (RC) vehicles, electric skateboards, and robotics.
Explore Projects Built with brushless esc
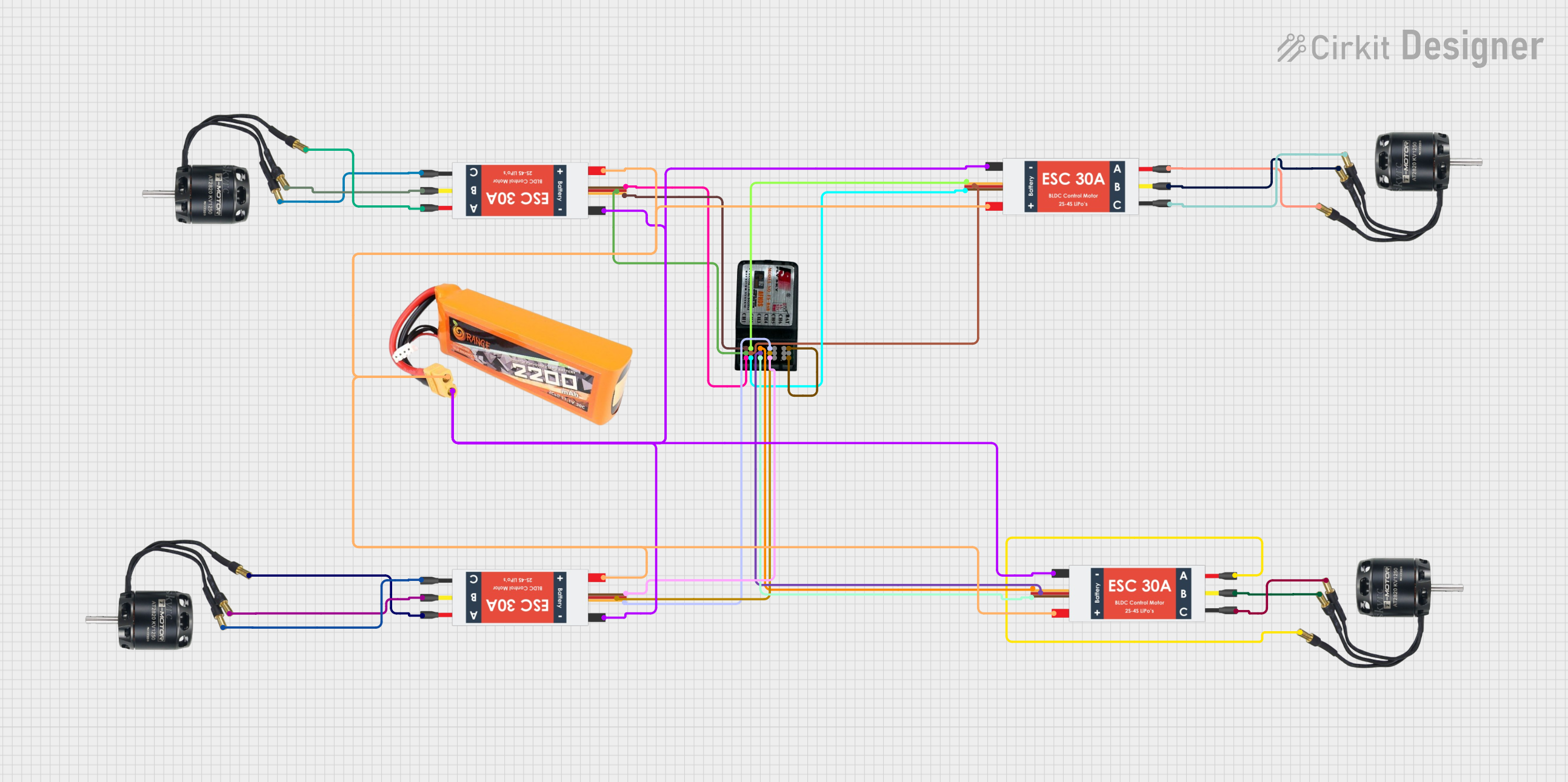
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer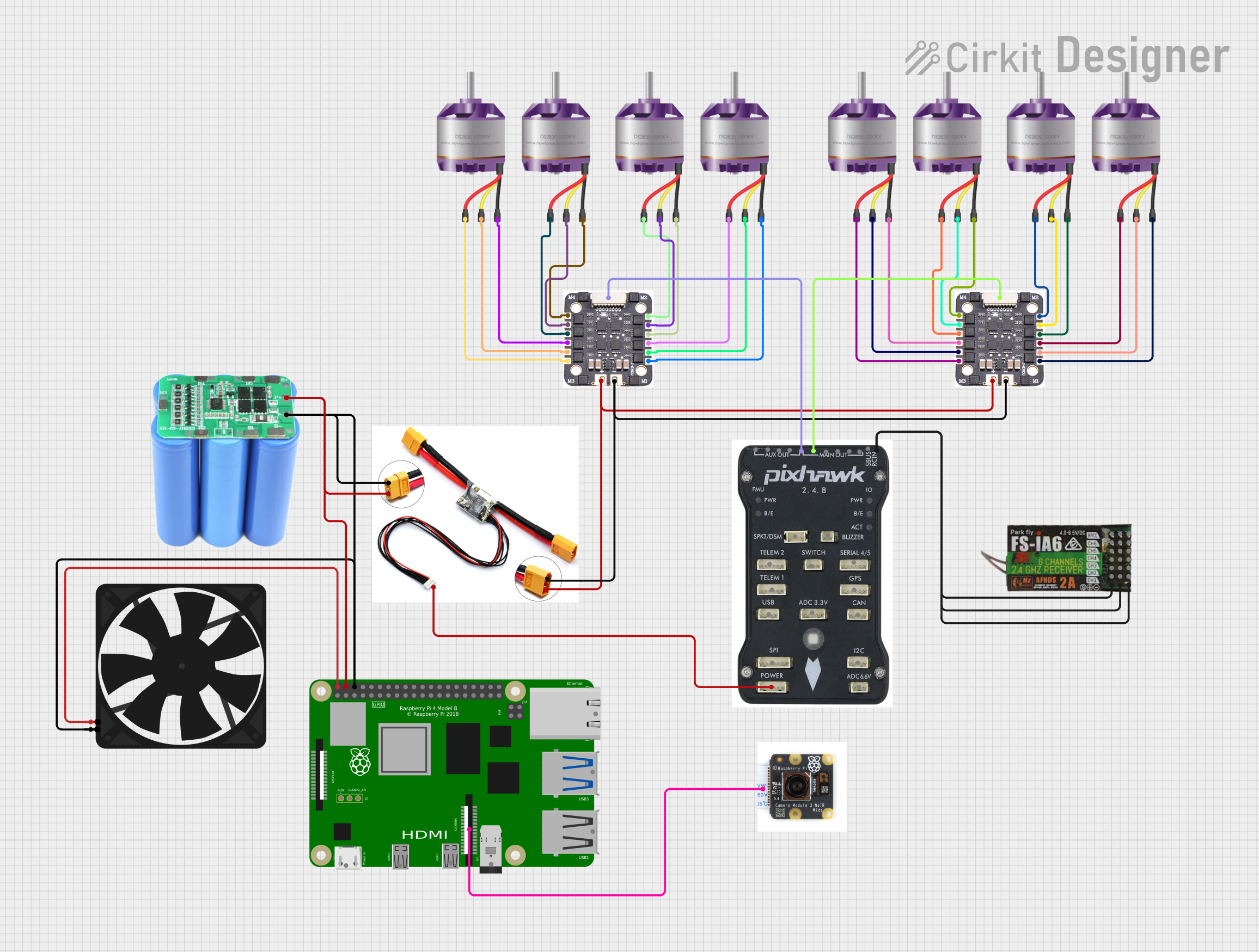
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer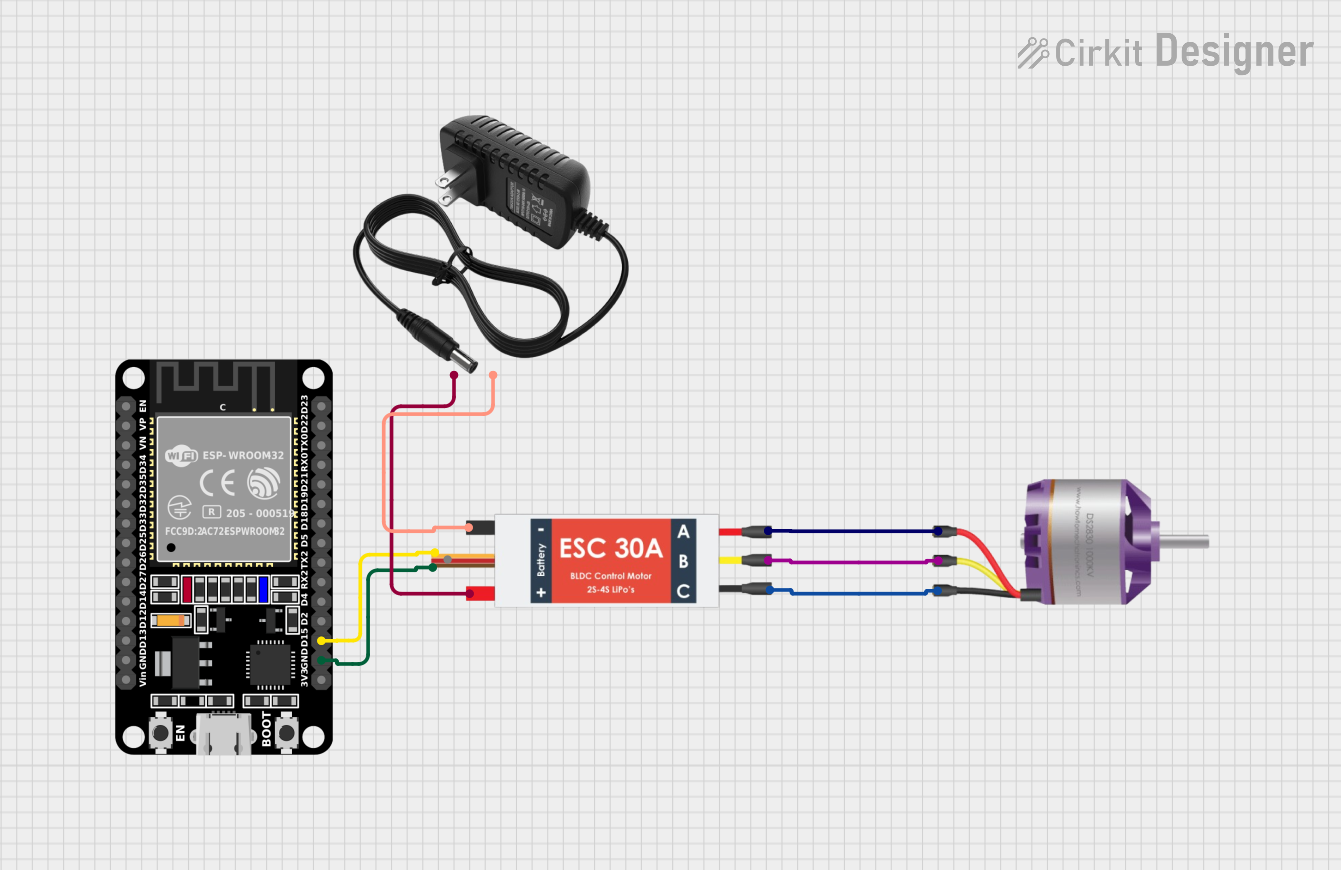
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer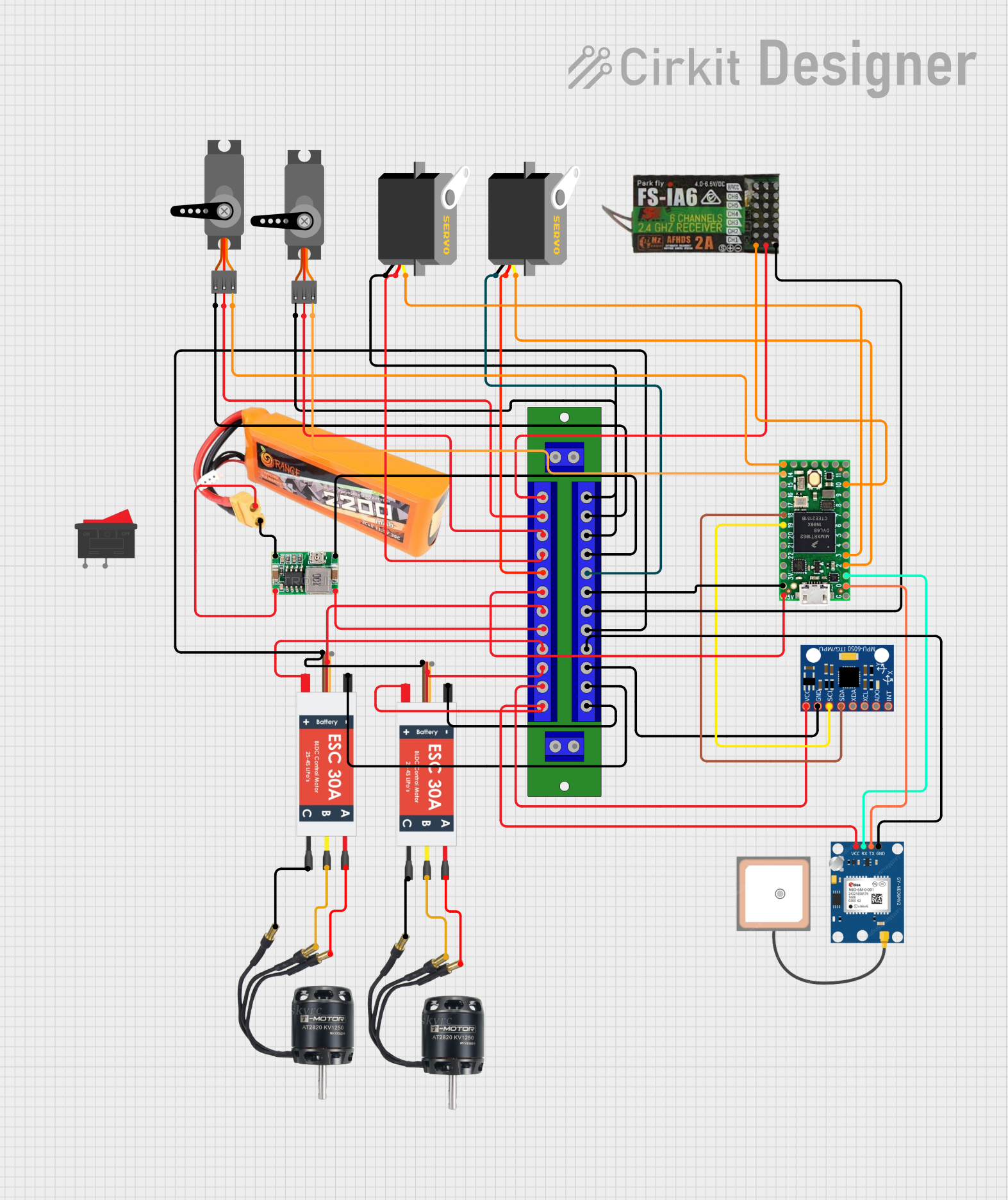
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with brushless esc

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Drones and quadcopters for motor speed control
- RC cars, boats, and airplanes
- Electric bicycles and skateboards
- Industrial automation and robotics
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical brushless ESC. Note that specific values may vary depending on the model and manufacturer.
Key Technical Details:
- Input Voltage Range: 6V to 50V (commonly 2S to 12S LiPo batteries)
- Continuous Current Rating: 10A to 200A (depending on the model)
- Peak Current Rating: Typically 1.5x to 2x the continuous current rating
- Supported Motor Types: Brushless DC (BLDC) motors
- Control Signal Input: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, typically 1ms to 2ms pulse width
- BEC (Battery Eliminator Circuit): 5V or 6V output for powering external devices (optional, depending on the ESC)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 85°C (varies by model)
- Weight: 10g to 100g (depending on size and power rating)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a brushless ESC typically includes the following connections:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Input (+) | Positive terminal for the power source (e.g., battery). |
| Power Input (-) | Negative terminal for the power source (e.g., battery). |
| Motor Phase A | First phase connection to the brushless motor. |
| Motor Phase B | Second phase connection to the brushless motor. |
| Motor Phase C | Third phase connection to the brushless motor. |
| Signal Input | PWM signal input from the flight controller, RC receiver, or microcontroller. |
| Ground (GND) | Ground connection for the signal input. |
| BEC Output (+) | Optional 5V or 6V output for powering external devices (e.g., microcontroller). |
| BEC Output (-) | Ground connection for the BEC output. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Brushless ESC in a Circuit:
Connect the Power Source:
- Connect the positive and negative terminals of the battery to the ESC's power input pins.
- Ensure the battery voltage is within the ESC's supported range.
Connect the Motor:
- Attach the three motor phase wires (A, B, C) from the ESC to the corresponding wires of the brushless motor.
- If the motor spins in the wrong direction, swap any two of the motor phase wires.
Connect the Signal Input:
- Connect the PWM signal input pin of the ESC to the signal output pin of a flight controller, RC receiver, or microcontroller.
- Connect the ESC's signal ground (GND) to the ground of the controlling device.
Optional: Use the BEC Output:
- If the ESC has a built-in BEC, use the BEC output to power external devices like a microcontroller or RC receiver.
Calibrate the ESC:
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions to calibrate the ESC for the throttle range of your controller.
Test the Setup:
- Power on the system and test the motor's response to the control signals. Ensure smooth operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices:
- Cooling: Ensure proper ventilation or cooling for the ESC, especially in high-current applications.
- Battery Compatibility: Use a battery with the correct voltage and discharge rating to avoid damaging the ESC.
- Signal Quality: Use a clean and stable PWM signal to prevent erratic motor behavior.
- Safety: Always disconnect the power source when making wiring changes to avoid short circuits or accidental motor starts.
Example: Using a Brushless ESC with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of controlling a brushless ESC using an Arduino UNO:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library to generate PWM signals
Servo esc; // Create a Servo object to control the ESC
void setup() {
esc.attach(9); // Attach the ESC signal wire to pin 9 on the Arduino
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Set the ESC to its minimum throttle (1ms pulse)
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds to allow the ESC to initialize
}
void loop() {
esc.writeMicroseconds(1500); // Set the throttle to 50% (1.5ms pulse)
delay(5000); // Run the motor at 50% throttle for 5 seconds
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Set the throttle to 0% (1ms pulse)
delay(5000); // Stop the motor for 5 seconds
}
Note: Always refer to the ESC's manual for specific initialization and calibration procedures.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
Motor Does Not Spin:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or uncalibrated ESC.
- Solution: Verify all connections and calibrate the ESC as per the manufacturer's instructions.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Cause: Incorrect motor phase wiring.
- Solution: Swap any two of the motor phase wires to reverse the direction.
ESC Overheats:
- Cause: Insufficient cooling or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Improve ventilation or use an ESC with a higher current rating.
Erratic Motor Behavior:
- Cause: Poor signal quality or electrical noise.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for the signal wire and ensure a stable power supply.
No Power to External Devices via BEC:
- Cause: BEC is not enabled or is damaged.
- Solution: Check the ESC's specifications and ensure the BEC is functional.
FAQs:
Q: Can I use a brushless ESC with a brushed motor?
A: No, brushless ESCs are specifically designed for brushless motors and are not compatible with brushed motors.Q: How do I choose the right ESC for my motor?
A: Match the ESC's current rating and voltage range to the motor's specifications. Ensure the ESC can handle the peak current draw of the motor.Q: Can I use a single ESC to control multiple motors?
A: No, each brushless motor requires its own ESC for independent control.Q: What happens if I exceed the ESC's voltage rating?
A: Exceeding the voltage rating can damage the ESC and potentially cause it to fail.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use a brushless ESC in your projects and troubleshoot common issues.