
How to Use GND: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with GND in Cirkit Designer
Design with GND in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ground (GND) is a fundamental component in electrical and electronic circuits. It serves as a reference point for measuring voltages and provides a common return path for electric current. GND is essential for ensuring the proper operation of circuits by maintaining a stable voltage reference and enabling current flow.
Explore Projects Built with GND
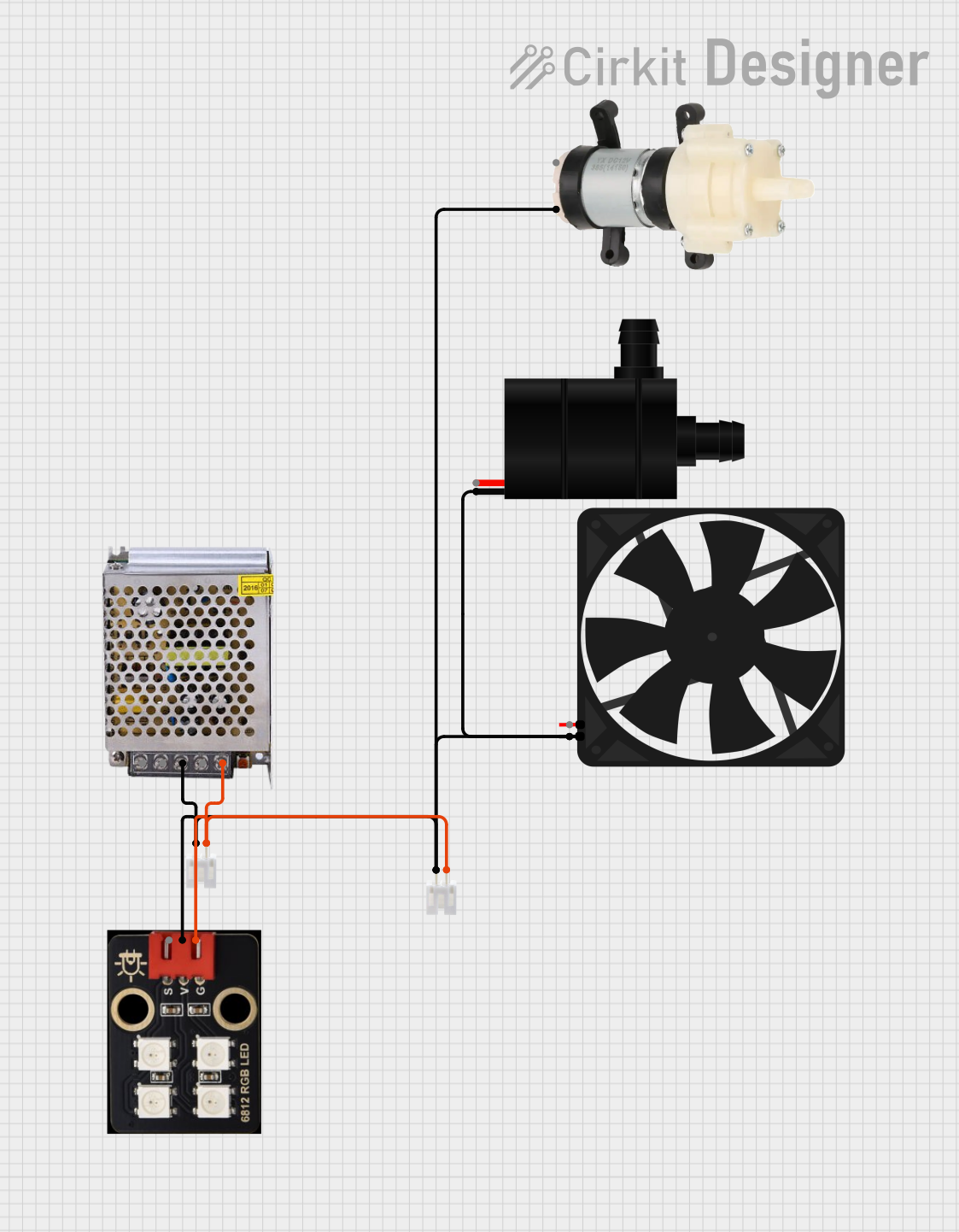
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer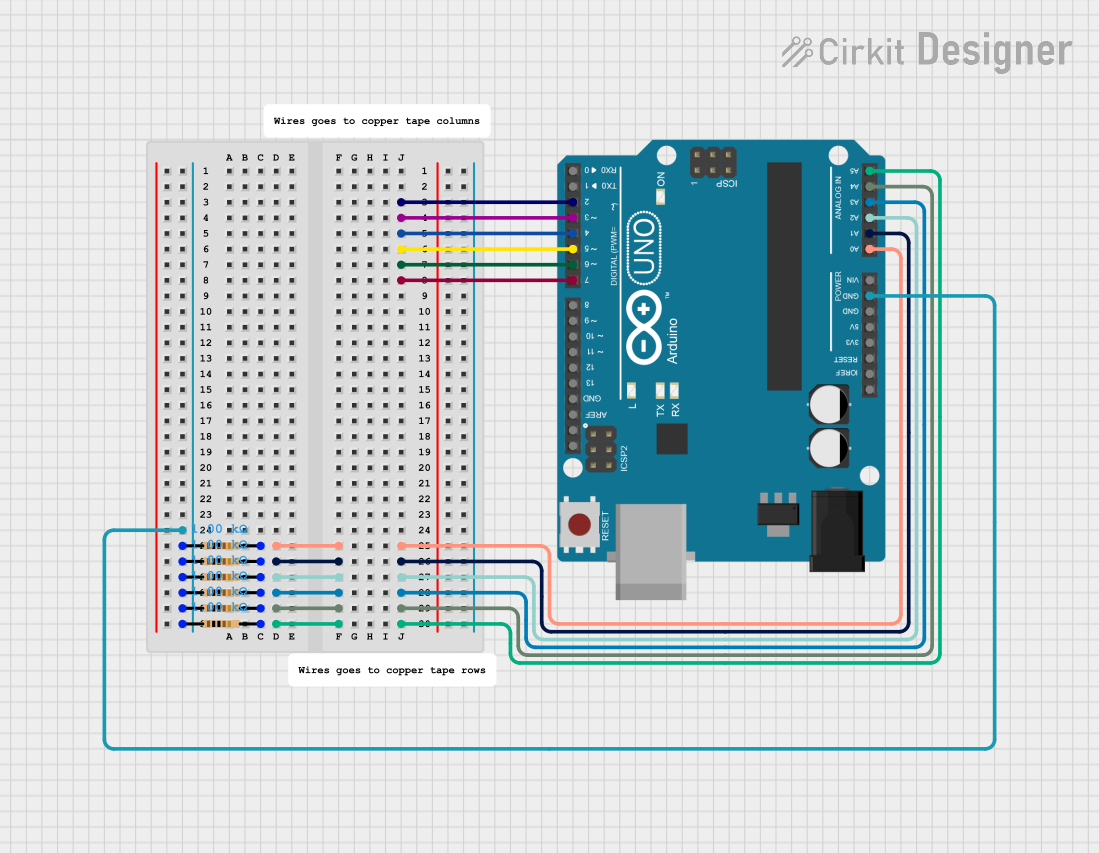
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GND

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voltage Reference: Used as a baseline for measuring voltages in a circuit.
- Current Return Path: Provides a path for current to return to the power source.
- Signal Integrity: Ensures proper operation of digital and analog signals by stabilizing voltage levels.
- Safety: Protects users and equipment by providing a path for fault currents in grounded systems.
Technical Specifications
The GND component itself does not have specific electrical ratings, as it is a conceptual and physical connection in a circuit. However, its implementation depends on the circuit design and the materials used for the ground plane or wiring.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GND connection is typically represented as a pin or terminal in electronic components and devices. Below is an example of how GND is commonly used in circuits:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| GND | Ground connection, used as a reference point for voltage and a return path for current. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use GND in a Circuit
- Connect Power Supply: Ensure that the negative terminal of the power supply is connected to the GND of the circuit.
- Establish a Common Ground: Connect all GND points in the circuit to a single common ground to avoid ground loops.
- Use Ground Planes: In PCB design, use a dedicated ground plane to reduce noise and improve signal integrity.
- Connect to Safety Ground: For safety-critical applications, connect the circuit ground to the earth ground.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Ground Loops: Ensure that all ground connections converge at a single point to prevent unwanted current paths.
- Minimize Resistance: Use thick wires or wide PCB traces for GND connections to reduce resistance and voltage drops.
- Separate Analog and Digital Grounds: In mixed-signal circuits, separate analog and digital grounds to minimize interference, and connect them at a single point.
- Check Polarity: Always verify that the GND connection is correctly identified and connected to avoid damage to components.
Example: Using GND with an Arduino UNO
When using an Arduino UNO, the GND pin is essential for completing the circuit. Below is an example of connecting an LED to the Arduino UNO with GND:
// Example: Blinking an LED with Arduino UNO
// Connect the LED's cathode (short leg) to GND and the anode (long leg) to pin 13
// through a 220-ohm resistor.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- No Voltage Reference: If GND is not properly connected, voltage measurements will be inaccurate or undefined.
- Circuit Malfunction: Missing or poor GND connections can cause erratic behavior in the circuit.
- Noise and Interference: Improper grounding can lead to noise in analog and digital signals.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Verify Connections: Check that all GND points are securely connected and form a common ground.
- Inspect PCB Layout: Ensure that the ground plane is continuous and not fragmented.
- Use a Multimeter: Measure continuity between GND points to confirm proper connections.
- Check for Ground Loops: If there are multiple ground paths, isolate and reconnect them to a single point.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the GND connection in your circuit is reliable and effective.