
How to Use NFC 4 Click ST25R3916: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
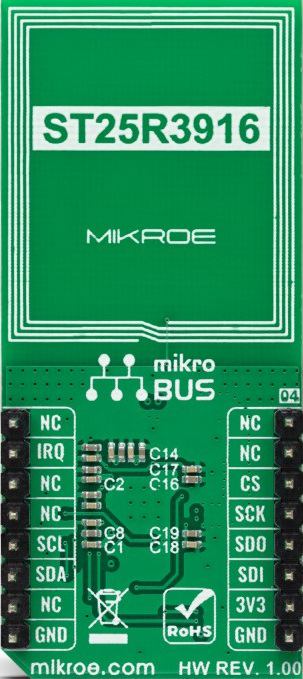
 Design with NFC 4 Click ST25R3916 in Cirkit Designer
Design with NFC 4 Click ST25R3916 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The NFC 4 Click ST25R3916 is a compact development board designed by Mikroe and powered by the ST25R3916 NFC/RFID reader IC. This versatile component supports multiple NFC modes, including reader, card emulation, and peer-to-peer communication, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of near-field communication (NFC) applications. Its high-performance design ensures reliable communication with NFC-enabled devices, making it ideal for prototyping and integrating NFC functionality into various projects.
Explore Projects Built with NFC 4 Click ST25R3916
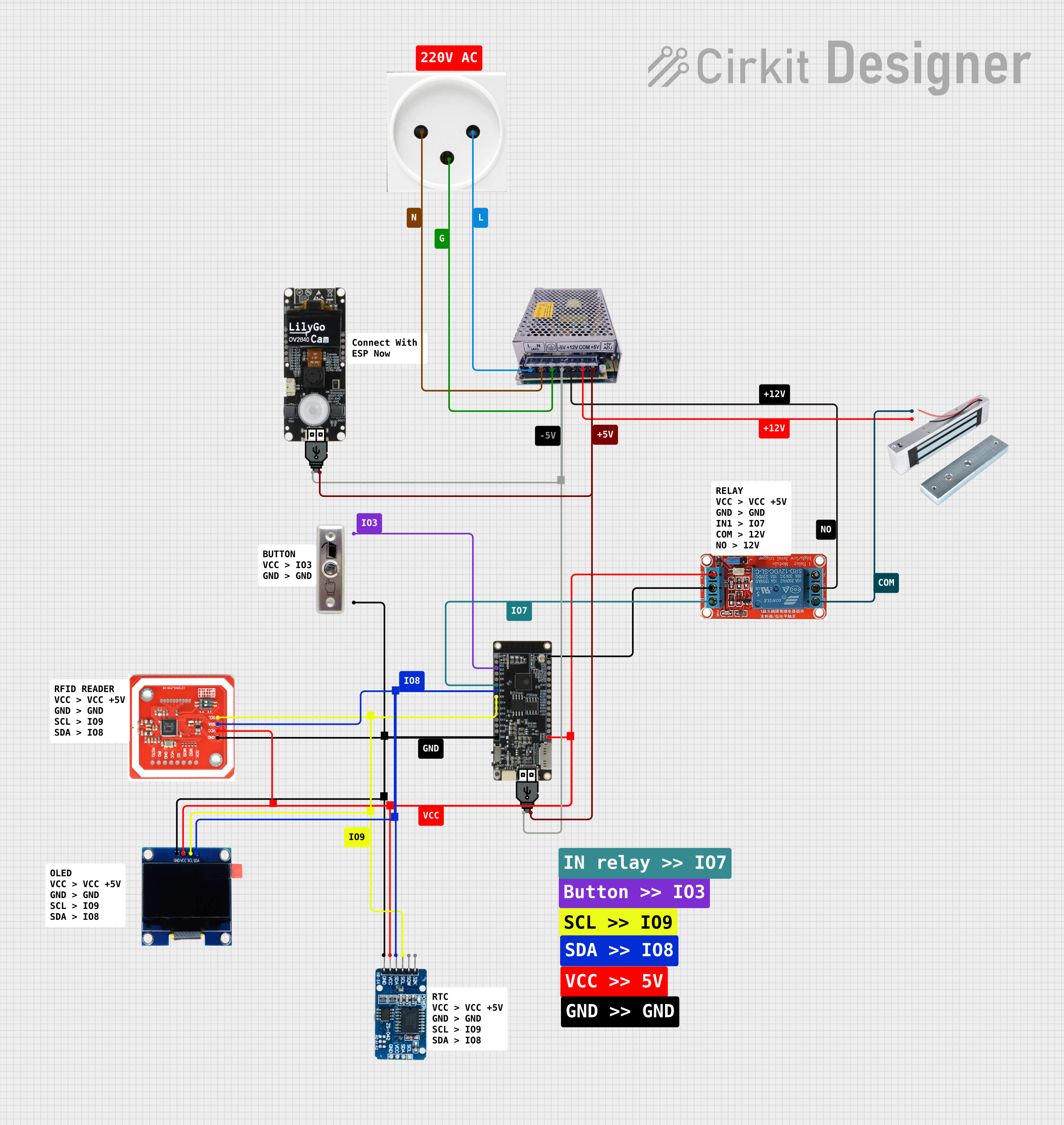
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer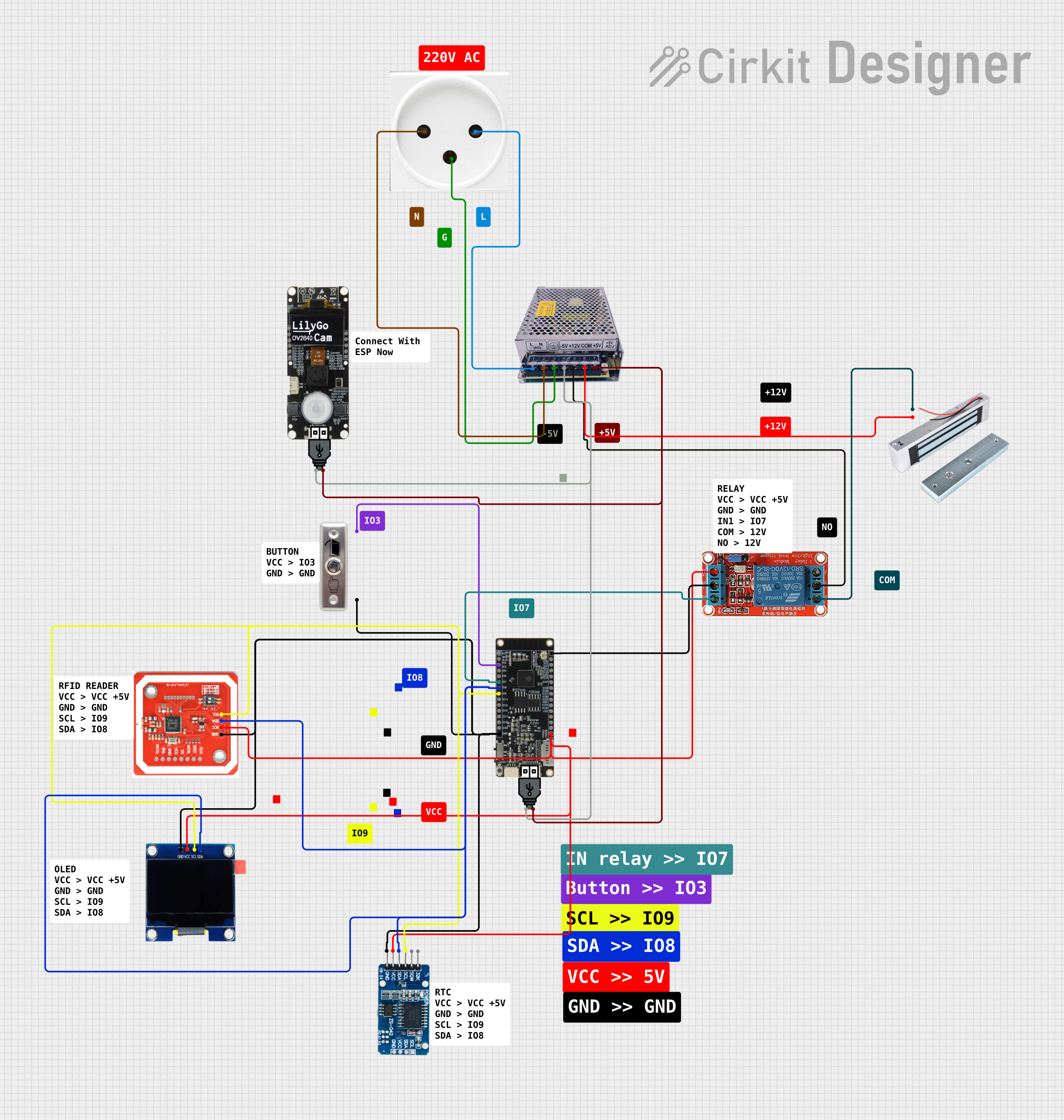
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer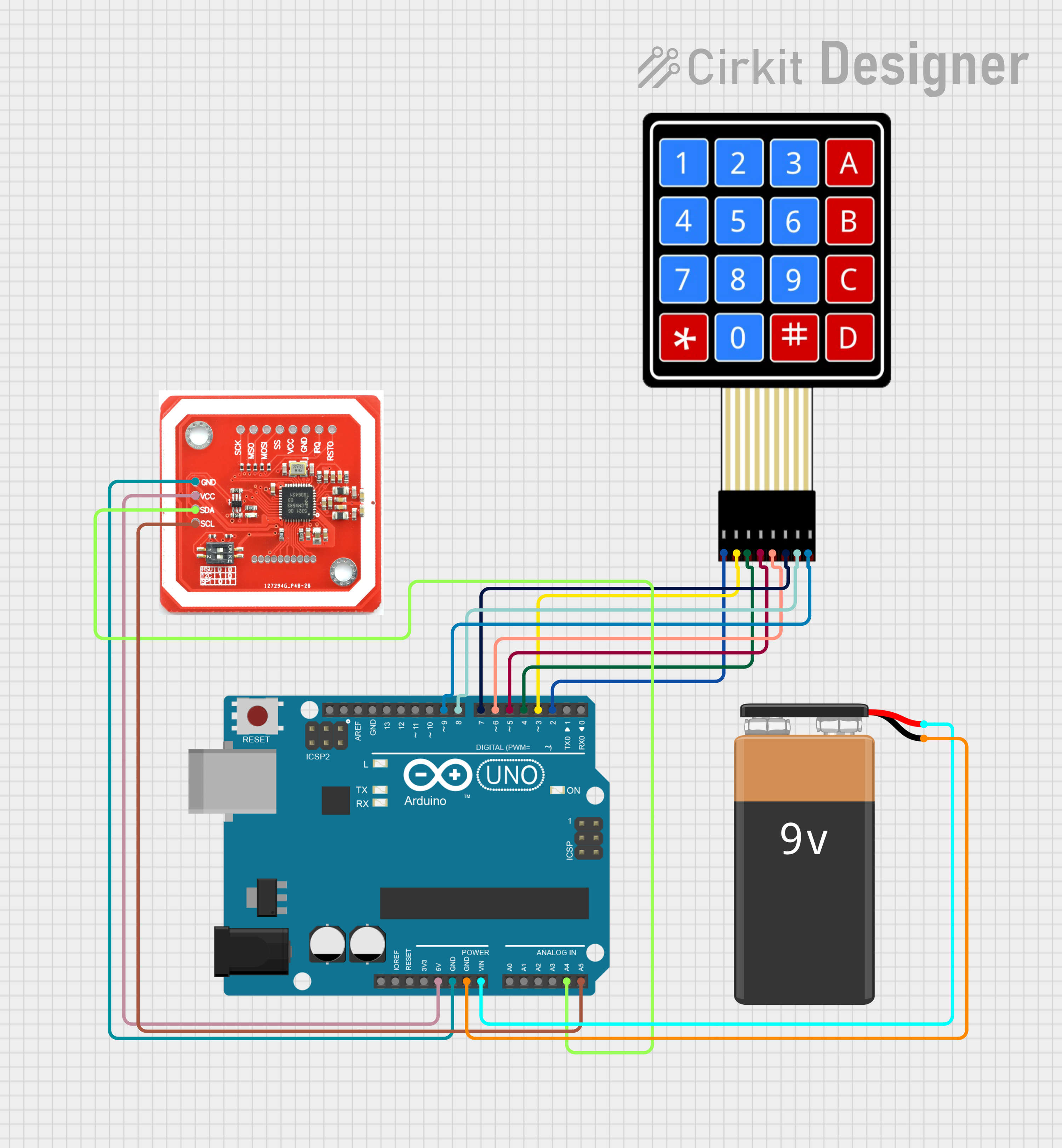
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with NFC 4 Click ST25R3916

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Contactless payment systems
- Access control and authentication
- NFC-enabled IoT devices
- Data exchange between NFC-enabled devices
- Smart posters and tags
- Inventory and asset tracking
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Mikroe |
| Part Number | ST25R3916 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Communication Interface | SPI |
| NFC Modes Supported | Reader, Card Emulation, Peer-to-Peer |
| Operating Frequency | 13.56 MHz |
| Maximum Output Power | 1.4 W |
| Antenna Driver Current | Up to 350 mA |
| ISO Standards Supported | ISO 14443A/B, ISO 15693, ISO 18092 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 42.9 mm x 25.4 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The NFC 4 Click board uses a standard mikroBUS™ socket for easy integration. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AN | 1 | Input | General-purpose analog pin |
| RST | 2 | Input | Reset pin for the ST25R3916 IC |
| CS | 3 | Input | SPI chip select |
| SCK | 4 | Input | SPI clock |
| MISO | 5 | Output | SPI master-in/slave-out |
| MOSI | 6 | Input | SPI master-out/slave-in |
| PWM | 7 | Output | General-purpose PWM pin |
| INT | 8 | Output | Interrupt signal from the IC |
| VCC | 9 | Power | Power supply (3.3V) |
| GND | 10 | Ground | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the NFC 4 Click to a 3.3V power source via the mikroBUS™ socket.
- SPI Communication: Ensure the SPI pins (CS, SCK, MISO, MOSI) are properly connected to your microcontroller or development board.
- Antenna Connection: The onboard antenna is pre-configured for NFC communication. No additional setup is required.
- Reset and Interrupt: Use the RST pin to reset the IC and monitor the INT pin for interrupt signals.
- Software Configuration: Use the provided Mikroe libraries or write custom SPI commands to configure the ST25R3916 for your desired NFC mode.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Requirements: Ensure a stable 3.3V power supply to avoid communication errors.
- Antenna Placement: Avoid placing the board near metal objects, as they can interfere with NFC communication.
- SPI Configuration: Set the SPI clock speed and mode according to the ST25R3916 datasheet for optimal performance.
- Interrupt Handling: Use the INT pin to detect events such as tag detection or communication errors.
- Firmware Updates: Check for updates to Mikroe's libraries to ensure compatibility with the latest features.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the NFC 4 Click with an Arduino UNO using SPI:
#include <SPI.h>
// Pin definitions for the NFC 4 Click
#define CS_PIN 10 // Chip Select pin
#define RST_PIN 9 // Reset pin
#define INT_PIN 2 // Interrupt pin
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize SPI communication
SPI.begin();
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RST_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(INT_PIN, INPUT);
// Reset the NFC module
digitalWrite(RST_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(RST_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
Serial.println("NFC 4 Click Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Example: Send a dummy SPI command to the NFC module
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Select the NFC module
SPI.transfer(0x00); // Send a dummy command
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deselect the NFC module
// Check for interrupt signal
if (digitalRead(INT_PIN) == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Interrupt detected!");
// Handle the interrupt (e.g., read tag data)
}
delay(500); // Wait for a while
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Response from the NFC Module
- Cause: Incorrect SPI configuration or wiring.
- Solution: Double-check the SPI connections and ensure the SPI clock speed matches the ST25R3916 requirements.
NFC Tag Not Detected
- Cause: Improper antenna placement or interference.
- Solution: Ensure the tag is within the NFC range and avoid placing the board near metal objects.
Interrupt Pin Not Triggering
- Cause: Incorrect interrupt handling or configuration.
- Solution: Verify the INT pin connection and ensure the firmware is configured to enable interrupts.
Power Supply Issues
- Cause: Insufficient or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Use a regulated 3.3V power source and check for voltage drops.
FAQs
Q: Can the NFC 4 Click work with 5V systems?
A: No, the board operates at 3.3V. Use a level shifter if interfacing with a 5V system.Q: What is the maximum NFC range?
A: The range depends on the antenna and tag size but typically extends up to 10 cm.Q: Does Mikroe provide software libraries for this board?
A: Yes, Mikroe provides libraries and example code for various platforms, including Arduino and MikroC.Q: Can I use this board for peer-to-peer communication?
A: Yes, the ST25R3916 supports peer-to-peer NFC communication.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the NFC 4 Click ST25R3916. For further assistance, refer to the official Mikroe documentation or contact their support team.