
How to Use T1 VTOL Tilt Servo (Lightweight): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with T1 VTOL Tilt Servo (Lightweight) in Cirkit Designer
Design with T1 VTOL Tilt Servo (Lightweight) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The T1 VTOL Tilt Servo by HEEWING is a lightweight, high-performance servo specifically designed for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) applications. It provides precise tilt control for rotor positioning, making it an essential component in drones and other aerial vehicles requiring smooth and accurate movement. Its lightweight design ensures minimal impact on the overall weight of the system, making it ideal for aerial applications where weight is a critical factor.
Explore Projects Built with T1 VTOL Tilt Servo (Lightweight)
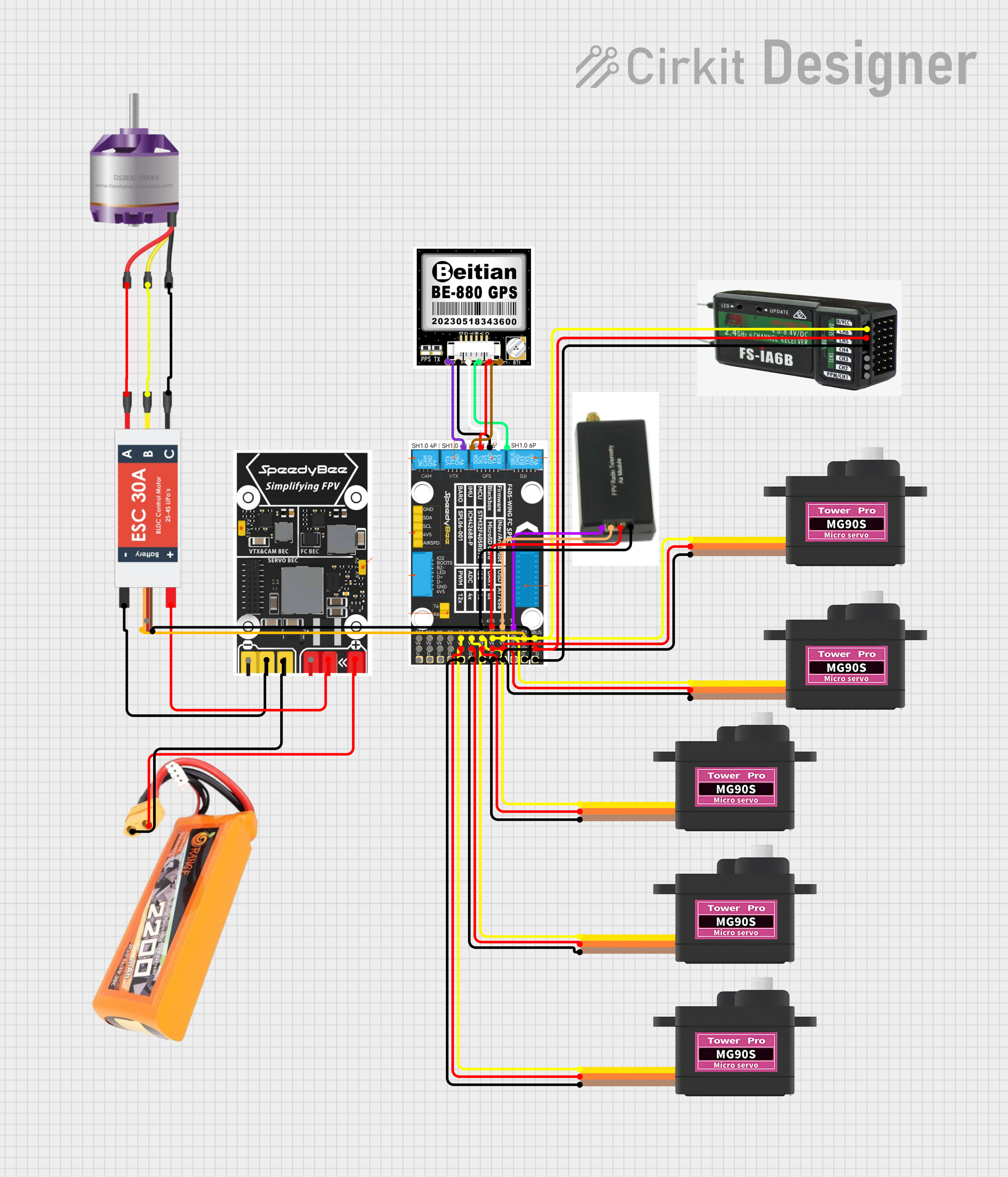
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer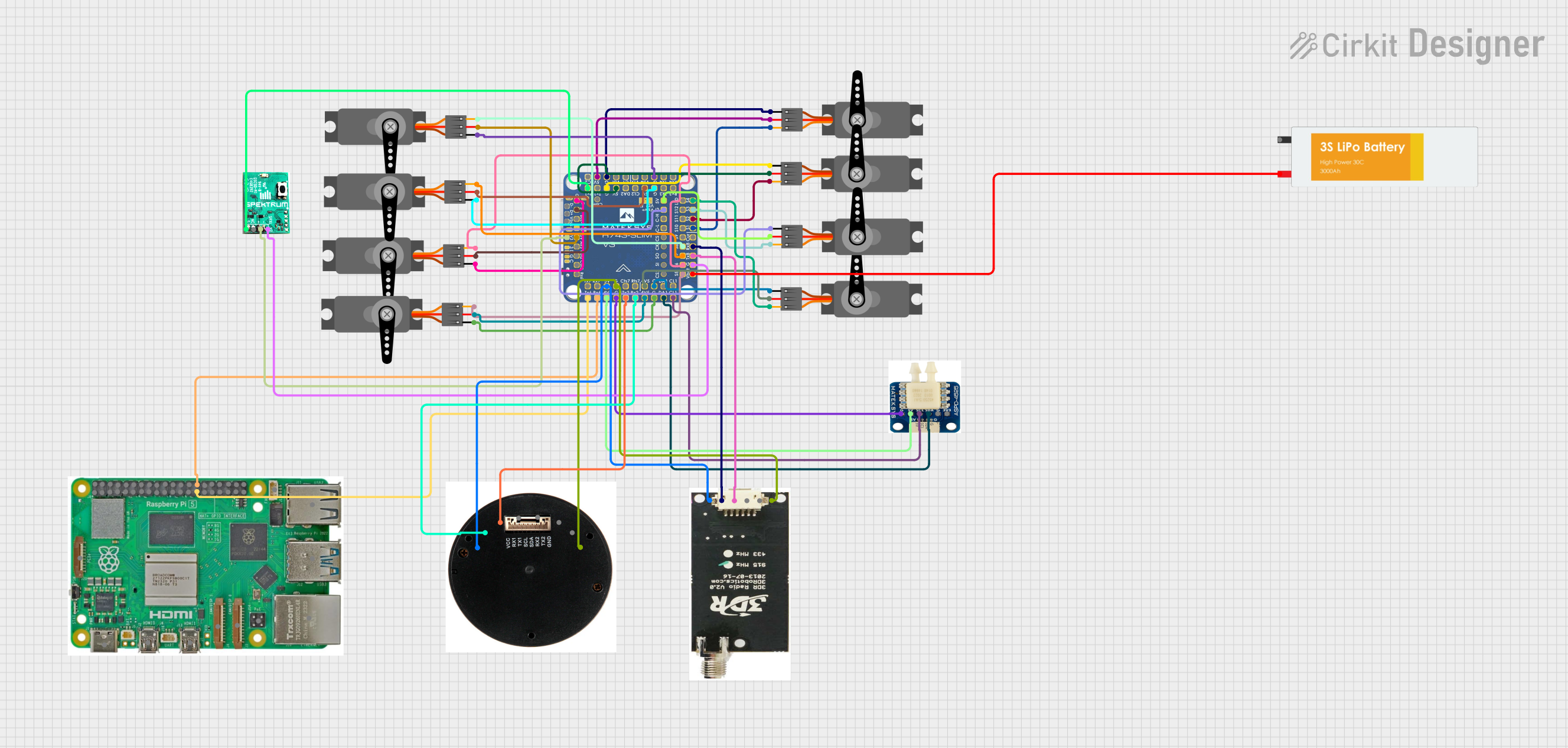
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer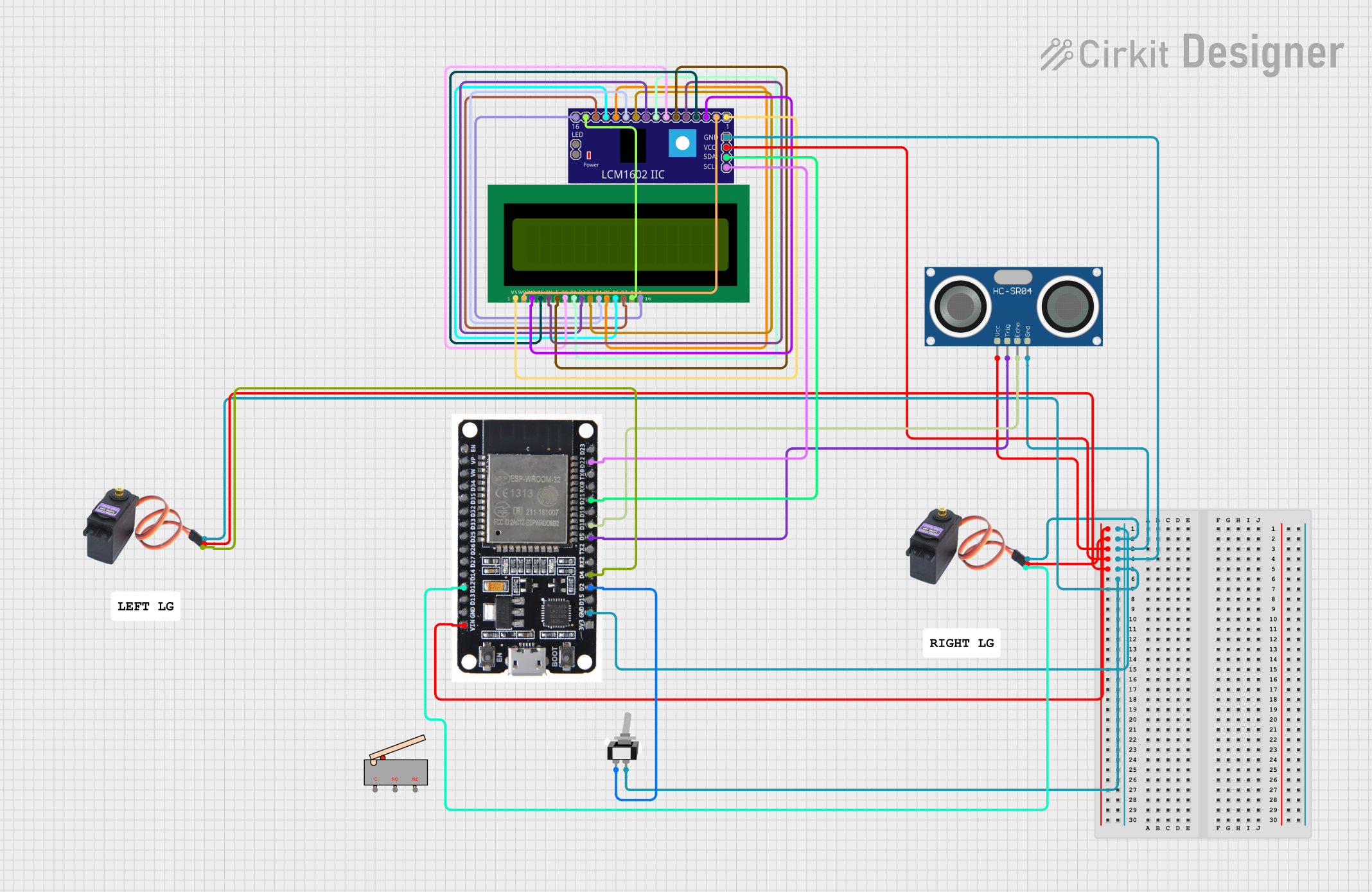
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer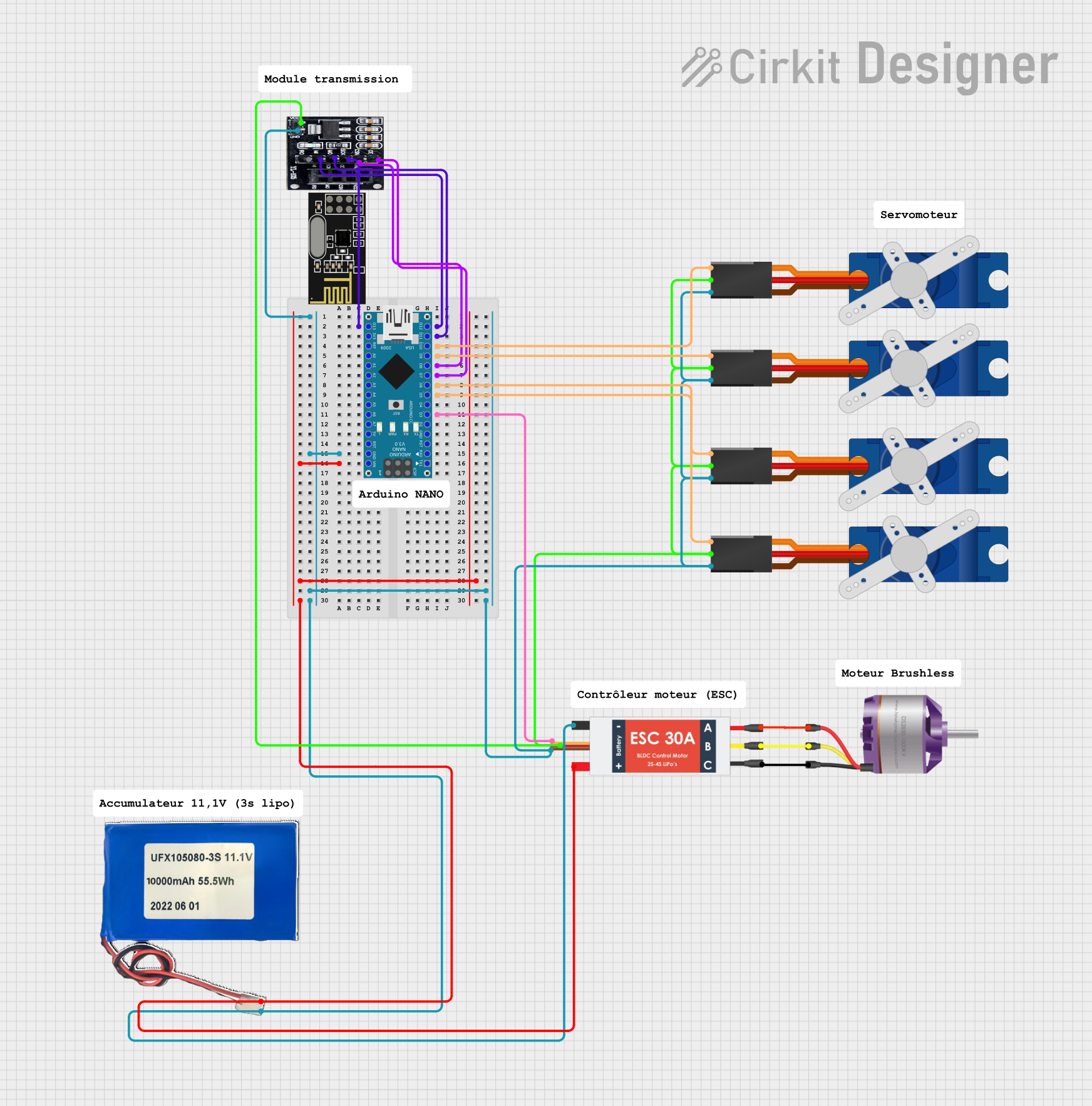
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with T1 VTOL Tilt Servo (Lightweight)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- VTOL drones for commercial, industrial, and recreational use
- Autonomous aerial vehicles (AAVs)
- Fixed-wing drones with tilt-rotor mechanisms
- Robotics requiring lightweight and precise servo control
- Experimental aircraft and UAV prototypes
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 4.8V - 6.0V |
| Stall Torque | 2.5 kg·cm @ 4.8V, 3.0 kg·cm @ 6.0V |
| Operating Speed | 0.12 sec/60° @ 4.8V, 0.10 sec/60° @ 6.0V |
| Weight | 18 grams |
| Dimensions | 35mm x 15mm x 30mm |
| Gear Material | Metal |
| Connector Type | 3-pin standard servo connector |
| Control Signal | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
| PWM Range | 500 µs - 2500 µs |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The T1 VTOL Tilt Servo uses a standard 3-pin connector. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brown | Ground (GND) |
| 2 | Red | Power (VCC) |
| 3 | Orange | Signal (PWM control input) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo in a Circuit
- Power Connection: Connect the red wire to a regulated power source (4.8V to 6.0V). Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for the servo's operation.
- Ground Connection: Connect the brown wire to the ground (GND) of your circuit.
- Signal Connection: Connect the orange wire to the PWM output pin of your microcontroller or flight controller.
- PWM Signal: Use a PWM signal with a pulse width between 500 µs and 2500 µs to control the servo's position. A pulse width of 1500 µs typically corresponds to the neutral (center) position.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Use a stable and noise-free power source to avoid erratic servo behavior.
- Current Requirements: Ensure your power supply can handle the servo's peak current draw, especially under load.
- Mounting: Securely mount the servo to prevent vibrations or movement during operation.
- Signal Timing: Verify that your microcontroller or flight controller can generate PWM signals within the required range.
- Calibration: Calibrate the servo's range of motion to avoid overdriving it, which could cause damage.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo using an Arduino UNO:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo tiltServo; // Create a Servo object to control the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo
void setup() {
tiltServo.attach(9); // Attach the servo to pin 9 on the Arduino
}
void loop() {
tiltServo.write(0); // Move the servo to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
tiltServo.write(90); // Move the servo to 90 degrees (neutral position)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
tiltServo.write(180); // Move the servo to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: The Servo.write() function accepts angles between 0° and 180°, which correspond to the servo's range of motion. Ensure the servo's physical range matches the angles used in your code.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Servo Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements.
Erratic Movement:
- Cause: Noisy power supply or incorrect PWM signal.
- Solution: Use a stable power source and verify the PWM signal timing.
Overheating:
- Cause: Prolonged operation under high load or overdriving the servo.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the servo and ensure it operates within its specified range.
Limited Range of Motion:
- Cause: Incorrect PWM signal range or mechanical obstruction.
- Solution: Verify the PWM signal range and check for any physical obstructions.
FAQs
Q1: Can the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo be used with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the signal pin can accept 3.3V PWM signals. However, the power supply for the servo must be within the 4.8V to 6.0V range.
Q2: What is the maximum load the servo can handle?
A2: The servo can handle a maximum torque of 3.0 kg·cm at 6.0V. Exceeding this limit may damage the servo.
Q3: Can I use this servo for non-VTOL applications?
A3: Yes, the T1 VTOL Tilt Servo can be used in any application requiring lightweight and precise servo control.
Q4: How do I extend the servo's lifespan?
A4: Operate the servo within its specified voltage, torque, and temperature limits. Avoid prolonged operation under heavy loads.