
How to Use wemos: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
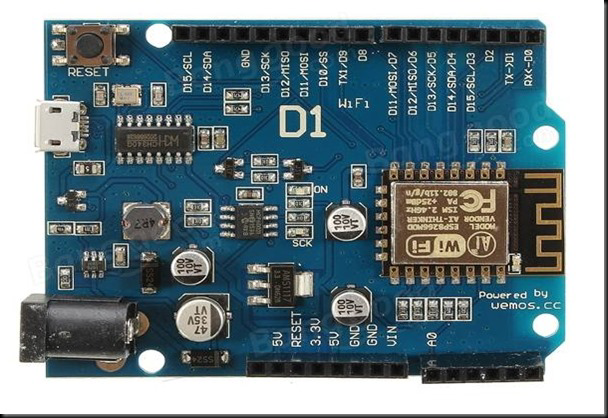
 Design with wemos in Cirkit Designer
Design with wemos in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
Wemos is a brand recognized for its development boards and modules that integrate Wi-Fi capabilities, making them ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) projects. These boards typically feature microcontrollers such as the ESP8266 or ESP32, which provide robust wireless connectivity and are easy to program. Wemos boards are widely used in applications like smart home automation, remote monitoring, and wireless sensor networks due to their compact size, affordability, and versatility.
Common applications and use cases include:
- IoT devices and smart home systems
- Wireless data logging and monitoring
- Remote control of devices via Wi-Fi
- Prototyping and educational projects
Explore Projects Built with wemos
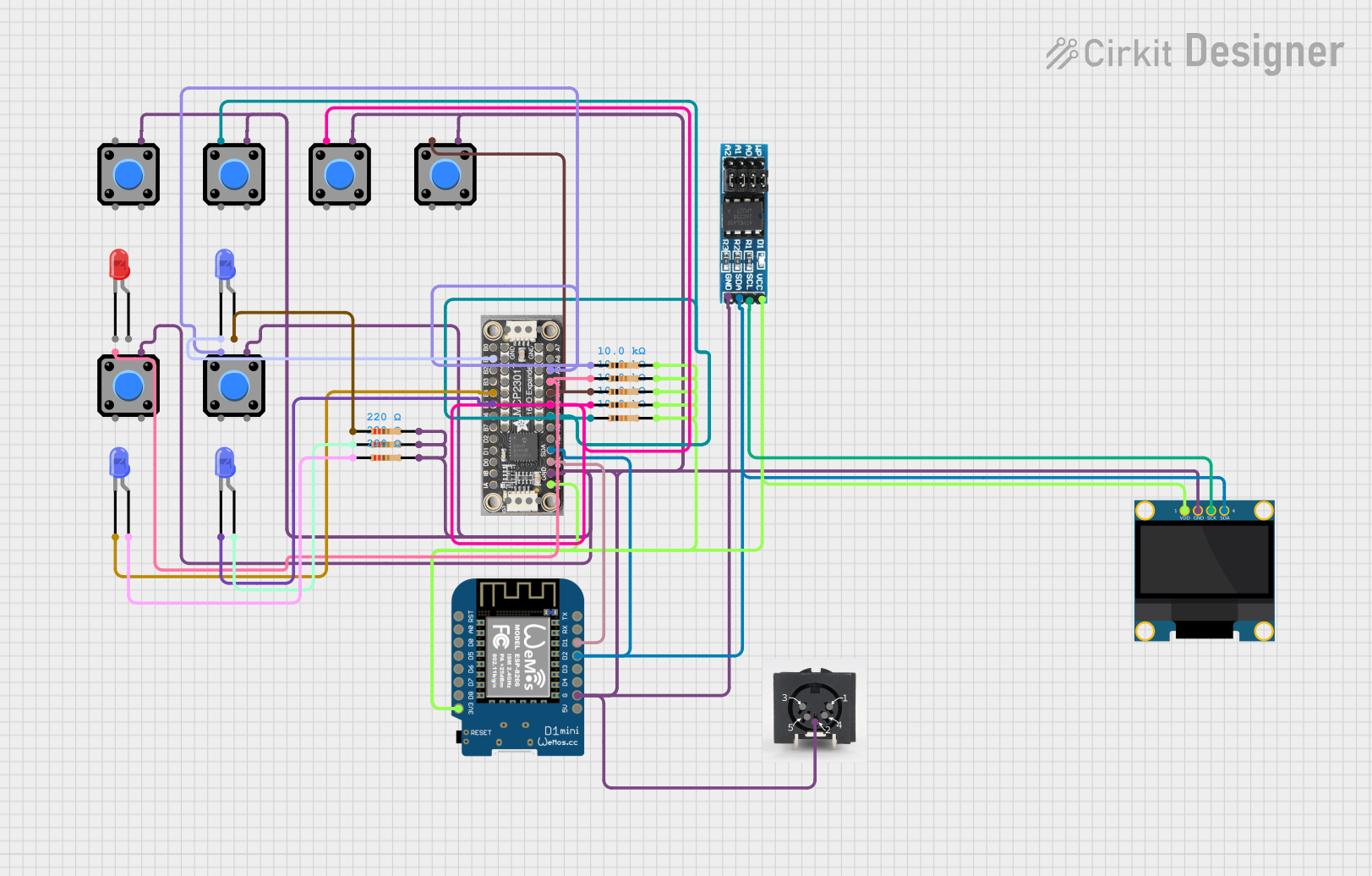
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer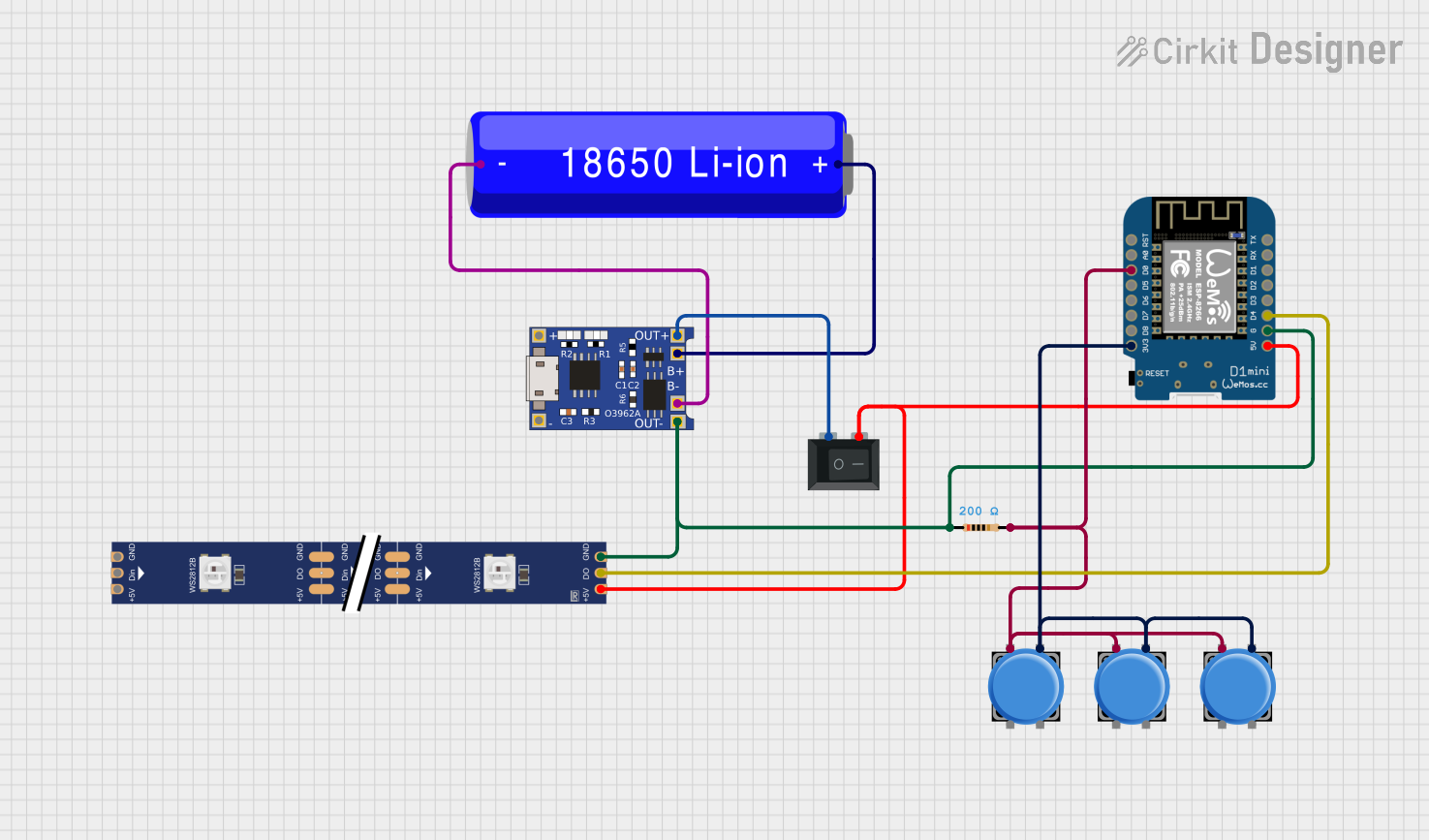
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer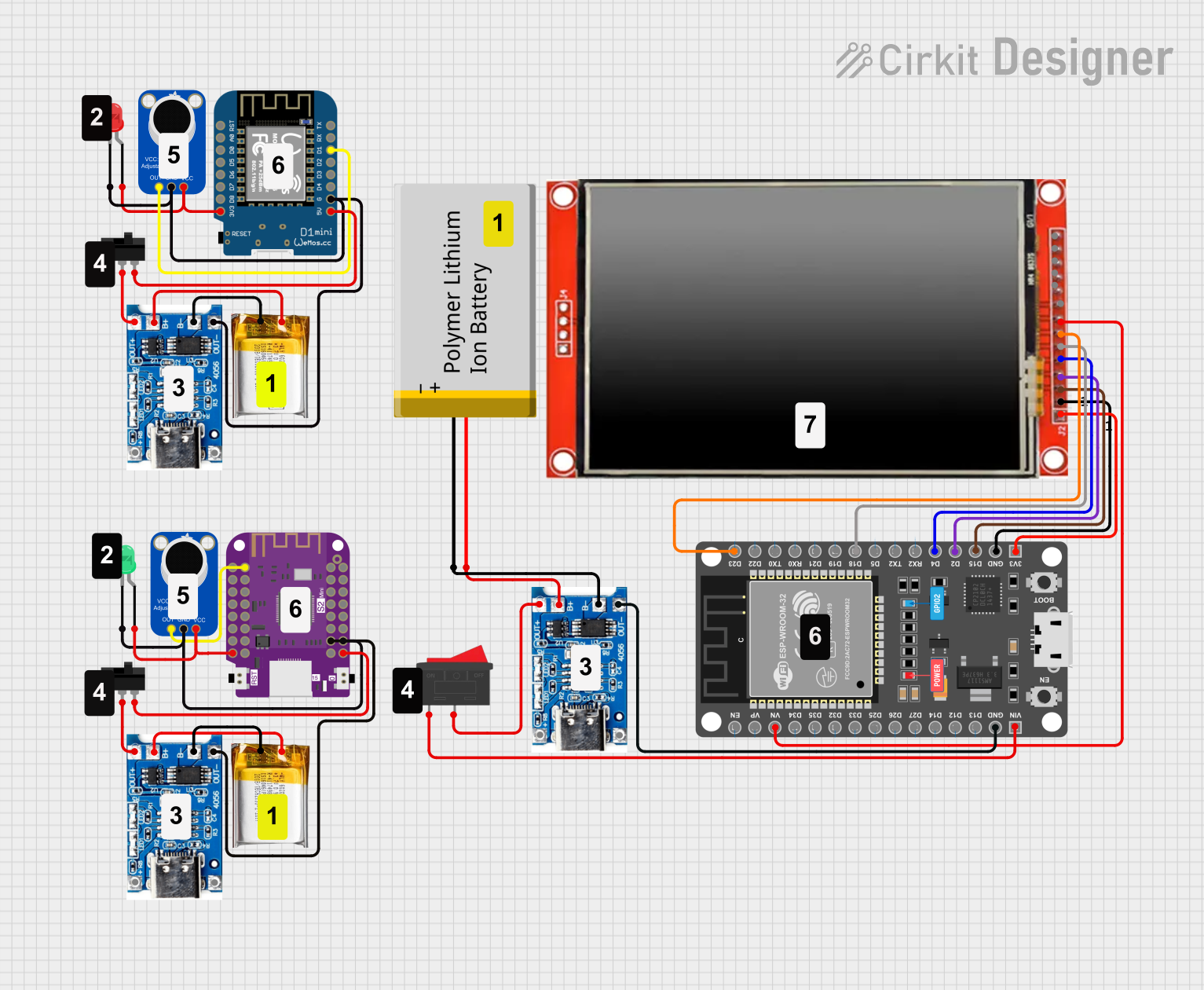
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with wemos

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical specifications for a typical Wemos board featuring the ESP8266 microcontroller:
General Specifications
- Microcontroller: ESP8266 (32-bit Tensilica L106 processor)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage: 5V (via USB) or 3.3V (via pin)
- Wi-Fi Standard: 802.11 b/g/n
- Flash Memory: 4MB (varies by model)
- Clock Speed: 80 MHz (can be overclocked to 160 MHz)
- Digital I/O Pins: 11
- Analog Input Pins: 1 (10-bit resolution)
- Power Consumption: ~70mA (idle), ~200mA (transmitting)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Wemos board typically uses a microcontroller with the following pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 | 3.3V power output |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | D0 (GPIO16) | General-purpose digital I/O pin |
| 4 | D1 (GPIO5) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for I2C (SCL) |
| 5 | D2 (GPIO4) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for I2C (SDA) |
| 6 | D3 (GPIO0) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, can also be used for boot mode selection |
| 7 | D4 (GPIO2) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often connected to the onboard LED |
| 8 | D5 (GPIO14) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for SPI (SCK) |
| 9 | D6 (GPIO12) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for SPI (MISO) |
| 10 | D7 (GPIO13) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for SPI (MOSI) |
| 11 | D8 (GPIO15) | General-purpose digital I/O pin, often used for SPI (CS) |
| 12 | A0 | Analog input pin (0-1V range) |
| 13 | RST | Reset pin, used to restart the microcontroller |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Wemos Board in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to a 5V USB power source or provide 3.3V directly to the 3V3 pin.
- Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current (at least 500mA) for stable operation.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE and add the ESP8266 board package via the Boards Manager.
- Select the appropriate Wemos board model (e.g., "Wemos D1 Mini") from the Tools menu.
- Connect the board to your computer using a USB cable and upload your code.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the digital I/O pins (D0-D8) for connecting sensors, actuators, or other devices.
- For analog sensors, connect them to the A0 pin, ensuring the input voltage does not exceed 1V.
Wi-Fi Configuration:
- Use the ESP8266WiFi library to connect the board to a Wi-Fi network.
- Configure the SSID and password in your code to establish a connection.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The Wemos board operates at 3.3V logic levels. Avoid connecting 5V signals directly to the pins to prevent damage.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid unexpected resets or instability during operation.
- Heat Management: The ESP8266 can get warm during operation. Ensure proper ventilation if used in enclosed spaces.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the firmware updated to ensure compatibility with the latest libraries and features.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to connect the Wemos board to a Wi-Fi network and control an onboard LED:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi network name
const char* password = "Your_Password"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi password
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); // Set the onboard LED pin as an output
// Connect to Wi-Fi
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The board is not detected by the computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Install the correct USB-to-serial driver for the Wemos board.
Wi-Fi connection fails:
- Double-check the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and not using unsupported security protocols.
The board resets unexpectedly:
- Verify that the power supply provides sufficient current.
- Check for loose connections or short circuits in your circuit.
Analog readings are inaccurate:
- Ensure the input voltage to the A0 pin does not exceed 1V.
- Use a voltage divider if necessary to scale down higher voltages.
FAQs
Can I use 5V sensors with the Wemos board?
Yes, but you must use a level shifter or voltage divider to step down the signal to 3.3V.How do I update the firmware on the Wemos board?
Use the ESP8266Flasher tool or the Arduino IDE to upload the latest firmware.Can the Wemos board be powered by batteries?
Yes, you can use a 3.7V LiPo battery with a suitable voltage regulator or a USB power bank.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the Wemos board in your IoT and wireless projects.