
How to Use Terminal PCB 2 Pin vcc gnd: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Terminal PCB 2 Pin vcc gnd in Cirkit Designer
Design with Terminal PCB 2 Pin vcc gnd in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Terminal PCB 2 Pin VCC GND is a compact and reliable two-pin terminal block designed for connecting power supply lines (VCC and GND) to a printed circuit board (PCB). It provides a secure and robust connection, ensuring stable power delivery to electronic components. This terminal block is widely used in various electronic projects and devices where a simple and efficient power connection is required.
Explore Projects Built with Terminal PCB 2 Pin vcc gnd
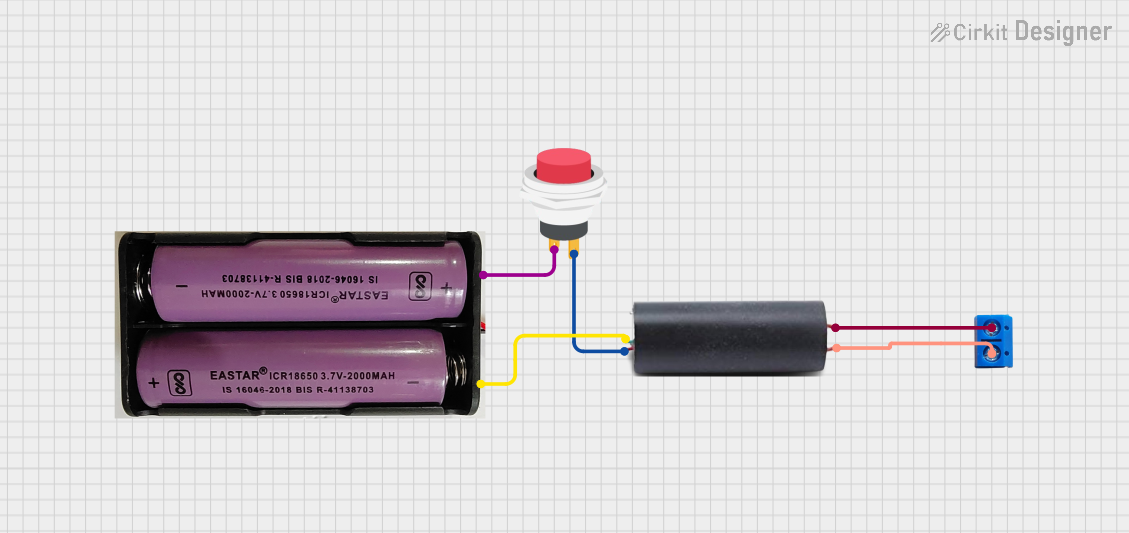
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer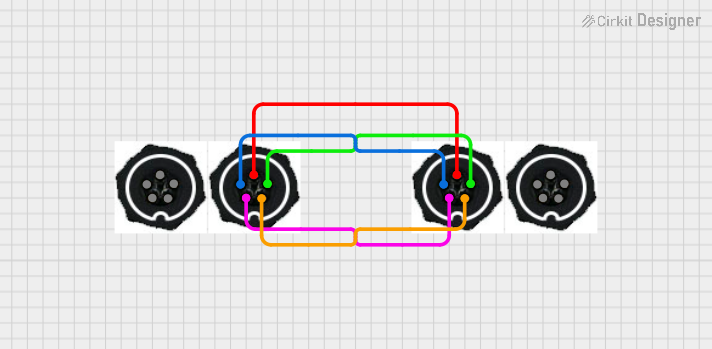
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Terminal PCB 2 Pin vcc gnd

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power supply connections in PCB-based circuits
- Prototyping and DIY electronics projects
- Industrial control systems
- Embedded systems and IoT devices
- Robotics and automation projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Terminal PCB 2 Pin VCC GND:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Number of Pins | 2 |
| Pin Labels | VCC, GND |
| Rated Voltage | Up to 300V |
| Rated Current | Up to 10A |
| Pin Pitch | 5.08 mm (standard spacing) |
| Material | Plastic housing, copper alloy pins |
| Mounting Type | Through-hole (THT) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +105°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Terminal PCB 2 Pin VCC GND has two pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Positive voltage input (power supply) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection (return path) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Soldering the Terminal Block:
- Insert the two pins of the terminal block into the corresponding through-hole pads on the PCB.
- Ensure the VCC and GND pins are aligned with the correct power supply traces on the PCB.
- Solder the pins securely to the PCB to ensure a reliable connection.
Connecting Wires:
- Strip the insulation from the ends of the power supply wires (VCC and GND).
- Insert the stripped wire ends into the terminal block's screw clamps.
- Tighten the screws to secure the wires in place, ensuring a firm connection.
Powering the Circuit:
- Connect the other ends of the wires to the power source.
- Double-check the polarity (VCC and GND) to avoid damage to the circuit.
- Turn on the power supply to energize the circuit.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity Check: Always verify the polarity of the connections (VCC and GND) before powering the circuit to prevent damage to components.
- Wire Gauge: Use wires of appropriate gauge to handle the current without overheating.
- Screw Tightening: Ensure the screws are tightened securely to prevent loose connections, which can cause intermittent power issues.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the rated voltage and current specifications of the terminal block.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Terminal PCB 2 Pin VCC GND can be used to supply power to an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to connect it:
- Solder the terminal block to a PCB designed to distribute power to the Arduino.
- Connect the VCC pin of the terminal block to the 5V pin of the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the terminal block to the GND pin of the Arduino.
- Use the following Arduino code to test the power connection:
// Simple Arduino code to test power connection
// This code blinks the onboard LED to confirm the Arduino is powered
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); // Set the onboard LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Connections:
- Issue: The wires are not securely connected, causing intermittent power delivery.
- Solution: Ensure the screws are tightened properly and the wires are firmly clamped.
Polarity Reversal:
- Issue: The VCC and GND connections are swapped, potentially damaging the circuit.
- Solution: Double-check the polarity of the connections before powering the circuit.
Overheating:
- Issue: The terminal block or wires become hot during operation.
- Solution: Verify that the current does not exceed the rated 10A and use appropriate wire gauge.
Poor Solder Joints:
- Issue: The terminal block is not securely soldered to the PCB, causing unreliable connections.
- Solution: Re-solder the pins, ensuring a clean and solid joint.
FAQs
Q1: Can this terminal block handle AC power?
A1: Yes, the terminal block can handle both AC and DC power, provided the voltage and current do not exceed the rated specifications.
Q2: What wire sizes are compatible with this terminal block?
A2: The terminal block typically supports wire sizes ranging from 16 AWG to 24 AWG.
Q3: Can I use this terminal block for high-frequency signals?
A3: This terminal block is primarily designed for power connections. For high-frequency signals, consider using connectors specifically designed for signal integrity.
Q4: Is the terminal block reusable?
A4: Yes, the terminal block can be reused, but ensure the screws and clamps remain in good condition for secure connections.