
How to Use 48V to 12v: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
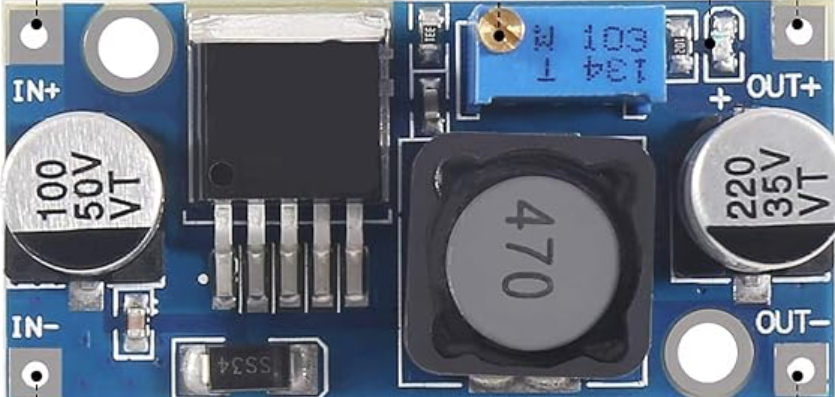
 Design with 48V to 12v in Cirkit Designer
Design with 48V to 12v in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 48V to 12V DC-DC converter is an electronic device that steps down voltage from 48 volts to 12 volts. These converters are essential in applications where the power supply voltage is higher than what the electronics require. They are commonly used in automotive systems, industrial machinery, and renewable energy setups where battery banks or power systems operate at 48V, but the equipment requires a 12V supply.
Explore Projects Built with 48V to 12v

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 48V to 12v

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive electronics
- Solar power systems
- Telecommunications equipment
- Industrial control systems
- LED lighting systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: 48V (Typical)
- Output Voltage: 12V
- Maximum Output Current: Specified by the model (e.g., 5A, 10A)
- Efficiency: Typically >90%
- Operating Temperature Range: Specified by the model (e.g., -40°C to +85°C)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input Voltage (48V) | Connect to the 48V supply |
| 2 | Ground | Connect to system ground |
| 3 | Output Voltage (12V) | Connect to the load or circuit |
| 4 | Ground | Connect to load or circuit ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Input: Attach the 48V supply to the input pin (Pin 1) and connect the ground from the power source to the ground pin (Pin 2).
- Connect the Output: Connect the output voltage pin (Pin 3) to the device or circuit that requires 12V. Ensure that the ground pin (Pin 4) is connected to the ground of the load.
- Power On: Once all connections are secure, power on the 48V supply. The converter will step down the voltage to 12V for use by the connected device.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Load Rating: Do not exceed the maximum output current rating of the converter.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate ventilation or heat sinking to manage heat generated by the converter.
- Input Voltage: Verify that the input voltage does not exceed the specified maximum for the converter.
- Polarity: Always check the polarity of connections to prevent damage to the converter and the connected devices.
- Short Circuit Protection: Use appropriate fuses or circuit breakers to protect against short circuits.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Insufficient Output Voltage: Check for overloading or short circuits in the connected load.
- Overheating: Ensure proper heat dissipation and verify that the load does not exceed the converter's rating.
- No Output: Verify input connections, polarity, and the integrity of the power source.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Loose or incorrect connections are common issues. Double-check all connections.
- Measure Input Voltage: Use a multimeter to ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.
- Inspect for Damage: Look for any visible signs of damage or overheating on the converter.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this converter in an automotive application?
- A: Yes, as long as the input voltage is within the specified range and the current does not exceed the converter's rating.
Q: Is the converter isolated?
- A: This depends on the specific model. Check the datasheet for isolation information.
Q: What is the efficiency of the converter?
- A: Efficiency is typically greater than 90%, but refer to the datasheet for exact figures.
Example Connection with Arduino UNO
While an Arduino UNO typically operates at 5V, you might use a 12V supply for peripherals that require higher voltage. Below is an example code snippet for turning on an LED strip that requires 12V, using a 48V to 12V converter to step down the voltage.
// Define the LED strip power control pin
#define LED_STRIP_PWR_PIN 7
void setup() {
// Set the power control pin as an output
pinMode(LED_STRIP_PWR_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the LED strip
digitalWrite(LED_STRIP_PWR_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED strip on for 1 second
// Turn off the LED strip
digitalWrite(LED_STRIP_PWR_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED strip off for 1 second
}
Note: The above code assumes that the Arduino UNO controls a relay or a transistor that switches the 12V line from the converter to the LED strip. The converter itself is not directly interfaced with the Arduino's pins, as the Arduino operates at 5V logic levels.