
How to Use upswave: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with upswave in Cirkit Designer
Design with upswave in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The UPSWave is a waveform generated by an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to provide backup power during electrical outages. It ensures a continuous power supply to connected devices, preventing data loss, hardware damage, or operational interruptions. The UPSWave is typically available in two forms: modified sine wave and pure sine wave.
- Modified Sine Wave: A stepped approximation of a sine wave, suitable for less sensitive devices.
- Pure Sine Wave: A smooth, continuous waveform identical to utility power, ideal for sensitive electronics.
Explore Projects Built with upswave
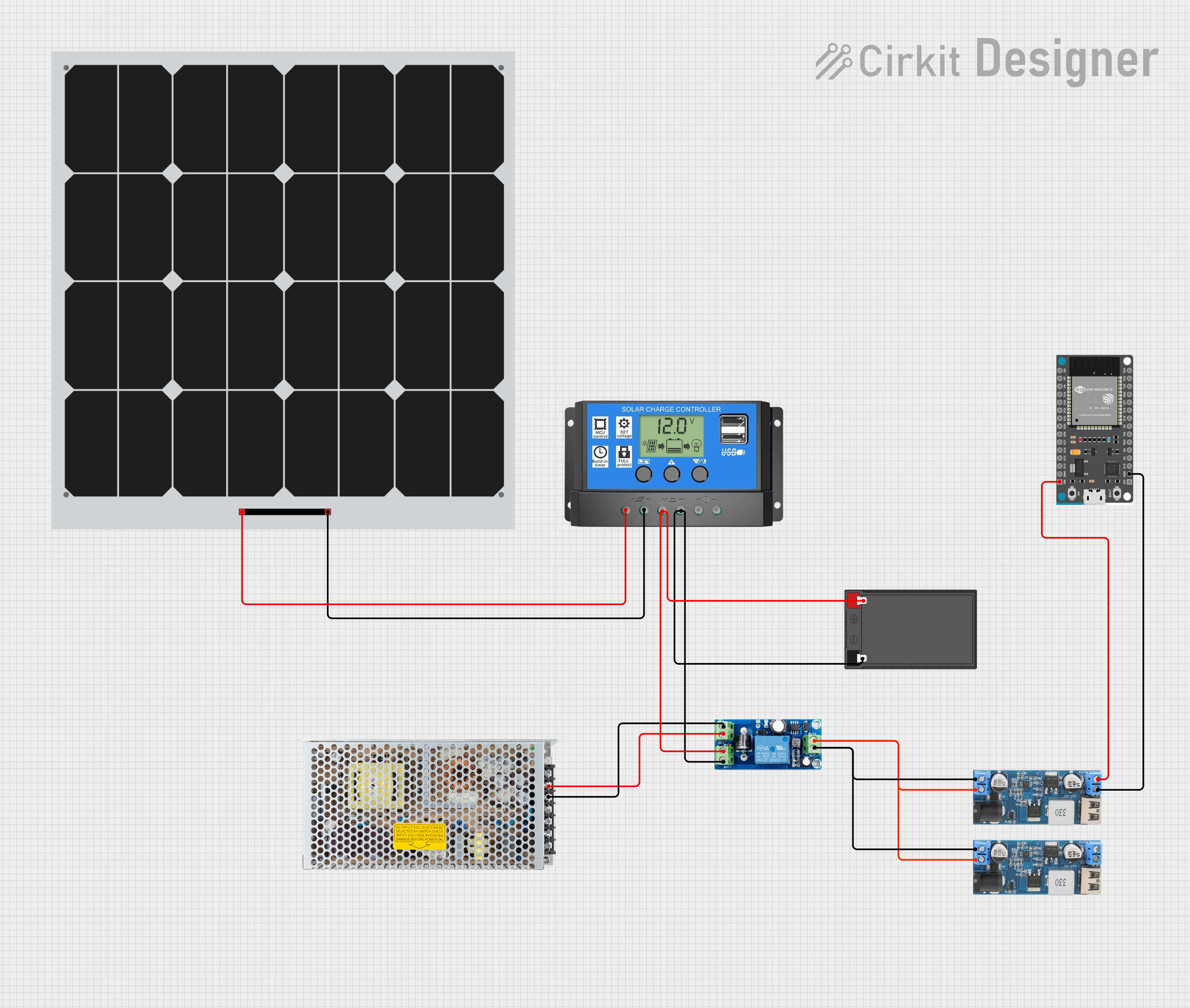
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer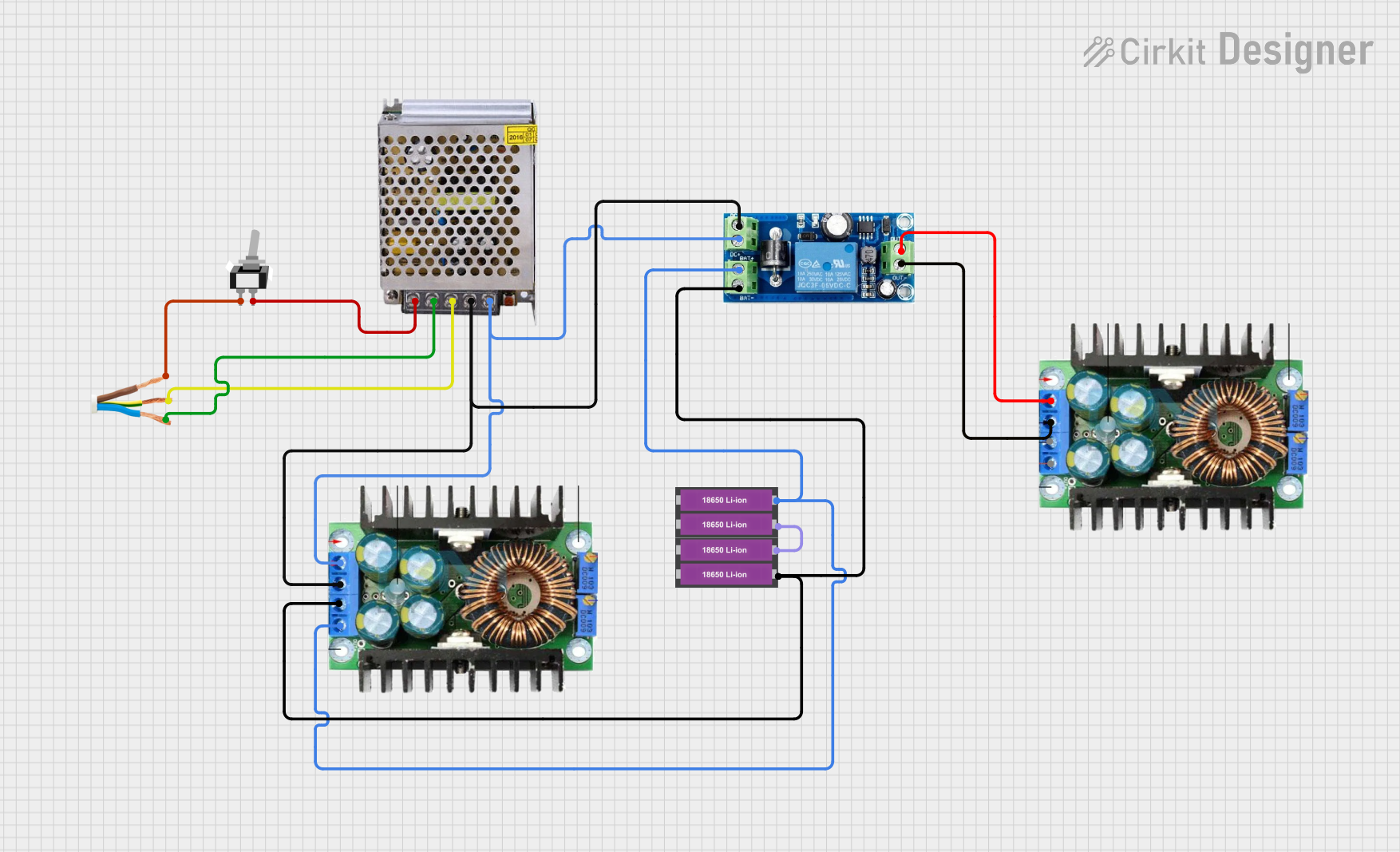
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer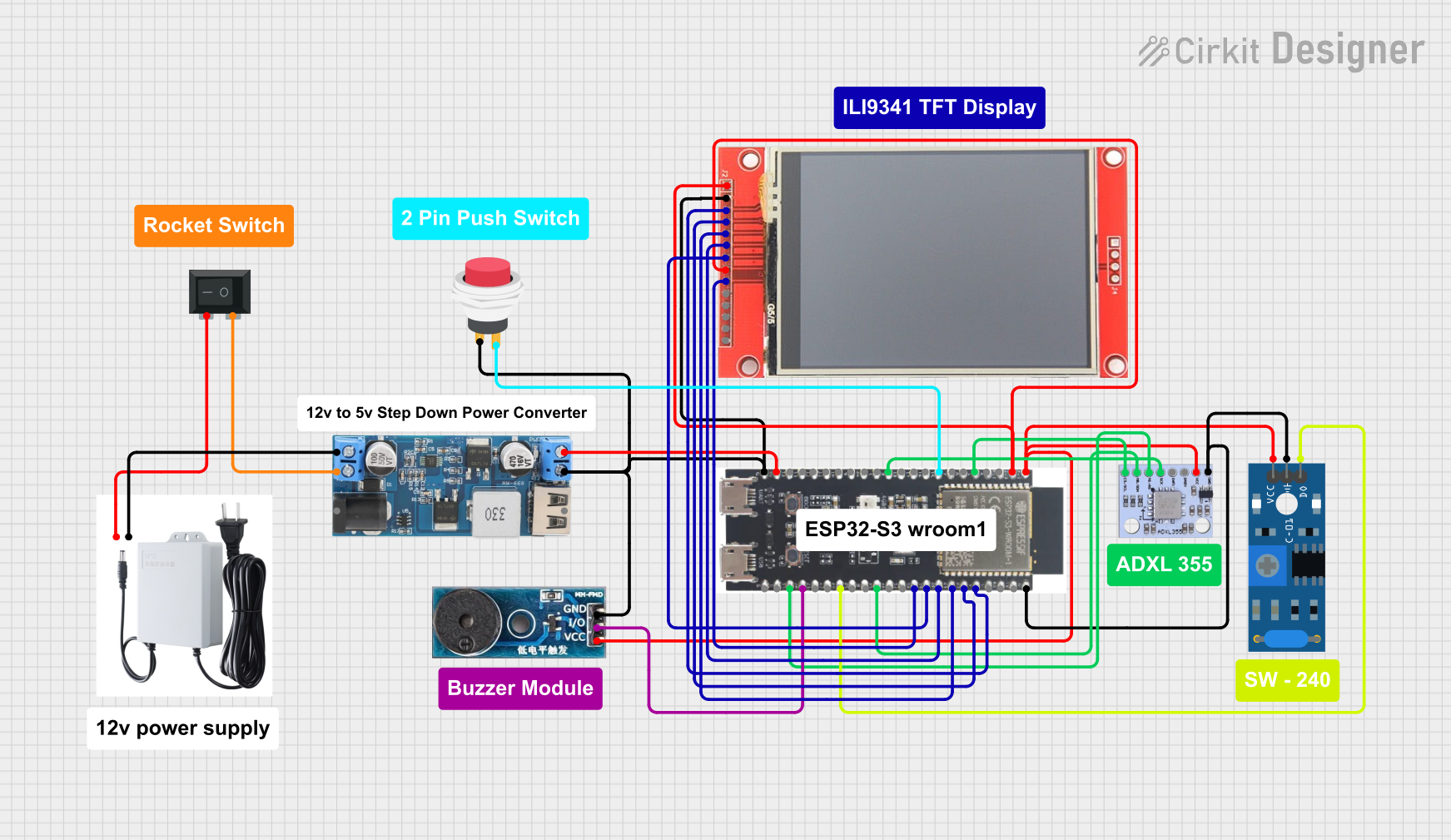
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with upswave

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Computers and Servers: Prevents data loss and hardware damage during power outages.
- Home Appliances: Powers devices like refrigerators, fans, and lights during blackouts.
- Medical Equipment: Ensures uninterrupted operation of critical devices.
- Industrial Systems: Maintains power for automation and control systems.
- Telecommunication: Keeps routers, modems, and communication systems operational.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Waveform Type | Modified Sine Wave or Pure Sine Wave |
| Input Voltage Range | 100V - 240V AC |
| Output Voltage | 110V or 220V AC (depending on model) |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Power Rating | 300W to 3000W (varies by UPS model) |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Battery Type | Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) or Lithium-Ion |
| Transfer Time | <10ms (typical) |
| THD (Total Harmonic Distortion) | <3% for pure sine wave, <25% for modified sine wave |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The UPSWave is not a discrete electronic component with pins but is part of a UPS system. However, the following table describes the key input/output connections typically found on a UPS:
| Pin/Port Name | Description |
|---|---|
| AC Input | Connects to the main power supply (100V-240V AC). |
| AC Output | Provides backup power to connected devices. |
| Battery Terminals | Connects to the internal or external battery. |
| USB/Serial Port | For communication with a computer or monitoring system. |
| Ground (GND) | Ensures safety and proper grounding of the system. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the UPSWave in a Circuit
Connect the UPS to the Main Power Supply:
- Plug the UPS into a standard AC wall outlet (100V-240V AC).
- Ensure the input voltage matches the UPS specifications.
Connect Devices to the UPS Output:
- Plug your devices into the AC output sockets of the UPS.
- For sensitive electronics, use a pure sine wave UPSWave for better compatibility.
Monitor Battery Status:
- Check the battery charge level using the UPS display or monitoring software.
- Replace the battery as per the manufacturer's recommendations.
Test the UPSWave:
- Simulate a power outage by disconnecting the UPS from the main power supply.
- Verify that the connected devices continue to operate without interruption.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Choose the Right Waveform: Use a pure sine wave UPSWave for sensitive electronics like computers, medical equipment, and audio systems.
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the total power consumption of connected devices does not exceed the UPS's power rating.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically test the UPS and replace the battery as needed.
- Ventilation: Place the UPS in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Grounding: Properly ground the UPS to avoid electrical hazards.
Example: Connecting a UPSWave to an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO during a power outage, connect the UPSWave output to a 5V DC adapter. Below is an example Arduino sketch to monitor the UPS status via a serial connection:
// Arduino code to monitor UPS status via serial communication
// Ensure the UPS is connected to the Arduino via a USB or serial port
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output for status indication
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String upsStatus = Serial.readString(); // Read UPS status from serial
Serial.println("UPS Status: " + upsStatus); // Print status to serial monitor
if (upsStatus.indexOf("Battery Low") != -1) {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn on LED if battery is low
} else {
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn off LED otherwise
}
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Devices not powering on | UPS is overloaded or battery is discharged | Reduce load or recharge/replace the battery. |
| Frequent beeping | Low battery or overload condition | Check battery status and reduce connected load. |
| UPS overheating | Poor ventilation or excessive load | Ensure proper airflow and reduce load if necessary. |
| No output during outage | Faulty battery or inverter circuit | Test and replace the battery or contact support. |
FAQs
What is the difference between a modified sine wave and a pure sine wave?
- A modified sine wave is a stepped approximation of a sine wave, suitable for basic devices. A pure sine wave is smooth and continuous, ideal for sensitive electronics.
Can I use a UPSWave with a refrigerator or air conditioner?
- Yes, but ensure the UPS has sufficient power capacity and uses a pure sine wave for compatibility with motor-driven appliances.
How often should I replace the UPS battery?
- Typically every 3-5 years, depending on usage and battery type.
Why does my UPS beep continuously?
- This usually indicates a low battery, overload, or fault condition. Check the UPS manual for specific beep codes.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and maintain a UPSWave to ensure uninterrupted power for your devices.