
How to Use TOF laser sensor GY-VL53L0X I2C: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
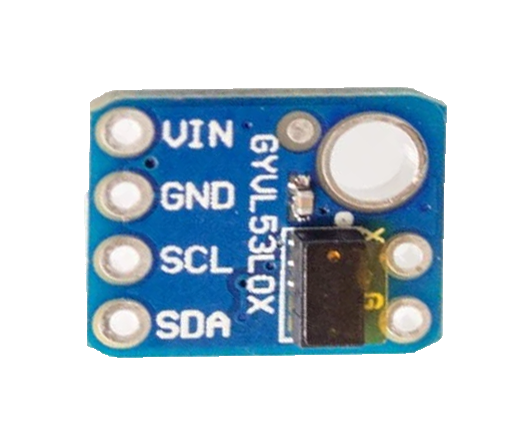

 Design with TOF laser sensor GY-VL53L0X I2C in Cirkit Designer
Design with TOF laser sensor GY-VL53L0X I2C in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The GY-VL53L0X is a compact Time-of-Flight (ToF) laser sensor module manufactured by Laskakit (Part ID: LA131093). It uses the I2C interface to measure distances with high precision by emitting laser pulses and calculating the time taken for the reflection to return. This sensor is ideal for applications requiring accurate distance measurement, such as robotics, obstacle detection, gesture recognition, and proximity sensing.
Explore Projects Built with TOF laser sensor GY-VL53L0X I2C
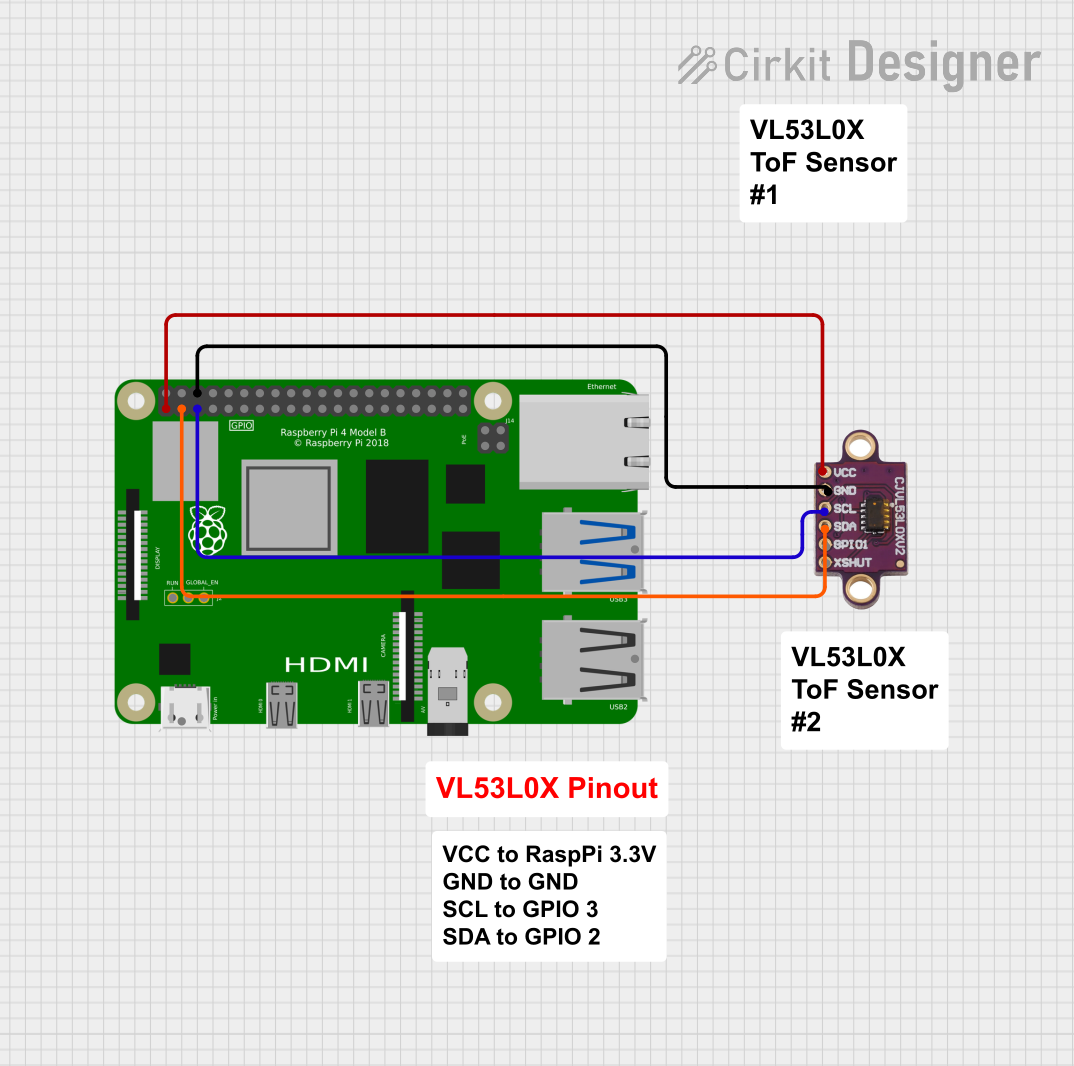
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer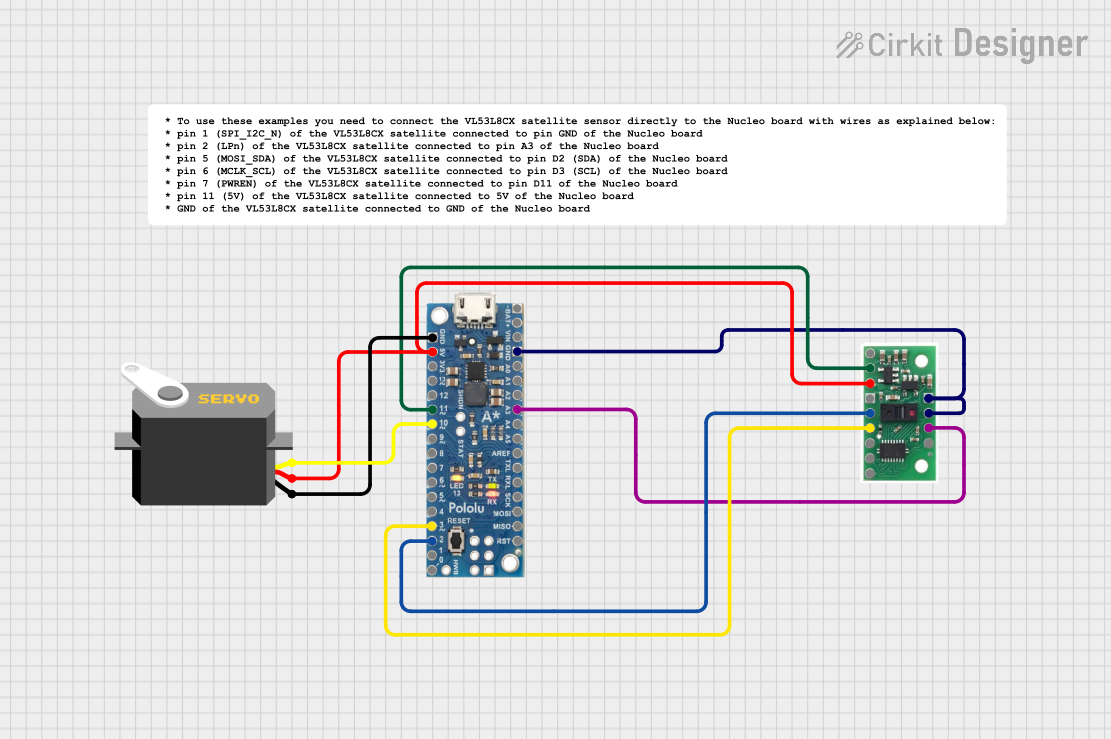
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer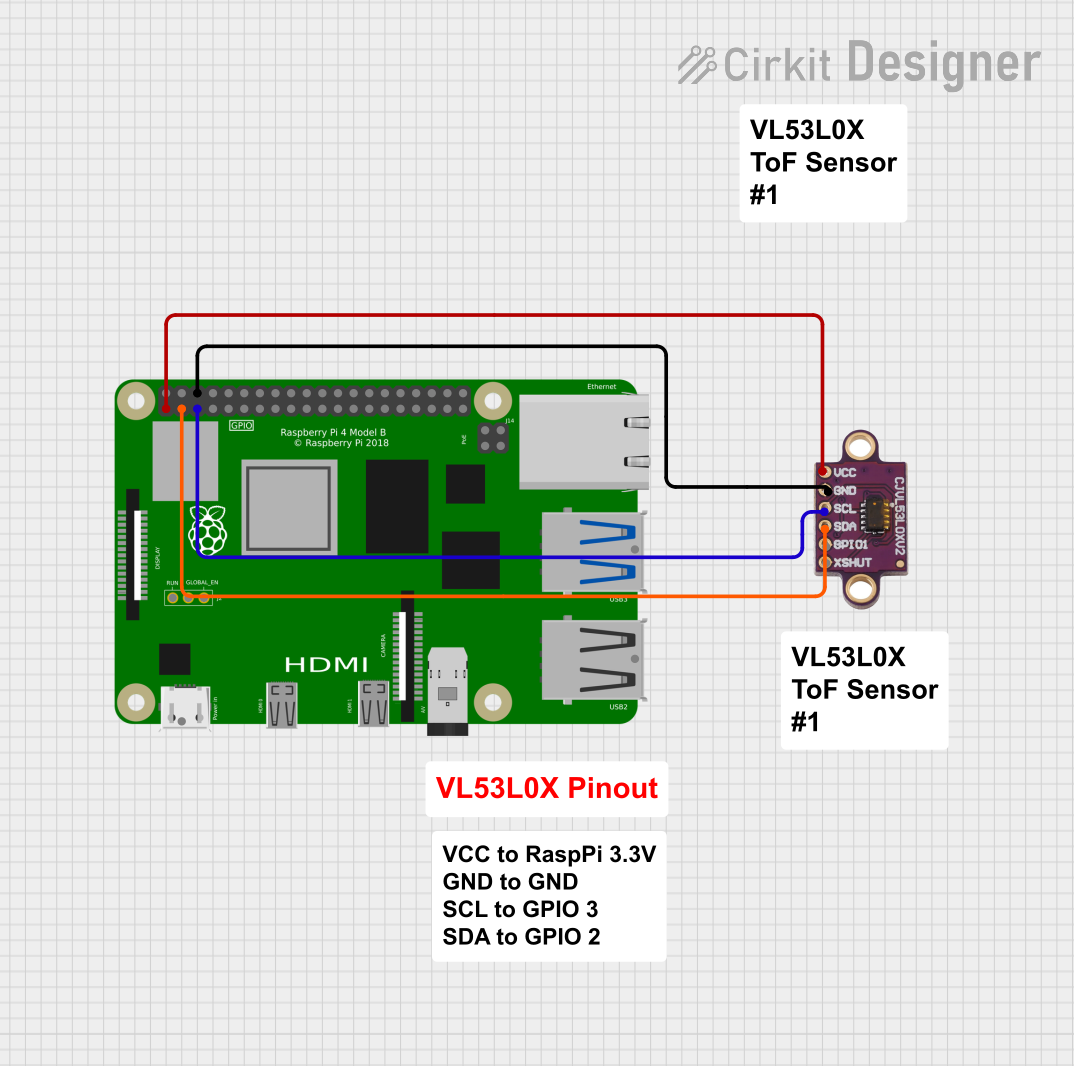
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer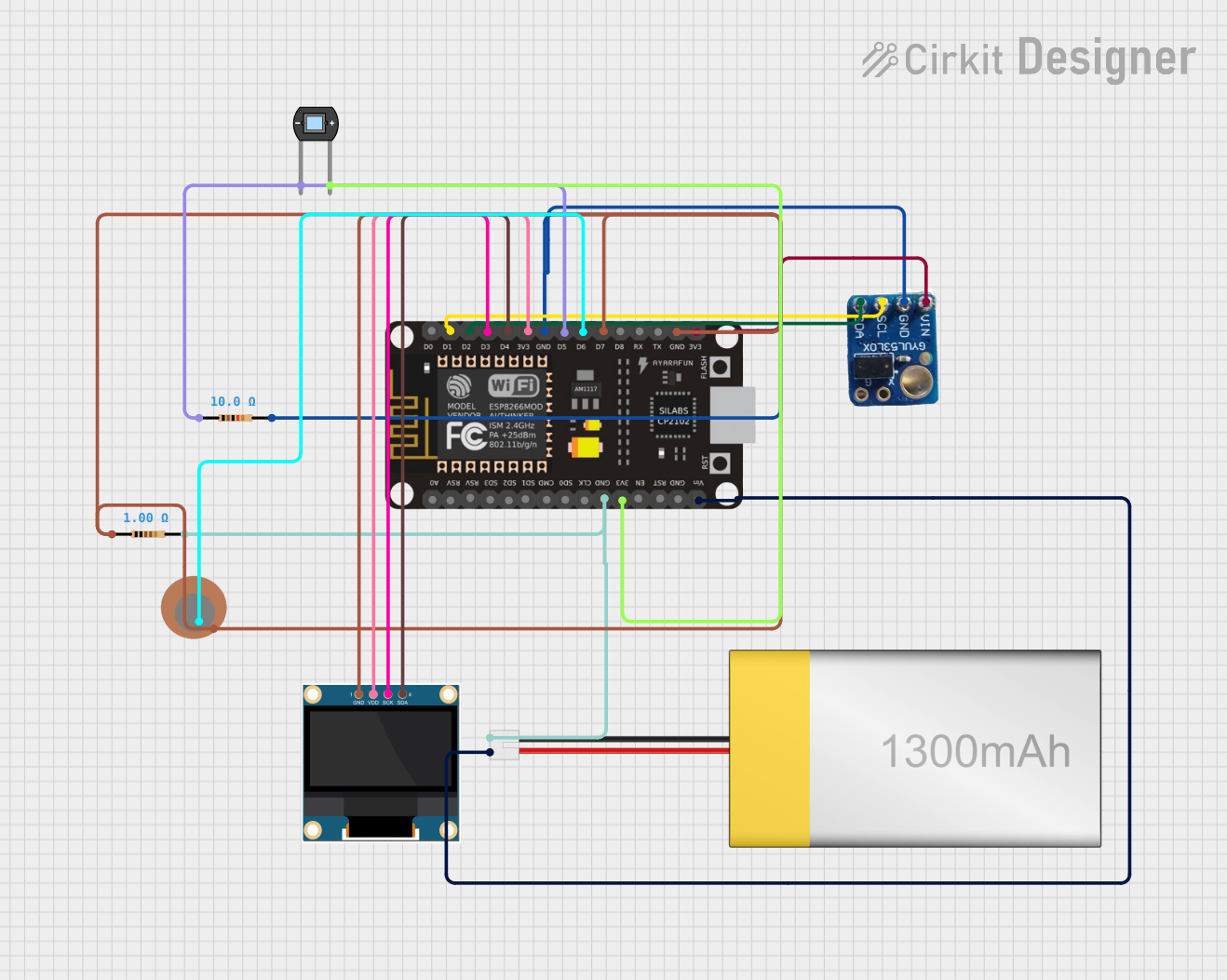
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TOF laser sensor GY-VL53L0X I2C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Obstacle detection in robotics
- Gesture-based user interfaces
- Proximity sensing in smart devices
- Object tracking and ranging
- Industrial automation and safety systems
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the GY-VL53L0X sensor:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.6V to 5.5V |
| Communication Interface | I2C (7-bit address: 0x29 by default) |
| Measuring Range | 30mm to 2000mm (2 meters) |
| Accuracy | ±3% (typical) |
| Field of View (FoV) | 25° |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +70°C |
| Power Consumption | 20mW (typical) |
| Dimensions | 10mm x 13mm x 4mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GY-VL53L0X module has six pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Power supply input (2.6V to 5.5V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| SDA | I2C data line |
| SCL | I2C clock line |
| XSHUT | Shutdown pin (active low, optional for power saving) |
| GPIO1 | Interrupt output (optional, configurable) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the GY-VL53L0X to an Arduino UNO
To use the GY-VL53L0X with an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
Wiring: Connect the sensor to the Arduino as shown below:
- VIN → 5V (Arduino)
- GND → GND (Arduino)
- SDA → A4 (Arduino I2C data line)
- SCL → A5 (Arduino I2C clock line)
- Optionally, connect XSHUT to a digital pin for shutdown control.
Install the VL53L0X Library:
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Go to Sketch → Include Library → Manage Libraries.
- Search for "VL53L0X" and install the library by Pololu.
Upload Example Code: Use the following example code to read distance measurements from the sensor:
#include <Wire.h> #include <VL53L0X.h> VL53L0X sensor; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication // Initialize the VL53L0X sensor if (!sensor.init()) { Serial.println("Failed to initialize VL53L0X sensor!"); while (1); // Halt execution if initialization fails } sensor.setTimeout(500); // Set timeout for measurements Serial.println("VL53L0X sensor initialized successfully."); } void loop() { // Read distance in millimeters uint16_t distance = sensor.readRangeSingleMillimeters(); // Check for timeout errors if (sensor.timeoutOccurred()) { Serial.println("Sensor timeout occurred!"); } else { Serial.print("Distance: "); Serial.print(distance); Serial.println(" mm"); } delay(100); // Wait 100ms before the next reading }
Important Considerations
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor is powered within its operating voltage range (2.6V to 5.5V). For 5V systems like Arduino UNO, no level shifter is required.
- I2C Address: The default I2C address is
0x29. If multiple sensors are used, you must change their addresses programmatically. - XSHUT Pin: Use the XSHUT pin to reset or power down the sensor when not in use to save power.
- Ambient Light: Avoid direct exposure to strong ambient light sources, as they may affect measurement accuracy.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Sensor Not Detected on I2C Bus:
- Ensure the SDA and SCL lines are correctly connected.
- Verify that pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) are present on the I2C lines if required.
- Check the I2C address (default:
0x29) and ensure no conflicts with other devices.
Incorrect or Fluctuating Distance Readings:
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to strong ambient light or reflective surfaces.
- Verify that the target object is within the sensor's measurement range (30mm to 2000mm).
- Check for stable power supply voltage.
Timeout Errors:
- Increase the timeout value in the code using
sensor.setTimeout(). - Ensure the sensor is not obstructed or facing a highly absorbent surface.
- Increase the timeout value in the code using
Multiple Sensors on the Same I2C Bus:
- Use the XSHUT pin to reset each sensor individually and assign a unique I2C address.
FAQs
Q: Can the GY-VL53L0X measure distances beyond 2 meters?
A: No, the maximum range of the sensor is 2 meters. For longer distances, consider using a different ToF sensor model.
Q: Is the GY-VL53L0X suitable for outdoor use?
A: While the sensor can operate in a wide temperature range, strong sunlight or rain may affect its performance. Use protective enclosures and filters for outdoor applications.
Q: How do I change the I2C address of the sensor?
A: Use the XSHUT pin to reset the sensor, then programmatically assign a new address using the VL53L0X library.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the sensor is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems. Ensure proper wiring for the I2C lines.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the GY-VL53L0X sensor into your projects for accurate and reliable distance measurements.