
How to Use Goku GM10 Nano V3.1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 is a compact and lightweight brushless motor controller designed for drones, RC vehicles, and other applications requiring precise motor control. Manufactured by Goku, this electronic speed controller (ESC) offers advanced programming options, high efficiency, and reliable performance in a small form factor. Its robust design makes it ideal for hobbyists and professionals working on high-performance projects.
Explore Projects Built with Goku GM10 Nano V3.1
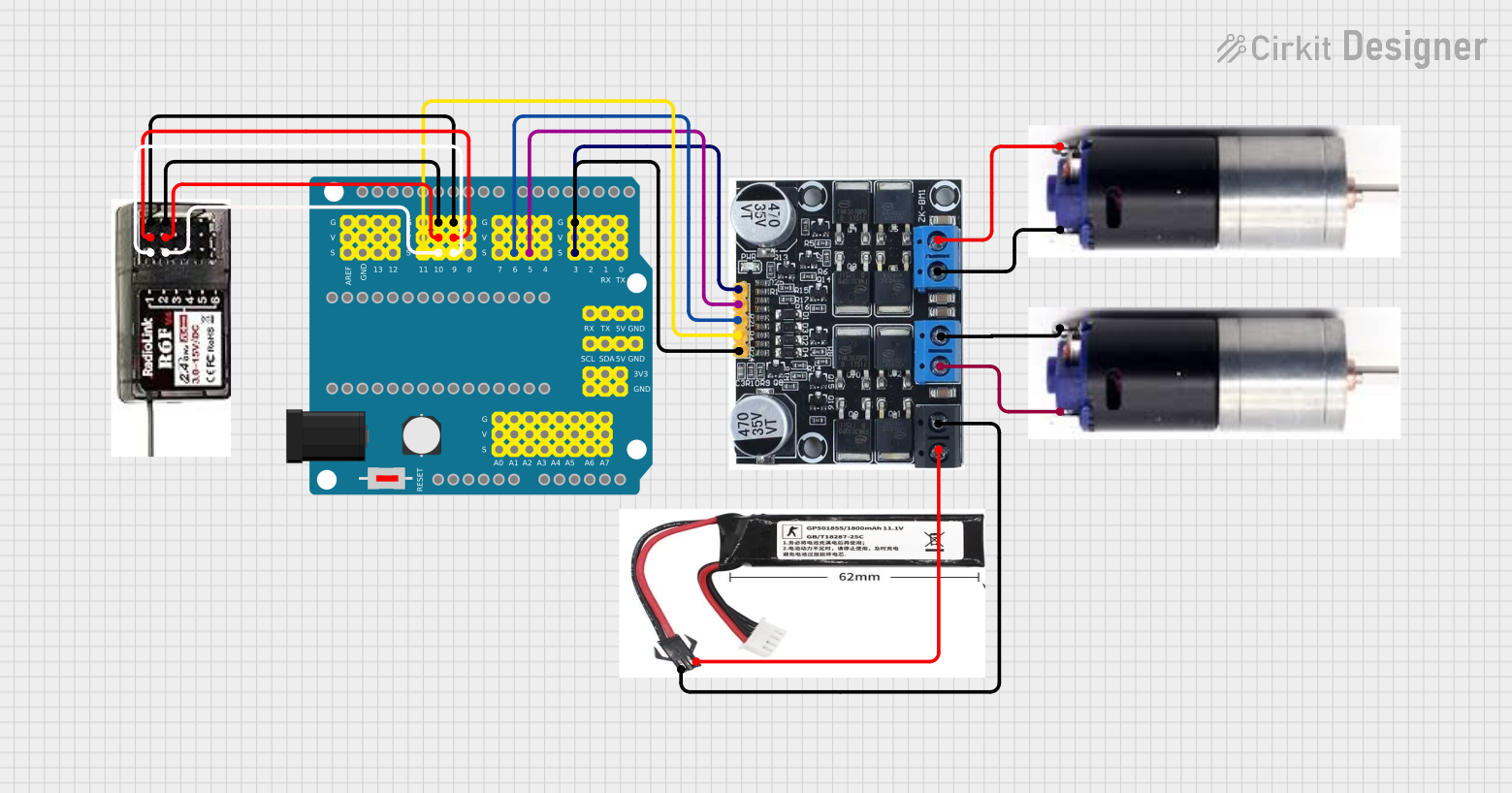
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer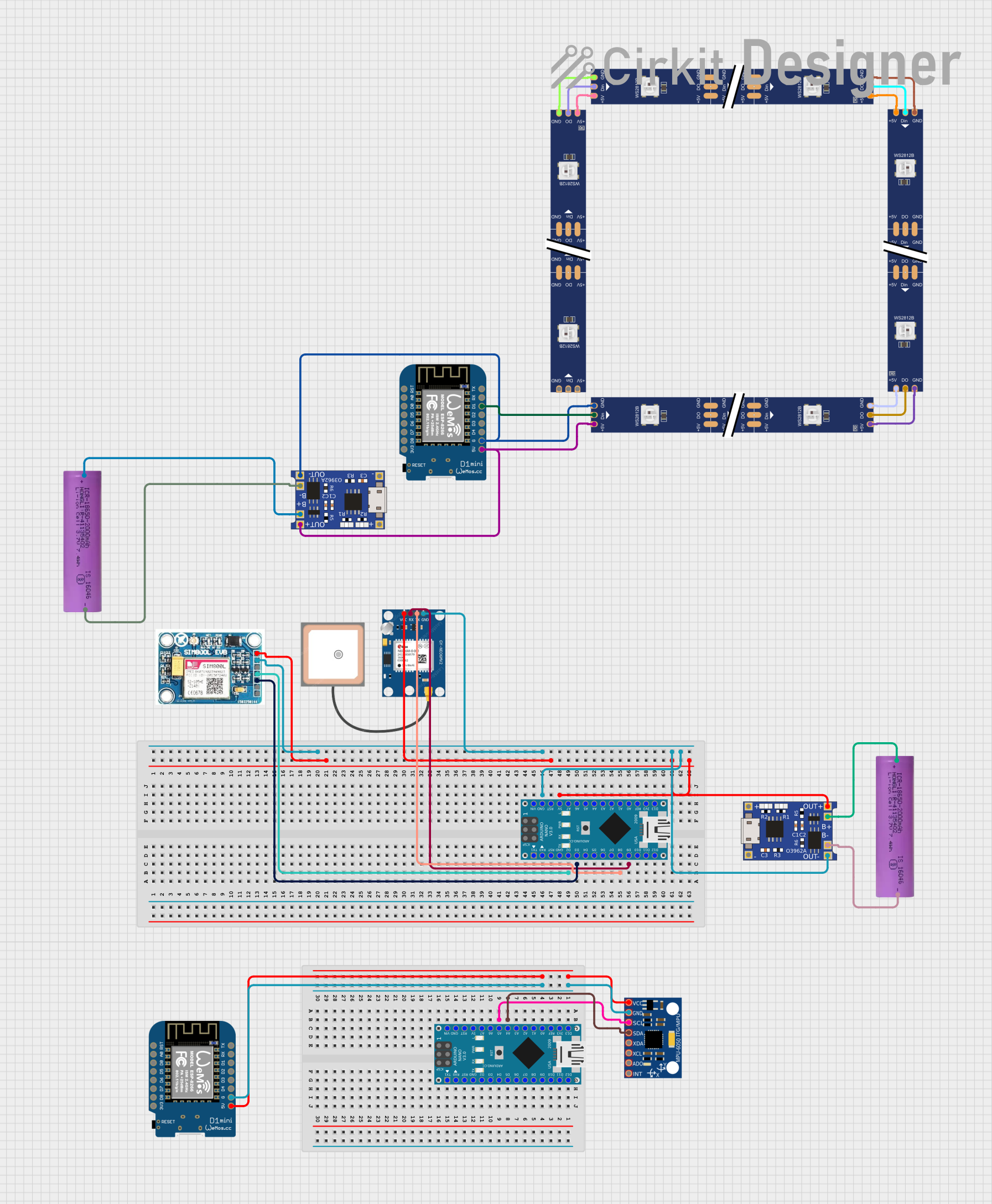
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer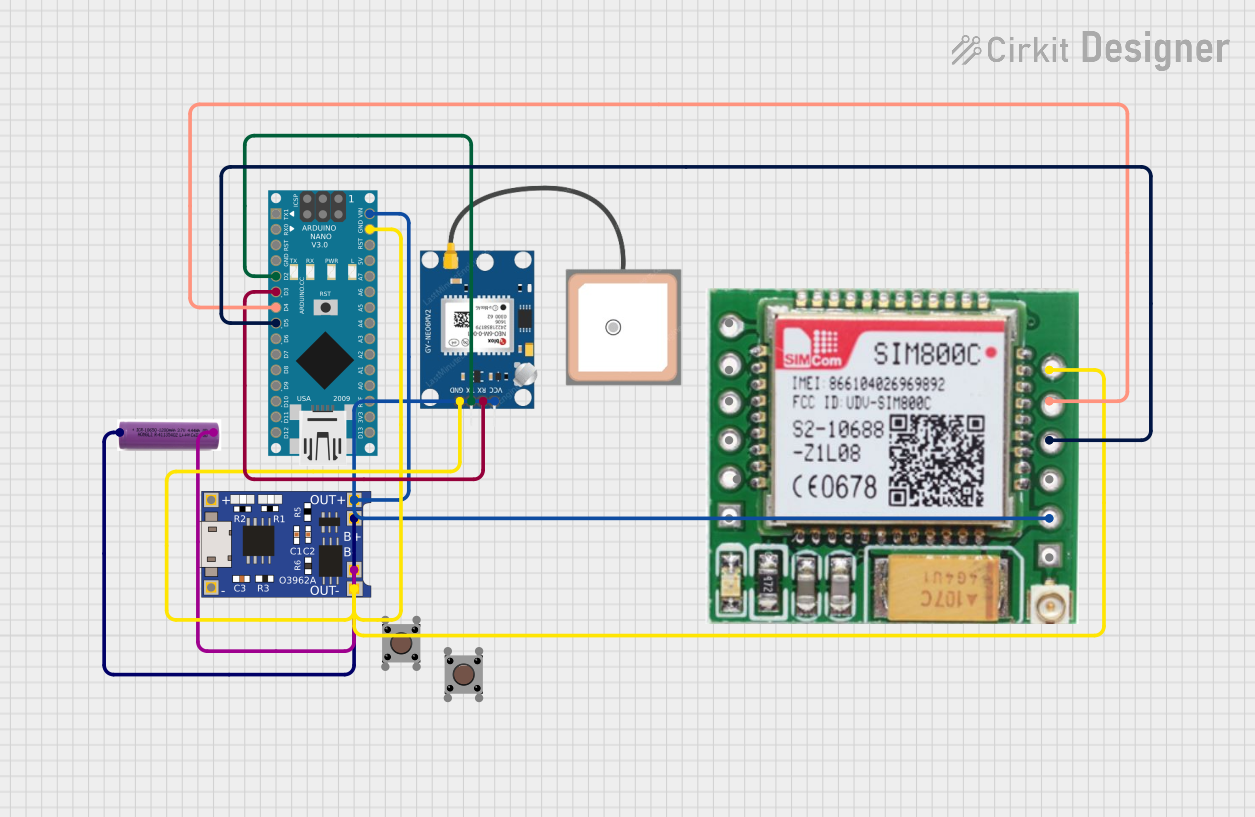
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Goku GM10 Nano V3.1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Drones (quadcopters, hexacopters, etc.)
- Remote-controlled (RC) cars, boats, and planes
- Robotics projects requiring brushless motor control
- DIY electric vehicles and e-bikes
- High-efficiency motor control in industrial applications
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the Goku GM10 Nano V3.1:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 2S–6S LiPo (7.4V–22.2V) |
| Continuous Current Rating | 10A |
| Peak Current Rating | 15A (for up to 10 seconds) |
| Supported Motor Types | Brushless DC (BLDC) motors |
| Signal Input | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
| Operating Frequency | 20 kHz–50 kHz |
| Dimensions | 23mm x 12mm x 5mm |
| Weight | 3.5g |
| Thermal Protection | Yes |
| Programming Options | Throttle range calibration, timing |
| Connector Type | JST-SH for signal, solder pads for power |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Signal (S) | PWM input signal for motor speed control |
| Ground (G) | Ground connection for signal and power |
| V+ | Positive power input (connect to battery positive) |
| V- | Negative power input (connect to battery ground) |
| Motor A | Output to motor phase A |
| Motor B | Output to motor phase B |
| Motor C | Output to motor phase C |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Power Supply:
- Connect the positive terminal of your battery to the V+ pin.
- Connect the negative terminal of your battery to the V- pin.
Ensure the input voltage is within the supported range (2S–6S LiPo).
Connect the Motor:
- Solder the three motor wires to the Motor A, Motor B, and Motor C pins.
- If the motor spins in the wrong direction, swap any two motor wires.
Connect the Signal Input:
- Use the Signal (S) pin to connect the PWM signal from your flight controller, RC receiver, or microcontroller.
- Connect the Ground (G) pin to the ground of your signal source.
Calibrate the Throttle Range (if required):
- Power on the ESC while holding the throttle at maximum.
- Wait for the confirmation tone, then move the throttle to the minimum position.
- Wait for the second confirmation tone to complete calibration.
Test the Setup:
- Gradually increase the throttle to ensure the motor responds correctly.
- Monitor the ESC temperature during operation to avoid overheating.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Cooling: Ensure adequate airflow around the ESC to prevent overheating during extended use.
- Voltage Limits: Do not exceed the maximum input voltage (22.2V) to avoid damaging the ESC.
- Signal Quality: Use a clean and stable PWM signal for optimal performance.
- Motor Compatibility: Verify that your motor is compatible with the ESC's current and voltage ratings.
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery when making wiring changes to prevent short circuits.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 can be controlled using an Arduino UNO. Below is an example code snippet to control the motor speed using PWM:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library for PWM signal generation
Servo esc; // Create a Servo object to control the ESC
void setup() {
esc.attach(9); // Attach the ESC signal pin to Arduino pin 9
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Set initial throttle to minimum (1000 µs)
delay(2000); // Wait for the ESC to initialize
}
void loop() {
// Gradually increase throttle from 1000 µs to 2000 µs
for (int throttle = 1000; throttle <= 2000; throttle += 10) {
esc.writeMicroseconds(throttle); // Send PWM signal to ESC
delay(50); // Wait 50 ms between steps
}
delay(2000); // Hold maximum throttle for 2 seconds
// Gradually decrease throttle back to 1000 µs
for (int throttle = 2000; throttle >= 1000; throttle -= 10) {
esc.writeMicroseconds(throttle); // Send PWM signal to ESC
delay(50); // Wait 50 ms between steps
}
delay(2000); // Hold minimum throttle for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no PWM signal.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the PWM signal is being sent correctly.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Cause: Motor phase wires are connected incorrectly.
- Solution: Swap any two motor wires to reverse the direction.
ESC Overheats:
- Cause: Insufficient cooling or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Improve airflow around the ESC and ensure the motor is within the ESC's current rating.
No Response from ESC:
- Cause: Throttle range not calibrated.
- Solution: Perform throttle range calibration as described in the usage instructions.
PWM Signal Issues:
- Cause: Signal frequency or voltage is incompatible.
- Solution: Ensure the PWM signal is within the ESC's supported range (20 kHz–50 kHz).
FAQs
Can I use the Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 with a 7.4V battery?
Yes, the ESC supports input voltages as low as 7.4V (2S LiPo).What happens if I exceed the maximum current rating?
The ESC may overheat or shut down to protect itself. Prolonged overcurrent conditions can permanently damage the ESC.Is the ESC waterproof?
No, the Goku GM10 Nano V3.1 is not waterproof. Use protective measures if operating in wet conditions.Can I program the ESC using a computer?
No, programming is done via throttle calibration and timing adjustments, not through a computer interface.What is the weight of the ESC?
The ESC weighs only 3.5g, making it ideal for lightweight applications.